

Scientists: Antarctica Ice Sheet Thinned 400 Meters 5000 Years Ago, And Natural Oceanic Cycles Drive Climate. Today we present two papers on climate reconstruction using proxy data.

One about East Antarctica and the other about belize. Hat-tip reader Mary Brown. AMO behind sea surface temperatures First we look at a paper authored by a team of German scientists: “Great Blue Hole (Lighthouse Reef, Belize): A continuous, annually-resolved record of Common Era sea surface temperature, Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation and cyclone-controlled run-off“. The team looked at 2000 years of proxy data from Belize and found interesting natural cycles at play. The authors note that the Holocene (<11.7 kyr BP) has been characterized by several periods of distinct climate changes and that the climate remains difficult to predict “due to the lack of comprehensive, annually-resolved and continuous sea-surface temperature (SST) data”. So what about them models? Snowmelt Reveals Remains Of Medieval Warm Period Penguins.
Antarctic research has discovered abandoned colonies of Adélie penguins which date from three warm periods starting at around 5000 B.P. and terminating by ca. 800 B.P., coinciding with the end of the Medieval Warm Period.
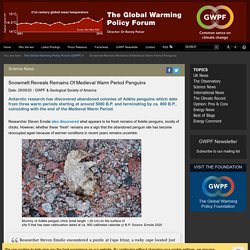
Researcher Steven Emslie also discovered what appears to be fresh remains of Adelie penguins, mostly of chicks. However, whether these “fresh” remains are a sign that the abandoned penguin site has become reoccupied again because of warmer conditions in recent years remains uncertain. Researcher Steven Emslie encountered a puzzle at Cape Irizar, a rocky cape located just south of the Drygalski Ice Tongue on the Scott Coast, Ross Sea. He found both ancient and what appeared to be fresh remains of Adelie penguins, mostly of chicks, which frequently die and accumulate at these colonies. Antarctica was warmer one thousand years ago — and life was OK. Remember when polar amplification was the rage?

So much for that theory Antarctica is twice the size of the US or Australia. Buried 2 km deep under domes of snow, it holds 58 meters of global sea level to ransom. The IPCC have been predicting its demise-by-climate-change for a decade or two. A new paper looks at 60 sites across Antarctica, considering everything from ice, lake and marine cores to peat and seal skins. Credit to the paper authors: Sebastian Lüning, Mariusz Gałka, and Fritz Vahrenholt Feast your eyes on the decidedly not unprecedented modern tiny spike: The little jaggy down after 2000 AD is real. We already knew the Medieval Warm Period was a global phenomenon, thanks to hundreds of proxies, and 6,000 boreholes. With an awesome dedication to detail, the team put all the big oceanic and other factors into one big graph.
Fig. 8. Looking at different parts of Antarctica some parts cooled while other parts warmed. Fig. 4. Related stories. The West Antarctic Ice Sheet Seems to Be Good at Collapsing. Scientists have discovered that the West Antarctic Ice Sheet underwent a major retreat between 10,000 and 12,000 years ago, at a time when the world was actually cooler than it is today.

Linking an ancient CO2 drop to the Antarctic Ice Sheet using algae as a proxy. From Purdue University , another “just in time for Durban” press release.

