

Earth's Rotation & Revolution: Crash Course Kids 8.1. Weather vs. Climate: Crash Course Kids #28.1. Because weather is awesome. For students and teachers, BOM. The Bureau of Meteorology is committed to supporting education and research through the provision of data and information.
A wide range of information is available on our website, other data may be available upon request (charges may apply). The Bureau also participates in the CSIRO STEM Professionals in Schools program. Weather planning. Australia's official weather forecasts & weather radar - Bureau of Meteorology. Weather Forecasting - BTN 17/02/2009. As we've seen over the past few weeks the temperature and the weather can have a huge affect on people's lives so predicting what they'll be in the future is really important.
All sorts of people rely on weather forecasts; from Emergency workers to farmers, sailors, pilots, and ordinary people planning the week ahead. But how DO weather forecasters know what will happen in the future? Sarah went to find out. SARAH LARSEN, REPORTER: What does your future hold? Weather Channels: Crash Course Kids #34.2. Severe Weather: Crash Course Kids #28.2. Effects of dry weather. Animals that like wet weather - Science (F,1) Explore the weather (game for laptops only) Unit study: Weather. Seasons and the Sun: Crash Course Kids 11.1. The Four Seasons. Earth's Seasons. Science >> Earth Science for Kids We divide up the year into four seasons: spring, summer, autumn, and winter.
Each season lasts 3 months with summer being the warmest season, winter being the coldest, and spring and autumn lying in between. The seasons have a lot of impact on what happens on the earth. In the spring, animals are born and plants come back to life. Summer is hot and is when kids are usually out of school and we take vacations to the beach. What Causes Seasons? The passing of a year can bring a marked change in the weather and the surrounding environment.
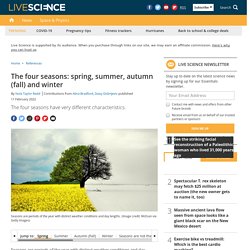
The four seasons — winter, spring, summer, autumn — can vary significantly in characteristics, and can prompt changes in the world around them. Let's take an overview of these four separate periods. Attributes of the seasons may vary by location, but there are still broad definitions that cross most of the boundaries. In the spring, seeds take root and vegetation begins to grow. The weather is warmer, and often wetter. In the summer, temperatures may increase to their hottest of the year. In the autumn, or fall, temperatures cool again. Winter often brings a chill. Error loading player: No playable sources found. Seasons in Australia — kidcyber. Seasons with Dirtgirl (video) Indigenous Weather Knowledge - Bureau of Meteorology. Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people have developed an intricate understanding of the environment over many thousands of years.

Artist: Laurie Nilsen The artwork used in the design of this website represents the relationships between seasonal, meteorological and astronomical changes - and how the Mandandanji people read these changes to inform life on country. About the Indigenous Weather Knowledge website Learn more about the Indigenous Weather Knowledge (IWK) website and the Bureau of Meteorology's commitment to strengthening respectful and collaborative relationships with Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people.
About the Indigenous Weather Knowledge website Language, culture and environmental knowledge See an overview of the relationships between language, culture and environmental knowledge. Language, culture and environmental knowledge Reconciliation Action Plan Download our RAP. Indigenous seasons across northern Australia - Geography (1,4) ABC online education. How to Make a Cloud. What is a cloud exactly?
We look at them every day, but few of us realize what they are made of. In a nutshell, clouds are collections of tiny water droplets, formed when the warm air that is being heated by the sun's rays meets the cold, damp air coming up off the cold ground. Little water drops form into clouds. The water drops are so small and light that they can float in the air. When enough water droplets have gathered together, they get too heavy to float and fall down as rain. How does rain form and what is the water cycle? Forms of Precipitation.