

Grecia. The Odyssey. From hiding inside a wooden horse to blinding a Cyclops, Odysseus has really been through the ringer.
In this Odyssey rap, we explore all the adventures he endured while trying to make it home to his wife and son. Will Penelope fall for one of her many suitors? Will Odysseus return home safely? How much does Poseidon really hate him? You may never have heard Homer’s Odyssey in a rap song. This video was produced through a partnership with READ Magazine. Intro This my Odyssey, they call me Odysseus, You want an epic? Yeah they got killed, I thought that was the end, It’s time to sail home, and kick it with my friends, And see my wife, yeah that would have been nice, But you can’t predict your fate like a roll of the dice, Next up? Home… Oh take me home, After all that I’ve been through I’m coming back to see you. But Penelope thinks it might be me, So she sets up a little test of archery, Yeah, I win the tournament; I’m a Hades-of-a-shot, The Odyssey is the sequel to Homer's The Iliad. Greek Mythology vs. Roman Mythology for Kids.
Greek Mythology Webquest. Gods, Heroes, and Myth: Search. Food in Ancient Greece. The Greek diet consisted of foods that were easily raised in the rocky terrain of Greece’s landscape.

Breakfast was eaten just after sunrise and consisted of bread dipped in wine. Lunch was again bread dipped in wine along with some olives, figs, cheese or dried fish. Supper was the main meal of each day. It was eaten near sunset. It consisted of vegetables, fruit, fish, and possibly honey cakes. Fish was the main source of protein in the Greek diet. Wine was the main drink in ancient Greece. The Greeks did not have any eating utensils, so they ate with their hands. Men often gathered for dinner parties called symposiums. Daily Life in Ancient Greece Children Clothing Fashion Food Home Life Marriage Men and Women's Roles Shopping Women Historyphoto101.com - Great History Photos, Right Price Follow our updates on Facebook or Twitter Pictures on this page are for viewing only.
Please see Pictures Galleries for Royalty Free images for Educational uses. See Our New Photo Site HistoryPhoto101.com. Greek Slaves. Slave woman playing a kithara.

You can tell she is a slave because she has short hair. In ancient Greece, most people who worked at jobs - teachers, doctors, nurses, construction workers, policemen, hair-dressers, mail carriers, cooks, nannies, bakers, miners, farmhands, dancers, musicians, craftspeople, and accountants - were slaves instead of free people. This was partly because free Greek people had no money to pay workers with (until the Archaic period), and because they had no clocks (to measure how long somebody had worked). But it was also because it is cheaper to force people to work for you than it is to pay them.
And, if people are slaves, they do not vote in your democracy - only free men could vote. A man cooking - probably a slave(Louvre Museum, Paris) Most people who were slaves in Greece had been born free. There were a lot of jobs, and so about a third of the people living in ancient Greece were slaves. A slave nanny taking the baby (see the loom behind her?) Ancient Greece - History, mythology, art, war, culture, society, and architecture. Ancient Greek Economy. Bronze Age storage jars at Knossos The Greeks did not have the same idea of an economy that we have.

The word "economy" is Greek, but to the Greeks it meant something like "rules of a household" (the "eco" part of economy is from the Greek word for house, "oikos", and the "nomy" part is from their word for law). Because they did not think about the economy as a whole, it is hard to talk of a government economic policy. Minoan civilization. Map of Minoan Crete The Minoan civilization was an Aegean Bronze Age civilization that arose on the island of Crete and flourished from approximately the 27th century BC to the 15th century BC.[1] It was rediscovered at the beginning of the 20th century through the work of British archaeologist Arthur Evans.
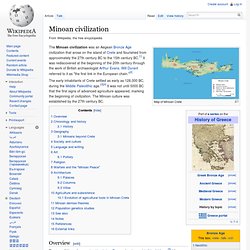
Will Durant referred to it as "the first link in the European chain. "[2] The early inhabitants of Crete settled as early as 128,000 BC, during the Middle Paleolithic age.[3][4] It was not until 5000 BC that the first signs of advanced agriculture appeared, marking the beginning of civilization. Overview[edit] The term "Minoan" was coined by Arthur Evans after the mythic "king" Minos.[5] Minos was associated in Greek myth with the labyrinth, which Evans identified with the site at Knossos.
Chronology and history[edit] Rather than associate absolute calendar dates for the Minoan period, archaeologists use two systems of relative chronology. History[edit] Ancient Greece - History, mythology, art, war, culture, society, and architecture. Ancient Greece. Athens, Greece: Practical Information, ATMs, shop hours, bus schedules, hospitals, clinics, embassy, churches, trains,