When you see phrases like “the mother of all tipping points” and you know this is overhyped control knob science. Drop in carbon dioxide levels led to polar ice sheet, study finds WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – A drop in carbon dioxide appears to be the driving force that led to the Antarctic ice sheet’s formation, according to a recent study led by scientists at Yale and Purdue universities of molecules from ancient algae found in deep-sea core samples. The key role of the greenhouse gas in one of the biggest climate events in Earth’s history supports carbon dioxide’s importance in past climate change and implicates it as a significant force in present and future climate.
New Science: Arctic AND Antarctic Sea Ice More Extensive Today Than Nearly All Of The Last 10,000 Years. By Kenneth Richard on 18.
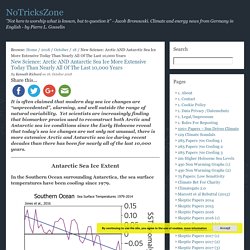
October 2018 It is often claimed that modern day sea ice changes are “unprecedented”, alarming, and well outside the range of natural variability. Yet scientists are increasingly finding that biomarker proxies used to reconstruct both Arctic and Antarctic sea ice conditions since the Early Holocene reveal that today’s sea ice changes are not only not unusual, there is more extensive Arctic and Antarctic sea ice during recent decades than there has been for nearly all of the last 10,000 years. Antarctic Sea Ice Extent. Finding: Antarctica’s Ross Ice Shelf has collapsed before. The front of the Ross Ice Shelf floats in the Ross Sea, as seen from the cockpit of an LC130 aircraft flown by the New York Air National Guard.
Photo by Matt Siegfried Retracing Antarctica’s Glacial Past. More settled science: The West Antarctic Ice Sheet is 20 million years older than thought. Antarctic Temperature Data Contradict Global Warming…”Much Warmer” 105 Years Ago! Growing sea ice Despite all the alarmist claims of an Antarctic meltdown, it is well known that the trend for sea ice extent at the South Pole has been one of growing ice rather than shrinking ice over the past 4 decades.
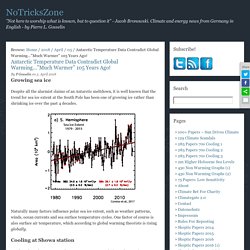
Naturally many factors influence polar sea ice extent, such as weather patterns, winds, ocean currents and sea surface temperature cycles. One factor of course is also surface air temperature, which according to global warming theorists is rising globally. Cooling at Showa station. During last warming period, Antarctica heated up 2 to 3 times more than planet average. Following Earth's last ice age, which peaked 20,000 years ago, the Antarctic warmed between two and three times the average temperature increase worldwide, according to a new study by a team of American geophysicists.
The disparity – Antarctica warmed about 11 degrees Celsius, nearly 20 degrees Fahrenheit, between about 20,000 and 10,000 years ago, while the average temperature worldwide rose only about 4 degrees Celsius, or 7 degrees Fahrenheit — highlights the fact that the poles, both the Arctic in the north and the Antarctic in the south, amplify the effects of a changing climate, whether it gets warmer or cooler. The calculations are in line with estimates from most climate models, proving that these models do a good job of estimating past climatic conditions and, very likely, future conditions in an era of climate change and global warming.
Cuffey and his colleagues, including Gary Clow of the U.S. Deglaciation in Antarctica Co-authors with Cuffey and Clow are Eric Steig, T.J. Glaciers In Antarctica Advanced During Little Ice Age. By Paul Homewood As we all know, Antarctica is melting, we’re all going to drown and its all your fault.
Well maybe not. There is a growing body of evidence that the Little Ice Age affected the Antarctic just as much as the rest of the world, and as a result glaciers there expanded. Antarctic Refrigerator Effect and Climate Sensitivity. Antarctic Refrigeration Effect, Climate Sensitivity, and Deformation Professionelle For the past 55 million years the global surface temperature has declined by more than 10°C from a “hot house” condition into an “ice house” with increasing temperature variability as depicted in Figure 1 (Mya = millions of years ago). During the Cretaceous and Early Cenozoic, glaciers and ice caps were absent from both Antarctica and Greenland.
Antarctica was covered in para-tropical vegetation and Greenland was home to crocodiles. More importantly for millions of years the oceans had been storing enormous amounts of heat. In contrast to near freezing temperatures today, Antarctic bottom waters averaged about 11°C, suggesting Antarctic coastal temperatures never dropped below 11°C even during the long polar nights. Antarctica cooling since Roman Times, climate models wrong (again)
A new study suggests temperatures across Antarctica have been falling for the last 1,600 years. This natural climate change would have been a threat to baby penguins, forcing them to walk much further across sea-ice for food. (Looks like it was even worse for polar bears. New Antarctic Temperature Reconstruction. Stenni et al (2017), Antarctic climate variability on regional and continental scales over the last 2000 years, was published pdf this week by Climate of the Past. It includes (multiple variations) of a new Antarctic temperature reconstruction, in which 112 d18O and dD isotope series are combined into regional and continental reconstructions. Its abstract warns that “projected warming of the Antarctic continent during the 21st century may soon see significant and unusual warming develop across other parts of the Antarctic continent [besides the peninsula]”, but no Steigian red spots of supposedly unprecedented warming.
Long-time CA readers will be aware of my long-standing interest in Antarctic ice core proxies, in particular, the highly resolved Law Dome d18O series. One of my first appearances in Climategate emails was a request for Law Dome data to Tas van Ommen in Australia, who immediately notified Phil Jones in Sauron’s Tower of this disturbance in the equilibrium of Middleearth. The Antarctic Peninsula: No Longer the Canary in the Coal Mine - Antarctic Peninsula Cooled Nearly 1°C During 1999–2014.
Paper Reviewed Oliva, M., Navarro, F, Hrbácek, F., Hernández, A., Nývlt, D., Pereira, P., Ruiz-Fernández, J. and Trigo, R. 2017. Recent regional climate cooling on the Antarctic Peninsula and associated impacts on the cryosphere. Science of the Total Environment 580: 210-223. Climate alarmists generally contend that current temperatures are both unnatural and unprecedented, as a result of global warming caused by anthropogenic CO2 emissions; and they claim that this "unnaturalness" is most strongly expressed throughout the world's polar regions.
A “New” Theory About the Formation of the Antarctic Ice Sheet. Guest post by David Middleton. Antarctic Temperatures Were ‘Up To 5°C Above Modern’ From 12,000–2,000 Years BP.