

Multipath propagation. Examples of multipath propagation[edit] Radar multipath echoes from an actual target cause ghosts to appear.
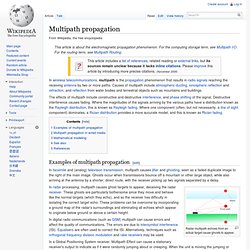
Calendar. Voyager Golden Record. Cover of the Voyager Golden Record The Voyager Golden Records are phonograph records which were included aboard both Voyager spacecrafts, which were launched in 1977.
They contain sounds and images selected to portray the diversity of life and culture on Earth, and are intended for any intelligent extraterrestrial life form, or for future humans, who may find them. The Phobia List. Newcomb's paradox. In philosophy and mathematics, Newcomb's paradox, also referred to as Newcomb's problem, is a thought experiment involving a game between two players, one of whom purports to be able to predict the future.
Whether the problem is actually a paradox is disputed. Eggs and Their Evolution. Eggs and Their Evolution Females of all vertebrates produce eggs, but the reptiles "invented" the eggshell -- a device that could keep the egg from drying out and allow reproduction away from water (or, at least, from extremely moist environments).

Transhumanism. Transhumanism (abbreviated as H+ or h+) is an international cultural and intellectual movement with an eventual goal of fundamentally transforming the human condition by developing and making widely available technologies to greatly enhance human intellectual, physical, and psychological capacities.[1] Transhumanist thinkers study the potential benefits and dangers of emerging technologies that could overcome fundamental human limitations, as well as the ethics of developing and using such technologies.
They speculate that human beings may eventually be able to transform themselves into beings with such greatly expanded abilities as to merit the label "posthuman".[1] History[edit] Cloud iridescence. Cloud iridescence Cloud iridescence is the occurrence of colors in a cloud similar to those seen in oil films on puddles, and is similar to irisation.
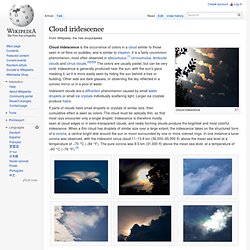
It is a fairly uncommon phenomenon, most often observed in altocumulus,[1] cirrocumulus, lenticular clouds and cirrus clouds.[2][3][4] The colors are usually pastel, but can be very vivid. Iridescence is generally produced near the sun, with the sun's glare masking it, so it is more easily seen by hiding the sun behind a tree or building. Moravec's paradox. Moravec's paradox is the discovery by artificial intelligence and robotics researchers that, contrary to traditional assumptions, high-level reasoning requires very little computation, but low-level sensorimotor skills require enormous computational resources.
The principle was articulated by Hans Moravec, Rodney Brooks, Marvin Minsky and others in the 1980s. As Moravec writes, "it is comparatively easy to make computers exhibit adult level performance on intelligence tests or playing checkers, and difficult or impossible to give them the skills of a one-year-old when it comes to perception and mobility. " Van Allen radiation belt. This video illustrates changes in the shape and intensity of a cross section of the Van Allen belts Van Allen radiation belts (cross section) A radiation belt is a layer of energetic charged particles that is held in place around a magnetized planet, such as the Earth, by the planet's magnetic field.
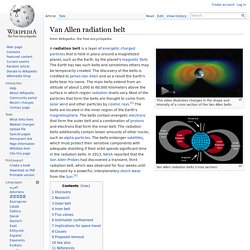
The Earth has two such belts and sometimes others may be temporarily created. Schumann resonances. Animation of Schumann resonance in Earth's atmosphere.
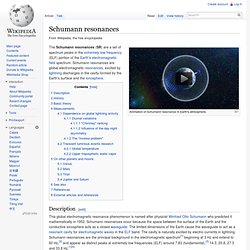
The Schumann resonances (SR) are a set of spectrum peaks in the extremely low frequency (ELF) portion of the Earth's electromagnetic field spectrum. Schumann resonances are global electromagnetic resonances, excited by lightning discharges in the cavity formed by the Earth's surface and the ionosphere. Description[edit] This global electromagnetic resonance phenomenon is named after physicist Winfried Otto Schumann who predicted it mathematically in 1952. South Magnetic Pole. Locations of South Magnetic Pole from direct observation and model prediction.[1] The South Magnetic Pole is the wandering point on the Earth's Southern Hemisphere where the geomagnetic field lines are directed vertically upwards.
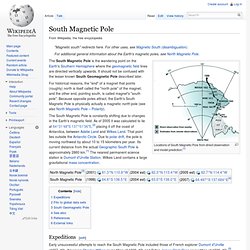
It should not be confused with the lesser known South Geomagnetic Pole described later. For historical reasons, the "end" of a magnet that points (roughly) north is itself called the "north pole" of the magnet, and the other end, pointing south, is called magnet's "south pole". Because opposite poles attract, the Earth's South Magnetic Pole is physically actually a magnetic north pole (see also North Magnetic Pole – Polarity).
The South Magnetic Pole is constantly shifting due to changes in the Earth's magnetic field. WikiMiniAtlas 64°31′48″S 137°51′36″E / 64.53000°S 137.86000°E / -64.53000; 137.86000,[2] placing it off the coast of Antarctica, between Adelie Land and Wilkes Land. Naga fireballs. The Naga fireballs (Thai: บั้งไฟพญานาค; RTGS: bang fai phaya nak), also known as the Mekong lights, and “bung fai paya nak” by the locals, is a phenomenon with unconfirmed source said to be often seen in Thailand’s Mekong river, which is also seen in (Nong Khai province in Isan) and in Laos (Vientiane Province)—in which glowing balls are alleged to naturally rise from the water high into the air.[1] The balls are said to be reddish and to have diverse sizes from smaller sparkles up to the size of basketballs;[2] they quickly rise up to a couple of hundred metres before disappearing. The number of fireballs reported varies between tens and thousands per night.[3] Description[edit]
The Nine Types of Intelligence. By Howard Gardner 1. Naturalist Intelligence (“Nature Smart”) Designates the human ability to discriminate among living things (plants, animals) as well as sensitivity to other features of the natural world (clouds, rock configurations). This ability was clearly of value in our evolutionary past as hunters, gatherers, and farmers; it continues to be central in such roles as botanist or chef. Genie (feral child) Genie (born 1957) is the pseudonym of a feral child who was the victim of extraordinarily severe abuse, neglect and social isolation. Her circumstances are recorded prominently in the annals of abnormal child psychology.[2] Born in Arcadia, California, United States, Genie's father kept her locked alone in a room from the age of 20 months to 13 years, 7 months, almost always strapped to a child's toilet or bound in a crib with her arms and legs completely immobilized.
During this time she was never exposed to any significant amount of speech, and as a result she did not acquire a first language during childhood. Her abuse came to the attention of Los Angeles child welfare authorities on November 4, 1970.[3][4] In the first several years after Genie's life and circumstances came to light, psychologists, linguists and other scientists focused a great deal of attention on Genie's case, seeing in her near-total isolation an opportunity to study many aspects of human development.
Victor of Aveyron. Victor of Aveyron (c. 1788 – 1828) was a French feral child who was found in 1800 after apparently spending the majority of his childhood alone in the woods. Upon his discovery, his case was taken up by a young physician, Jean Marc Gaspard Itard, who worked with the boy for five years and gave him his name, Victor. Itard was interested in determining what Victor could learn. He devised procedures to teach the boy words and recorded his progress. Based on his work with Victor, Itard broke new ground in the education of the developmentally delayed.
Early life[edit] Victor is estimated to have been born around 1788. Study[edit]