

Gold Rush. WordPress.com ‹ Log In. Login. Login. Login. Golden Victoria. Australian Gold, History & Culture Info/Chinese On The Australian Gold Fields - Historic Gold Rush Village Mogo South Coast NSW Australia. Most migrants who joined the Australian goldrush left behind family and home.

This was particularly difficult for the Chinese who came from a traditional culture that focused heavily on parents, family and the ancestral village. The majority of Chinese men who came to NSW were not individual fortune hunters, but came as a family representative seeking an essential and supplementary income for his family and his wife who had been left at home to honour her primary role as support for her in-laws. Added to that was the "credit-ticket" system whereby the family, villagers and brokers set up a co-operative venture to pay for the ticket.
Australian Aboriginals and Chinese immigrants were especially identified in populations statistics. Chinese travelling outside of NSW had to get special re-entry certificates. Mei Quong Tart By the 1870's 10% of the population of Majors Creek were Chinese. Chinese Entrepreneurial Activities Anti-Chinese Laws. Riot or Revolution (2005) clip 1 on ASO.
This clip starts approximately 20 minutes into the documentary.
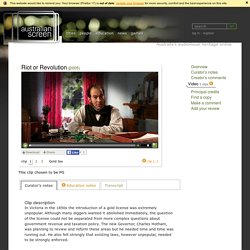
We are shown illustrations of a landscape scene of a port, men working in a minefields and a congregation of squatters. This is intermittently cut into a reenactment of an actor playing Governor Hotham accompany a narration. We hear sound effects of mean talking and chamber music under the narration. There is a portrait of La Trobe against a Union Jack, we then see illustration of men debating in parliament and diggers and policemen in mining camps. There is a graphic of a newspaper clipping that reads, ‘Abolition License Tax, Great Open Air Meeting, To the Public of Bendigo, Meeting, On Saturday next, August 26. Narrator Most government revenue was raised through indirect taxes, primarily import duties. Actor playing Governor Hotham You ask me to do a very serious thing – to do away with a large portion of public revenue. Life on the goldfields living there.
Hangouts in History: The Goldrush. The Australian Gold Rush (animation) State Library of New South Wales. The gold rushes and the diggers who worked the goldfields are etched into Australian folklore.
Follow the story of the people who sought the glittering prize. Edward Hammond Hargraves is credited with finding the first payable goldfields at Ophir, near Bathurst, New South Wales, on 12 February 1851. News of gold spread quickly around the world and in 1852 alone, 370,000 immigrants arrived in Australia. By 1871, the national population had trebled to 1.7 million. Australian gold rushes. Australian gold diggings, by Edwin Stocqueler, c. 1855 After the California gold rush began in 1848, causing many people to leave Australia for California to look for gold there, the New South Wales government rethought its position, and sought approval from the Colonial Office in England to allow the exploitation of the mineral resources and also offered rewards for the finding of payable gold.[2] The first gold rush in Australia began in May 1851 after prospector Edward Hargraves claimed to have discovered payable gold near Orange, at a site he called Ophir.[3] Hargraves had been to the Californian goldfields and had learned new gold prospecting techniques such as panning and cradling.
National Museum of Australia. Eureka Stockade 1854: Rebellion of goldminers at the Eureka Stockade, Ballarat, Victoria On 1 December 1854, miners, disgruntled with the way the colonial government had been administering the goldfields, built a stockade at the Eureka diggings near Ballarat, Victoria and swore allegiance to the Southern Cross flag.

Early on the morning of Sunday 3 December, when the stockade was only lightly guarded, government troops attacked. Twenty-two diggers and five soldiers were killed. Victorian goldfields nugget. Bealiba gold nugget. Defining Moments: Gold rushes and the Bealiba nugget. National Museum of Australia. Defining Moments: Gold rushes and the Bealiba nugget. Gold Rush in Australia: About life on the goldfields from 1851 — kidcyber. Towards the end of August 1851, James Reagan and John Dunlop discovered the richest goldfield the world has ever seen in a place the Aborigines called Balla arat, which means 'camping place', now the city of Ballarat.

