

Noble Eightfold Path. Diagramme de causes et effets. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
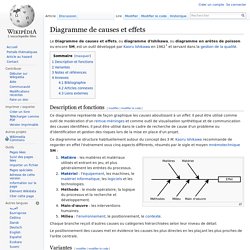
Le Diagramme de causes et effets, ou diagramme d'Ishikawa, ou diagramme en arêtes de poisson ou encore 5M, est un outil développé par Kaoru Ishikawa en 1962[1] et servant dans la gestion de la qualité. Ba gua. The bagua (Chinese: 八卦; literally "eight symbols") are eight trigrams used in Taoist cosmology to represent the fundamental principles of reality, seen as a range of eight interrelated concepts.
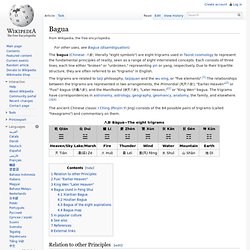
Each consists of three lines, each line either "broken" or "unbroken," representing yin or yang, respectively. Due to their tripartite structure, they are often referred to as "trigrams" in English. The ancient Chinese classic I Ching (Pinyin:Yi Jing) consists of the 64 possible pairs of trigrams (called "hexagrams") and commentary on them.
Relation to other Principles[edit] Wu Xing. Diagram of the interactions between the Wu Xing.
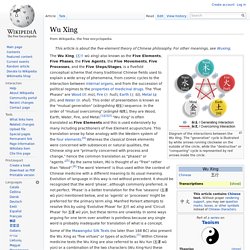
The "generative" cycle is illustrated by white arrows running clockwise on the outside of the circle, while the "destructive" or "conquering" cycle is represented by red arrows inside the circle. Some of the Mawangdui Silk Texts (no later than 168 BC) also present the Wu Xing as "five virtues" or types of activities.[7] Within Chinese medicine texts the Wu Xing are also referred to as Wu Yun (五運 wŭ yùn) or a combination of the two characters (Wu Xing-Yun) these emphasise the correspondence of five elements to five 'seasons' (four seasons plus one).
Another tradition refers to the wŭ xíng as wŭ dé 五德, the Five Virtues (zh:五德終始說). The system of five phases was used for describing interactions and relationships between phenomena. Noble Chemin Octuple. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
Eight Consciousnesses. The eightfold network of primary consciousnesses[edit] All surviving schools of buddhist thought accept – "in common" – the existence of the first six primary consciousnesses (Sanskrit: vijñāna, Tibetan: རྣམ་ཤེས་, Wylie: rnam-shes).[1] The internally coherent Yogācāra school associated with Maitreya, Asaṅga, and Vasubandhu, however, uniquely – or "uncommonly" – also posits the existence of two additional primary consciousnesses, kliṣṭamanas and ālayavijñāna, in order to explain the workings of karma.[2] The first six of these primary consciousnesses comprise the five sensory faculties together with mental consciousness, which is counted as the sixth.[3] According to Gareth Sparham, The ālaya-vijñāna doctrine arose on the Indian subcontinent about one thousand years before Tsong kha pa.
Arts-budhist-cheatsheet1.jpg (Image JPEG, 2200x1700 pixels) - Redimensionnée (46%) Index of Buddhism-related articles. Seven virtues. History[edit] The first virtues were identified by the Greek philosophers Aristotle and Plato, who regarded temperance, wisdom, justice, and courage as the four most desirable character traits.
After the New Testament was written, these four virtues became known as the cardinal virtues, while faith, hope and charity were referred to as the theological virtues. But Stalker, in his book The Seven Cardinal Virtues, says, "It is of distinct advantage to be reminded that the Christian character has a natural foundation... but certainly the latter are cardinal also--that is, hinge virtues; and it is convenient to have a single adjective for designating the whole seven".[1] Knightly Virtues. Chivalry, or the chivalric code, is a code of conduct associated with the medieval institution of knighthood.
Chivalry arose from an idealized German custom.[1] It developed first in the north of France among horse soldiers who served in Charlemagne′s heavy cavalry.[2] It was originally conceived of as an aristocratic warrior code — the term derives from the French term chevalerie, meaning horse soldiery[3] — involving gallantry, individual training, and service to others. Over time its meaning has been refined to emphasise more ideals such as the knightly virtues of honour, courtly love, courtesy, and less martial aspects of the tradition.
The Knight's Code of Chivalry was a moral and honorable system that stated all knights should protect others who can not protect themselves, such as widows, children, and elders. Knights vowed to be loyal, generous, and "of noble bearing". Knights were required to tell the truth and respect the honour of women. Terminology and definitions[edit] Seven Archangels. Archangels in current church traditions[edit] The Catholic Church in the Roman Rite only explicitly names 3 archangels: Gabriel, Michael and Raphael.
Gabriel and Michael are the only two named in the New Testament of the Bible. However, the same passages that name Raphael in the book of Tobit also states that he is "one of the seven who stand before God. " The other names can be derived from traditional Jewish teaching. Vertus théologales. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
Leur source dans le Nouveau Testament se trouve dans la première épitre de saint Paul aux Corinthiens (I Co 13,13). Présentation des trois vertus[modifier | modifier le code] Les vertus théologales sont au nombre de trois : Ce groupe tire son origine d'un passage fameux de la Première Épître de saint Paul aux Corinthiens (I Co 13, 13) : « Maintenant donc, ces trois-là demeurent, la foi (pistis), l’espérance (helpis) et l’amour (ou : charité, agapè) mais l’amour est le plus grand. » Ces vertus sont infusées par Dieu dans l’âme des fidèles pour les rendre capables d’agir comme ses enfants et de mériter la vie éternelle. The Seven Sins of Memory. The Seven Sins of Memory: How the Mind Forgets and Remembers is a book (ISBN 0-618-21919-6) by Daniel Schacter, former chair of Harvard University's Psychology Department and a leading memory researcher.
