

Earthship. Default - Passive house. Passive house (German: Passivhaus) is a rigorous, voluntary standard for energy efficiency in a building, reducing its ecological footprint.[1] It results in ultra-low energy buildings that require little energy for space heating or cooling.[2][3] A similar standard, MINERGIE-P, is used in Switzerland.[4] The standard is not confined to residential properties; several office buildings, schools, kindergartens and a supermarket have also been constructed to the standard.
Passive design is not an attachment or supplement to architectural design, but a design process that is integrated with architectural design.[5] Although it is mostly applied to new buildings, it has also been used for refurbishments. History[edit] Bo Adamson, co-originator of the passive house concept. Default - Superinsulation. The passivhaus standard combines superinsulation with other techniques and technologies to achieve ultra-low energy use.
Superinsulation is an approach to building design, construction, and retrofitting that dramatically reduces heat loss (and gain) by using much higher levels of insulation and airtightness than normal. Superinsulation is one of the ancestors of the passive house approach. Definition[edit] Sustainable Architecture. Earthships 101 part II EcoSchool - Making LCD into Solar Panel EcoSchool - HOME-MADE: LOW COST august 2005 PHOTOVOLTAIC. Earthships - Trombe wall. Passive solar design using an unvented Trombe wall and summer shading A Trombe wall is a passive solar building technique where a wall is built on the winter sun side of a building with a glass external layer and a high heat capacity internal layer separated by a layer of air.
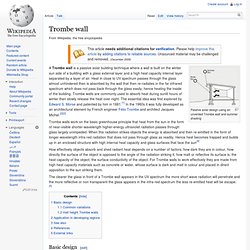
Heat in close to UV spectrum passes through the glass almost unhindered then is absorbed by the wall that then re-radiates in the far infrared spectrum which does not pass back through the glass easily, hence heating the inside of the building. Trombe walls are commonly used to absorb heat during sunlit hours of winter then slowly release the heat over night. The essential idea was first explored by Edward S. Earthships - Rammed earth. A typical Hmong house-building technique in the tropical climate of Vietnam Overview of use[edit] Model showing construction of rammed-earth wall on foundation The construction of an entire wall begins with a temporary frame (formwork), usually made of wood or plywood, to act as a mould for the desired shape and dimensions of each wall section.
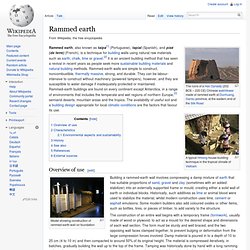
The form must be sturdy and well braced, and the two opposing wall faces clamped together, to prevent bulging or deformation from the large compression forces involved. Earthships - Design Build Bluff. DesignBuildBLUFF is a non-profit organization based in Park City, Utah that designs and builds sustainable housing, and is noted for its award-winning and innovative home designs.[1] It is named after Bluff, Utah where their campus facility is located and because of Bluff's close proximity to the Navajo Nation.
Each year, graduate-level architecture students from the University of Utah College of Architecture and Planning, and more recently, The University of Colorado Denver, design and build a home for a member of the Navajo Nation, at no charge to the home recipient. The homes are built with sustainable architecture techniques and feature locally produced construction materials. The program is currently expanding to other universities in The Four Corners region.[2][3][4][5][6][7] History[edit] DesignBuildBLUFF was founded in 2000 by University of Utah Professor, Hank Louis.
Earthships - Deep cycle battery. A deep cycle battery traffic signal A deep-cycle battery is a lead-acid battery designed to be regularly deeply discharged using most of its capacity.
In contrast, starter batteries (e.g. most automotive batteries) are designed to deliver short, high-current bursts for cranking the engine, thus frequently discharging only a small part of their capacity. While a deep-cycle battery can be used as a starting battery, the lower "cranking amps" imply that an oversized battery may be required. Earthships - Desulfation. The lead–acid battery was invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté and is the oldest type of rechargeable battery.
Despite having a very low energy-to-weight ratio and a low energy-to-volume ratio, its ability to supply high surge currents means that the cells have a relatively large power-to-weight ratio. These features, along with their low cost, makes it attractive for use in motor vehicles to provide the high current required by automobile starter motors. As they are inexpensive compared to newer technologies, lead-acid batteries are widely used even when surge current is not important and other designs could provide higher energy densities. Earthships - Lithium-ion battery. Lithium-ion batteries are common in consumer electronics.
They are one of the most popular types of rechargeable battery for portable electronics, with one of the best energy densities, no memory effect (note, however, that new studies have shown signs of memory effect in lithium-ion batteries[6]), and only a slow loss of charge when not in use. Beyond consumer electronics, LIBs are also growing in popularity for military, electric vehicle and aerospace applications.[7] For example, Lithium-ion batteries are becoming a common replacement for the lead acid batteries that have been used historically for golf carts and utility vehicles.
