

Neural Networks. The Frame Problem. 1.
Introduction The frame problem originated as a narrowly defined technical problem in logic-based artificial intelligence (AI). Google's AI Is Now Smart Enough to Play Atari Like the Pros. Last year Google shelled out an estimated $400 million for a little-known artificial intelligence company called DeepMind.
Since then, the company has been pretty tight-lipped about what’s been going on behind DeepMind’s closed doors, but here’s one thing we know for sure: There’s a professional videogame tester who’s pitted himself against DeepMind’s AI software in a kind of digital battle royale. The battlefield was classic videogames. And according to new research published today in the science magazine Nature, Google’s software did pretty well, smoking its human competitor in a range of Atari 2600 games like Breakout, Video Pinball, and Space Invaders and playing at pretty close to the human’s level most of the time.
This Robot Just Passed a Rudimentary Self-awareness Test. Slugsnot comments on TIL there was a 3-day Go championship game ongoing in Hiroshima when the city was nuked. The building was damaged and several spectators were injured, but play resumed normally after lunch break and concluded later that day. Pandemonium Explains Why Computers Will Share Human Biases. IBM Will Use Watson To Battle Brain Cancer. New Computer Programming Language Imitates The Human Brain. Indicators of Humanhood: A Tentative Profile of Man - FLETCHER - 2012 - Hastings Center Report.
Non-Human Consciousness Exists Say Experts. Now What? Non-Human Consciousness Exists Say Experts.
Now What? Phillip Low at Singularity University Have you ever considered the consciousness, or unconsciousness, of your dog? Well, a group of neuroscientists have been thinking on the subject pretty seriously, and it was announced last week that "humans are not the only conscious beings in the universe". Earlier this month, some of the leading scientists from around the world congregated at the Hotel Du Vin in Cambridge to discuss the evidence that has amassed over the years. The declaration of consciousness. How artificial intelligences will see us. Jeff Hawkins: How brain science will change computing. P versus NP problem. Diagram of complexity classes provided that P≠NP.
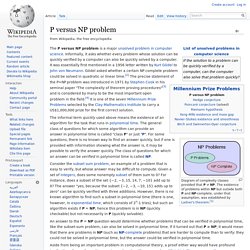
The existence of problems within NP but outside both P and NP-complete, under that assumption, was established by Ladner's theorem.[1] The P versus NP problem is a major unsolved problem in computer science. Informally, it asks whether every problem whose solution can be quickly verified by a computer can also be quickly solved by a computer. It was essentially first mentioned in a 1956 letter written by Kurt Gödel to John von Neumann. Gödel asked whether a certain NP complete problem could be solved in quadratic or linear time.[2] The precise statement of the P=NP problem was introduced in 1971 by Stephen Cook in his seminal paper "The complexity of theorem proving procedures"[3] and is considered by many to be the most important open problem in the field.[4] It is one of the seven Millennium Prize Problems selected by the Clay Mathematics Institute to carry a US$1,000,000 prize for the first correct solution.
Context[edit] Automated Grading Software In Development To Score Essays As Accurately As Humans. Roboreaders that can score essays in standardized tests could also help teachers grade and students becomes better writers.
April 30 marks the deadline for a contest challenging software developers to create an automated scorer of student essays, otherwise known as a roboreader, that performs as good as a human expert grader. In January, the Hewlett Foundation of Hewlett-Packard fame introduced the Automated Student Assessment Prize (ASAP…get it?) Offering up $100,000 in awards to “data scientists and machine learning specialists” to develop the application.
In sponsoring this contest, the Foundation has two goals in mind: improve the standardized testing industry and advance technology in public education. The contest is only the first of three, with the others aimed at developing automated graders for short answers and charts and graphs. But many tests include some assessment of student writing and for those sections, testing companies need human graders. Moravec's paradox. Moravec's paradox is the discovery by artificial intelligence and robotics researchers that, contrary to traditional assumptions, high-level reasoning requires very little computation, but low-level sensorimotor skills require enormous computational resources.
The principle was articulated by Hans Moravec, Rodney Brooks, Marvin Minsky and others in the 1980s. As Moravec writes, "it is comparatively easy to make computers exhibit adult level performance on intelligence tests or playing checkers, and difficult or impossible to give them the skills of a one-year-old when it comes to perception and mobility. " Linguist and cognitive scientist Steven Pinker considers this the most significant discovery uncovered by AI researchers. Introducing: Flickr PARK or BIRD. Tl;dr: Check it out at parkorbird.flickr.com!

We at Flickr are not ones to back down from a challenge. Especially when that challenge comes in webcomic form. Facial Recognition Software Distinguishes Between Real And Phony Smiles. MIT researchers know when you're smiling for real (left) or out of frustration (right), but odds are you can't tell.
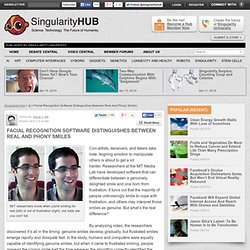
Con-artists, deceivers, and fakers take note: feigning emotion to manipulate others is about to get a lot harder. Researchers at the MIT Media Lab have developed software that can differentiate between a genuinely delighted smile and one born from frustration. It turns out that the majority of people unknowingly smile to cope with frustration, and others may interpret those smiles as genuine. But what’s the real difference? By analyzing video, the researchers discovered it’s all in the timing: genuine smiles develop gradually, but frustrated smiles emerge rapidly and dissipate fast. The motive behind the research is to help individuals who have difficulty interpreting face-to-face communication, such as those on the autistic spectrum, but the research also has some profound implications for artificial intelligence.
The study revealed some curious findings about smiling. Robotic Quintet Composes And Plays Its Own Music. Sound Machines 2.0 is Festo's latest effort to create robotic musicians.
The German engineering firm Festo has developed a self-playing robotic string quintet that will listen to a piece of music and generate new musical compositions in various musical styles effortlessly.