The book revolves around the theory that "the seven sins of memory" are similar to the Seven deadly sins, and that if you try to avoid committing these sins, it will help to improve your ability to remember. He argues that these features of human memory are not necessarily bad, and that they actually serve a useful purpose in memory. List of virtues. A virtue is a characteristic of a person which supports individual moral excellence and collective well being. Such characteristics are valued as a principle and recognized as a good way to be. This list is necessarily incomplete. Four discourses. The French psychoanalyst Jacques Lacan argued that there were four fundamental types of discourse. He defined four discourses, which he called Master, University, Hysteric and Analyst, and showed how these relate dynamically to one another.
Discourse of the Master - Struggle for mastery / domination / penetration. Tinbergen's four questions. Tinbergen's four questions, named after Nikolaas Tinbergen, are complementary categories of explanations for behaviour. It suggests that an integrative understanding of behaviour must include both a proximate and ultimate (functional) analysis of behaviour, as well as an understanding of both phylogenetic/developmental history and the operation of current mechanisms. [1] Four categories of questions and explanations[edit] When asked about the purpose of sight in humans and animals, even elementary school children can answer that animals have vision to help them find food and avoid danger (adaptation).
Fourth Way. According to this system, the chief difference between the three traditional schools, or ways, and the fourth way is that "they are permanent forms which have survived throughout history mostly unchanged, and are based on religion. Where schools of yogis, monks or fakirs exist, they are barely distinguishable from religious schools. The fourth way differs in that it is not a permanent way. It has no specific forms or institutions and comes and goes controlled by some particular laws of its own. " It always has some work of a specific import, and is never without some task around which and in connection with which it can alone exist. Quand on retrouve Evagre le Pontique. Seven deadly sins. According to Catholic moral thought, the seven deadly sins are not discrete from other sins, but are instead the origin ("capital" comes from the Latin caput, head) of the others.
Vices can be either venial or mortal, depending on the situation, but "are called 'capital' because they engender other sins, other vices".[2] Péché capital. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre. Les sept péchés capitaux identifiés par Thomas d'Aquin sont l’acédie (ou la paresse spirituelle), l’orgueil, la gourmandise, la luxure, l’avarice, la colère et l’envie. Historique[modifier | modifier le code] Seven princes of Hell. There have been various demonologies (classifications of demons) in Christian demonology and classical occultism and Renaissance magic. Classification systems are based on the nature of the demon, the sin with which they tempt people, the month in which their power was strongest, the saints that were their adversaries, or other characteristics. Classification by domain[edit] It can be noted that according to each author listed below, the domain of each demon is very different (with the exception of Francesco Maria Guazzo, who seem to have copied Michael Psellus with little difference).
It can also be seen that each author chooses and classifies demons differently. Demonology (occultism) There have been various demonologies (classifications of demons) in Christian demonology and classical occultism and Renaissance magic. Classification systems are based on the nature of the demon, the sin with which they tempt people, the month in which their power was strongest, the saints that were their adversaries, or other characteristics. Classification by domain[edit] It can be noted that according to each author listed below, the domain of each demon is very different (with the exception of Francesco Maria Guazzo, who seem to have copied Michael Psellus with little difference).
It can also be seen that each author chooses and classifies demons differently. Christian demonology. Théorie du cerveau triunique. 8-Circuit Model of Consciousness. The eight-circuit model of consciousness is a theory proposed by Timothy Leary and expanded on by Robert Anton Wilson and Antero Alli. The 8-Circuit Model of Consciousness. I. Level of consciousness (Esotericism) Consciousness is a loosely defined concept that addresses the human awareness of both internal and external stimuli. The 42 Commandments of Ancient Egypt. Théorie des intelligences multiples. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
La théorie des intelligences multiples suggère qu'il existe plusieurs types d'intelligence chez l'enfant d'âge scolaire et aussi, par extension, chez l'Homme. Enneagram of Personality. Four Noble Truths. Quatre nobles vérités. Trente-sept éléments de l'Éveil. 21 symptômes de l'éveil spirituel : le cauchemar du nouvel ordre mondial. The Sequence of Archetypes in Individuation. 25 Ways To Thrive In The Midst Of Chaos — Life Advices. Category:Esoteric cosmology.
Tree of life (Kabbalah) Tarot-quicksheet1.jpg (Image JPEG, 1700x2200 pixels) Category:Ethics. Category:Ethical principles. Éthique de la vertu. Pleine conscience. Category:Cultural lists. Liste des concepts de la philosophie. Category:Philosophical concepts. Catégorie:Liste en rapport avec la philosophie. Catégorie:Concept philosophique. Classical element. Category:Emotions. Emotion. Category:Psychological attitude. Inner-gifts.jpg (Image JPEG, 1100x850 pixels) - Redimensionnée (95%)
Chakra. Paramita. The Seven Spiritual Laws of Success by Deepak Chopra. Indriya. Skandha. Indriya.