

The following resources will further discuss on how children learn masculine or feminine identities, preference and behaviours through gender-role development theory ( involving of differential reinforcement and observational learning ). AS AQB gender SLTBasics. Gender Schema Theory - an overview. 5.1.2 Effects of gender identity on behavior Gender roles also create sex differences in behavior when people adopt them as gender identities.
Masculine and feminine identities guide behavior through self-regulatory processes. That is, people use their gender identity as a personal standard by against which to evaluate and guide their behavior (Moretti & Higgins, 1999; Wood, Christensen, Hebl, & Rothgerber, 1997). Just as agency and communion are typical themes of social expectations, people commonly internalize aspects of gender roles involving agency and communion (Wood & Eagly, 2009). Open Education Sociology Dictionary. Definition of Gender Role (noun) The expected role determined by an individual’s sex and the associated attitudes, behaviors, norms, and values.
Examples of Gender Role The idea that men are breadwinners (money makers) outside the home and women are homemakers that bake the bread and take care of children.The idea that men as masculine people are aggressive, competitive, and violent, and women as feminine people are gentle, passive, and nurturing. Gender Role Pronunciation Pronunciation Usage Guide. At What Age Does Gender Identity Develop? Research shows that children recognize their own gender and gender in others starting as early as two or three years old.
Research shows that children recognize their own gender and gender in others starting when they are very young. You may notice children behaving in ways typical of their gender as early as two or three years old. By the age of five, most children can identify the gender of other people. Children whose gender identity doesn’t match the gender they were assigned at birth may behave in ways that don’t match their assigned gender. For example, a child who was assigned female at birth might prefer to play with "boy toys" like trucks and tools. Since young, children are taught to perceive “sex-appropriate” colour, toys, hairstyle, dress code as well as interest. Based on the image below, we can see that gender identity are categorised in terms of personalities, characteristics and behaviours. Gender Identity and Expression in the Early Childhood Classroom: Influences o... BandurasTheory. Albert Bandura’s social cognitive theory argues that social learning theory (SLT) and social cognitive learning theory (SCLT) is based on observation.
Bobo Doll Experiment. Bobo Doll Experiment By Dr. Saul McLeod, updated 2014. Albert Bandura's Social Learning Theory. Albert Bandura's Social Learning Theory By Saul McLeod, updated 2016 Social learning theory, proposed by Albert Bandura, emphasizes the importance of observing, modelling, and imitating the behaviors, attitudes, and emotional reactions of others.

Social learning theory considers how both environmental and cognitive factors interact to influence human learning and behavior. In social learning theory, Albert Bandura (1977) agrees with the behaviorist learning theories of classical conditioning and operant conditioning. What is Differential Reinforcement? Differential reinforcement is a strategy used in applied behavior analysis (ABA) to address challenging or undesirable behavior, usually in children.
While there are a number of techniques used in differential reinforcement, the goal is always the same: to encourage appropriate behavior by giving or withholding reinforcement. The theory behind differential reinforcement is that people tend to repeat behaviors that are reinforced or rewarded and are less likely to continue behaviors that aren’t reinforced. Differential reinforcement consists of two components: Reinforcing the appropriate behaviorWithholding reinforcement of the inappropriate behavior ‘Appropriate’ behavior in differential reinforcement may be recognized as: (1) not behaving inappropriately; or (2) choosing a positive response over a negative one.
What Is Observational Learning? - Explore Psychology. (Last Updated On: September 2, 2021) Observational learning is a way of acquiring skills and knowledge by observing and imitating others.
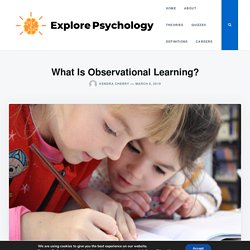
People watch others perform a skill, remember what they have observed, and later replicate this knowledge through their own behaviors. Children learn how to display appropriate facial expression through observing, same goes to gender role and identities. The image below demonstrate a good example on how people acquire skills via observational learning. Observational Learning occurs through processes of attention, retention, processing and hence motivation.