

The Ninety-Five Theses. The Ninety-Five Theses (original Latin: Disputatio pro declaratione virtutis indulgentiarum) were written by Martin Luther in 1517 and are widely regarded as the initial catalyst for the Protestant Reformation.
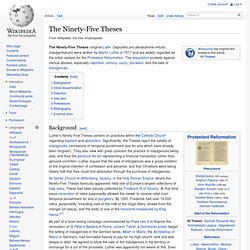
The disputation protests against clerical abuses, especially nepotism, simony, usury, pluralism, and the sale of indulgences. Background[edit] Martin Luther. Martin Luther OSA (German: [ˈmaɐ̯tiːn ˈlʊtɐ] ( ); 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German monk, Catholic priest, professor of theology and seminal figure of the 16th-century movement in Christianity known later as the Protestant Reformation.[1] He strongly disputed the claim that freedom from God's punishment for sin could be purchased with monetary values. He confronted indulgence salesman Johann Tetzel, a Dominican friar, with his Ninety-Five Theses in 1517.
His refusal to retract all of his writings at the demand of Pope Leo X in 1520 and the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V at the Diet of Worms in 1521 resulted in his excommunication by the Pope and condemnation as an outlaw by the Emperor. Luther taught that salvation and subsequently eternity in heaven is not earned by good deeds but is received only as a free gift of God's grace through faith in Jesus Christ as redeemer from sin and subsequently eternity in Hell. Protestant Reformation. Although the core motivation behind these changes was theological, many other factors played a part, including the rise of nationalism, the Western Schism which eroded people's faith in the Papacy, the corruption of the Curia, and the new learning of the Renaissance which questioned much traditional thought.
On a technological level the invention of the printing press proved extremely significant in that it provided the means for the rapid dissemination of new ideas. The Roman Catholic Church responded with a Counter-Reformation initiated by the Council of Trent and spearheaded by the new order of the Society of Jesus (Jesuits) specifically organized to counter the Protestant movement. In general, Northern Europe, with the exception of most of Ireland, turned Protestant.