Other discoveries soon followed in Mount Alexander, now called Castlemaine, in Daylesford, Creswick, Maryborough, Bendigo and McIvor, now called Heathcote. Thousands of people left their homes and jobs and set off to the diggings to find their fortune. Gold civilisation teachers colour. Gold civilisation student colour.
History Hill Museum Australia's Golden History - History Hill Museum. It is said that in excess of 95% of the world’s gold has been unearthed during the past 10,000 years.

Of this, the most colourful and exciting period was that of the 1840’s onto the turn of the century when the circumnavigation of the earth together with the settlement and communication, primitive but effective, were completed. In 1848, the discovery of gold by an American engineer of the James Wilson Marshall sparked of the first major international migration to seek out and extract gold. This discovery took place while Marshall was working for Captain John Suttor at Suttors Mill on the Sacramento River in California in the United States of America . Diggers from all over the world armed with picks, shovels and above all, hope swarmed in the New American El Dorado. They were christened the 49’ers and were born into a rough clad society of multi-national races, encumbering gold seekers, fortune hunters, con-men and other all willing to do anything to earn a dollar.
Gold Rush in Australia: About life on the goldfields from 1851 — kidcyber. ~ GOLD ~ Gold Rush: 23/02/2010, Behind the News. Have you ever heard about the gold rush of the past and wished you could strike it rich?

Well now might be your chance! Gold mines that have been closed for years are opening up again, but before you grab a pick-axe and start digging, Sarah discovered that it's new technology that's blowing the cobwebs off some historic mine sites. SARAH LARSEN, REPORTER: It was the precious metal that transformed Australia. When a spec was found in a Victorian creek in 1851 gold fever took hold. Gold Rush: 23/02/2010, Behind the News.
Education Resources - Central Deborah Gold Mine. Bendigo is the home of the biggest gold rush in Australian history.
During the period from 1851-1954 a staggering 700 000 kilograms of gold was found, which would be worth about $28billion today! The I Files - Gold Rushes (Australia) Can you strike it rich during the Gold Rush? Australian History Mysteries. The promise of gold. Race to the Gold Diggings of Australia is a boxed, children’s board game produced in England around 1855.
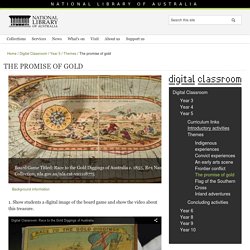
It is the earliest known board game that has Australia as its theme. Inside a printed wooden box is a brightly coloured game board (a linen-mounted, hand-coloured lithographic sheet), a printed sheet of rules, six ships made of painted metal and painted wood (to be used as counters), two dice, three wooden pegs, and a cardboard teetotum (spinning top). Manufactured at the height of the Australian gold rushes, the game was a nineteenth-century marketing tool designed to attract much-needed skilled migration to the developing colony.
The game board features an oval track, divided into 80 sections, representing the voyage from England to Australia. Australian Gold Rush Resource Pack Teaching Resource – Teach Starter. 27 pages of worksheets, posters and classroom decorations about the Australian Gold Rush Era. This Australian Gold Rush Teaching Resource pack includes: Title page / posterAustralian Gold Rush Immigration posterWord Wall poster and cardsGoldfields around Australia worksheet and map puzzleLife on the Goldfields letter writing activity3 x page borders2 x pages cork bord boarders6 x pages of cut-out decorations / narrative writing scene stimuliGold Rush timeline (single page and 4 page banner version) You might also like these educational posters: A version of this teaching resource document can be opened and edited in Microsoft Word, allowing you to add your own custom content.
Need help opening and editing this Word document? "I love teach starter and am so thankful to have found such a great resource collection. The Australian gold rush. JCF Johnson, A Game of Euchre, col. wood engraving, Australasian Sketcher Supplement [Melbourne], 25 December, 1876. Image courtesy of the National Library of Australia: nla.pic-an8927787. The gold rushes of the nineteenth century and the lives of those who worked the goldfields – known as 'diggers' – are etched into our national folklore. There is no doubt that the gold rushes had a huge effect on the Australian economy and our development as a nation.
It is also true to say that those heady times had a profound impact on the national psyche. The camaraderie and 'mateship' that developed between diggers on the goldfields is still integral to how we – and others – perceive ourselves as Australians. Indeed, mateship and defiance of authority have been central to the way our history has been told. Even today, nothing evokes more widespread national pride than groups of irreverent Aussie 'blokes' beating the English at cricket, or any other sport for that matter!