

Man contracts 'flesh-eating bacteria' from using roomie's razor. He tried to get a smooth chin — and got anything but.
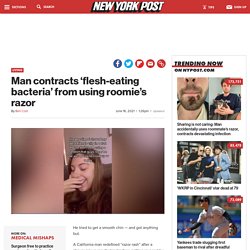
A California man redefined “razor rash” after a shaver mixup resulted in his face getting ravaged by flesh-eating bacteria. His disfiguring fiasco first came to light in April via a series of viral TikTok videos, but the poor soul hadn’t divulged the full story until now. “I got these deep pustules and sores on my chin and along my jawline,” Nick Holterman, 24, told Jam Press of the infection, which began innocuously after he used his housemate’s razor to shear off some unsightly stubble on his chin and cheeks.
Drug-resistant microbes kill about 35,000 people in the U.S. per year. Flesh-eating bacteria cure cannot come soon enough. A Texas man survived a flesh-eating infection he contracted from Hurricane Harvey’s floodwaters after intensive treatment at a Houston hospital.
Many victims of such bacterial illnesses suffer a worse fate. But improved therapies and vaccines might be on the way, if scientists can use some new findings from that same hospital on how some bacteria that cause these infections work. On August 29, J.R. Atkins kayaked through floodwaters left by Hurricane Harvey to check on his neighbors. When he woke up on Wednesday, he noticed that the swelling he’d seen the day before had begun to spread down his arm. Mysterious flesh-eating bacteria is raging in Australia. New superbug breaks through the last line of antibiotic defense. Rare Brain-Eating Amoeba Kills Woman Who Filled Her Neti Pot With Tap Water.
Brain Parasites, California’s Hidden Health Problem. Sara Alvarez was afraid.
The doctors told her she needed surgery — brain surgery. Operations on such a complex organ are never simple, but this procedure was exceptionally difficult. There was a high risk of complications, of debilitation, of post-op problems. Fungal Meningitis Pathogen Discovers New Appetite for Human Brains. The nation's ongoing fungal meningitis outbreak has killed 30 and sickened 419 people so far, but the fungus responsible has never wrought such havoc before.
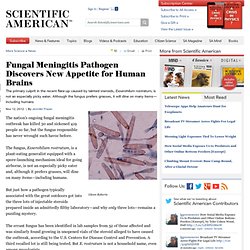
The fungus, Exserohilum rostratum, is a plant-eating generalist equipped with a spore-launching mechanism ideal for going airborne, is not an especially picky eater and, although it prefers grasses, will dine on many items—including humans. But just how a pathogen typically associated with the great outdoors got into the three lots of injectable steroids prepared inside an admittedly filthy laboratory—and why only three lots—remains a puzzling mystery. The errant fungus has been identified in lab samples from 52 of those affected and was similarly found growing in unopened vials of the steroid alleged to have caused the outbreak, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A third recalled lot is still being tested. Fungus responsible for 5 deaths in the wake of massive tornado. Public release date: 14-Dec-2012 [ Print | E-mail Share ] [ Close Window ] Contact: Steve Yozwiaksyozwiak@tgen.org 602-343-8704The Translational Genomics Research Institute FLAGSTAFF, Ariz. — Dec. 14, 2012 — A fast growing, flesh-eating fungus killed 5 people following a massive tornado that devastated Joplin, Mo., according to two new studies based on genomic sequencing by the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen) and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Health officials should be aware of infections caused by the fungus Apophysomyces, according to the studies, which tracked 13 people infected by the pathogen during the Class EF-5 tornado — the most powerful category — whose 200-plus mph winds plowed through Joplin on May 22, 2011, initially killing 160 and injuring more than 1,000.
Anti-microbial hydrogel offers new weapon against drug-resistant bacteria. Only a few bacteria are left over, after the hydrogel was used to destroy a solid bacterial biofilm Whether it’s in hospitals, restaurant kitchens or our homes, harmful bacteria such as E.coli are a constant concern.