Instead of heavy lead plates and acid electrolyte, the trend is to use a lightweight lithium/carbon negative electrodes and lithium iron phosphate positive electrodes. Lithium-ion batteries can provide the same voltage as lead-acid batteries, so no modification to the vehicle's drive system is required.[8] Earthships - Lithium iron phosphate battery. The lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO 4) battery, also called LFP battery (with "LFP" standing for "lithium ferrophosphate"), is a type of rechargeable battery, specifically a lithium-ion battery, which uses LiFePO 4 as a cathode material.
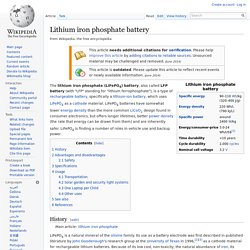
LiFePO 4 batteries have somewhat lower energy density than the more common LiCoO 2 design found in consumer electronics, but offers longer lifetimes, better power density (the rate that energy can be drawn from them) and are inherently safer. Earthships - Septic drain field. Septic drain fields, also called leach fields or leach drains are used to remove contaminants and impurities from the liquid that emerges from the septic tank.
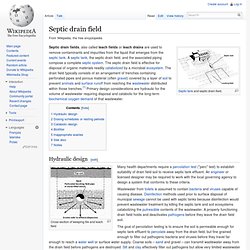
A septic tank, the septic drain field, and the associated piping compose a complete septic system. The septic drain field is effective for disposal of organic materials readily catabolized by a microbial ecosystem. The drain field typically consists of an arrangement of trenches containing perforated pipes and porous material (often gravel) covered by a layer of soil to prevent animals and surface runoff from reaching the wastewater distributed within those trenches.[1] Primary design considerations are hydraulic for the volume of wastewater requiring disposal and catabolic for the long-term biochemical oxygen demand of that wastewater.
Earthships - Photovoltaics. Earthships - Concentrated solar power. Concentrated solar power (also called concentrating solar power, concentrated solar thermal, and CSP) systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate a large area of sunlight, or solar thermal energy, onto a small area. Electrical power is produced when the concentrated light is converted to heat, which drives a heat engine (usually a steam turbine) connected to an electrical power generator or powers a thermochemical reaction (experimental as of 2013).[1][2][3] CSP is being widely commercialized and the CSP market has seen about 740 MW of generating capacity added between 2007 and the end of 2010. More than half of this (about 478 MW) was installed during 2010, bringing the global total to 1095 MW. CSP growth is expected to continue at a fast pace. As of January 2014, Spain had a total capacity of 2,204 MW making this country the world leader in CSP. CSP is not to be confused with concentrated photovoltaics (CPV).
Earthships - Carburizing. A modern computerised Gas Carburising furnace Carburizing[1] or carburising (chiefly British English) is a heat treatment process in which iron or steel absorbs carbon liberated when the metal is heated in the presence of a carbon bearing material, such as charcoal or carbon monoxide, with the intent of making the metal harder. Depending on the amount of time and temperature, the affected area can vary in carbon content. Longer carburizing times and higher temperatures typically increase the depth of carbon diffusion. When the iron or steel is cooled rapidly by quenching, the higher carbon content on the outer surface becomes hard via the transformation from austenite to martensite, while the core remains soft and tough as a ferritic and/or pearlite microstructure.[2] Method[edit] Earthships - Passive solar building design. Elements of passive solar design, shown in a direct gain application In passive solar building design, windows, walls, and floors are made to collect, store, and distribute solar energy in the form of heat in the winter and reject solar heat in the summer.
This is called passive solar design or climatic design because, unlike active solar heating systems, it doesn't involve the use of mechanical and electrical devices.[1] The key to designing a passive solar building is to best take advantage of the local climate. Elements to be considered include window placement and glazing type, thermal insulation, thermal mass, and shading.[2] Passive solar design techniques can be applied most easily to new buildings, but existing buildings can be adapted or "retrofitted".
Earthships - Solar chimney. This article refers to a device for ventilation. For the power generation technology, see Solar updraft tower. The solar chimney has been in use for centuries, particularly in the Middle east and Near East by the Persians, as well as in Europe by the Romans. Earthships - Double envelope house. Earthships - File:RegularEarthshipDesign.svg - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Cancel Edit Delete Preview revert Text of the note (may include Wiki markup) Could not save your note (edit conflict or other problem). Please copy the text in the edit box below and insert it manually by editing this page. Earthships - Earthship.