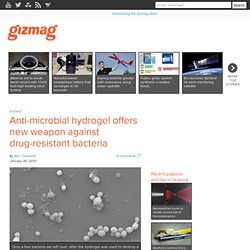
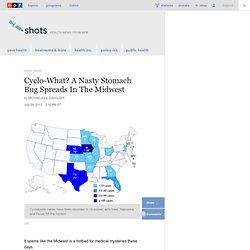
Making matters worse is the fact that such bacteria are increasingly developing a resistance to antibiotics. This has led to a number of research projects, which have utilized things such as blue light, cold plasma and ozone to kill germs. One of the latest non-antibiotic bacteria-slayers is a hydrogel developed by IBM Research and the Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology in Singapore. The hydrogel consists of water (over 90 percent of its composition), along with special polymers. Cyclo-What? A Nasty Stomach Bug Spreads In The Midwest : Shots - Health News. Hide captionCyclospora cases have been recorded in 14 states, with Iowa, Nebraska and Texas hit the hardest Cyclospora cases have been recorded in 14 states, with Iowa, Nebraska and Texas hit the hardest It seems like the Midwest is a hotbed for medical mysteries these days.
Earlier this week, scientists traced a brand-new virus to ticks in Missouri. Where 'Nightmare Bacteria' Came From, And How Our Inattention Helped Them Emerge - Wired Science. Cast your minds back a few months ago, to when the director of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced, “We have a very serious problem” with “nightmare bacteria,” and the chief medical officer of the United Kingdom backed him up a few days later, describing a “ticking time bomb” that threatens national security as seriously as terrorism.
Both public health chiefs were talking about a form of antibiotic resistance that is relatively new, and has suddenly emerged as much more serious — yet that the general public, and even much of the medical establishment, knows relatively little about. The acronym for this resistance is CRE, for carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae; breaking it down, that’s a family of gut-dwelling bacteria, a very common cause of hospital infections, that no longer respond to a group of last-ditch antibiotics called carbapenems. When Dr. What happens when an amoeba “eats” your brain. Last week, nine-year-old Hally Yust died after contracting a rare brain-eating amoeba infection while swimming near her family’s home in Kansas.
The organism responsible, Naegleria fowleri, dwells in warm freshwater lakes and rivers and usually targets children and young adults. Once in the brain it causes a swelling called primary meningoencephalitis. The infection is almost universally fatal: it kills more than 97 percent of its victims within days. The Math Behind Social Distancing. As we wait for scientists and healthcare professionals to develop a vaccine for COVID-19, there is another, more readily available tool at our disposal.

Social distancing, defined as measures taken to reduce physical contact, is the first line of defense for containing an infectious disease like COVID-19. That’s because these infections spread when people cough, sneeze, or touch surfaces on which the virus resides. To help us grasp the impact these measures can actually have, today’s infographic illustrates how a reduction in social exposure can theoretically contain the spread of infection. 9 Terrifying Parasites. Cymothoa Exigua: Replaces the Fish's Tongue Also called the "tongue-eating louse," this parasitic crustacean of the family Cymothoidae enters fish through the gills, then attaches itself at the base of the fish's tongue.
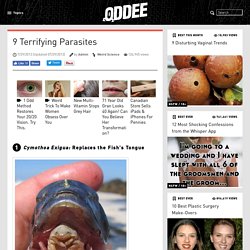
Once there, it extracts blood through its front claws, causing the tongue to atrophy from lack of blood, then it replaces the fish's tongue by attaching its own body to the muscles at the tongue's stub. They are supposedly not harmful to humans unless picked up alive, in which case they can bite. (Source) Mosquito Magnet clears an acre. It's not just those infernal bites that drive adults, children and animals to the edge, it's the increasing risk of diseases like Ross River Fever transmitted via mosquitoes that makes any new approach to the problem worth investigating. The recently released Mosquito Magnet emits a plume of carbon dioxide, heat and moisture to mimic a large mammal and combines this with the attractant octenol to control female mosquitoes (the ones that bite), midges, black flies and sandflies over an area up to an acre in size. The insects are trapped and killed using patented "Counterflow Technology" - a vacuum from the flared outer tube surrounds the inner plume of CO2 and drives the insects into a net as they approach the attractant.
Mosquito Magnet is based on research by the American Biophysics Corp. dating back to 1991 showing that blood seeking insects find a host by following carbon dioxide. Share.