

Mythologies. Greek mythology. Greek mythology is explicitly embodied in a large collection of narratives, and implicitly in Greek representational arts, such as vase-paintings and votive gifts.
Pygmalion et Galatée. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
Mythe[modifier | modifier le code] Ayant nié la divinité d'Aphrodite, les Propétides sont punies par la déesse qui allume dans leur cœur le feu de l'impudicité. Ayant fini par perdre toute honte, elles sont insensiblement changées en ivoire. Les noms de Πυγμαλίων καὶ Γαλατεία Pugmalíôn kaì Galateía évoquent respectivement le poing/coude/bras Πύγμα du sculpteur travaillant au maillet et ciseau, et le lait Γάλα, couleur de la statue mais aussi des Propétides transformées en ivoire. Origines et interprétations[modifier | modifier le code] Gods and Godesses of Duat. Khepri. Khepri (also spelled Khepera, Kheper, Khepra, Chepri) is a god in ancient Egyptian religion.
Osiris. Osiris (/oʊˈsaɪərɨs/; also Usiris), is an Egyptian god, usually identified as the god of the afterlife, the underworld and the dead.
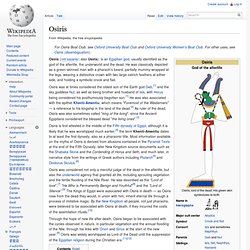
He was classically depicted as a green-skinned man with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive crown with two large ostrich feathers at either side, and holding a symbolic crook and flail. Osiris is first attested in the middle of the Fifth dynasty of Egypt, although it is likely that he was worshipped much earlier;[4] the term Khenti-Amentiu dates to at least the first dynasty, also as a pharaonic title. Horus. Horus is one of the oldest and most significant deities in ancient Egyptian religion, who was worshipped from at least the late Predynastic period through to Greco-Roman times.
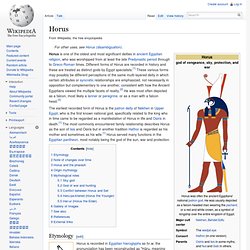
Different forms of Horus are recorded in history and these are treated as distinct gods by Egypt specialists.[1] These various forms may possibly be different perceptions of the same multi-layered deity in which certain attributes or syncretic relationships are emphasized, not necessarily in opposition but complementary to one another, consistent with how the Ancient Egyptians viewed the multiple facets of reality.[2] He was most often depicted as a falcon, most likely a lanner or peregrine, or as a man with a falcon head.[3] Etymology[edit] Horus was also known as Nekheny, meaning "falcon".
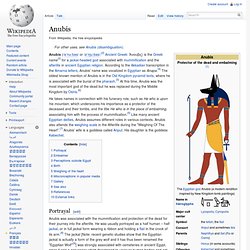
Some have proposed that Nekheny may have been another falcon-god, worshipped at Nekhen (city of the hawk), with which Horus was identified from early on. Anubis. Anubis (/əˈnuːbəs/ or /əˈnjuːbəs/;[2] Ancient Greek: Ἄνουβις) is the Greek name[3] for a jackal-headed god associated with mummification and the afterlife in ancient Egyptian religion.
Hathor. Hathor (/ˈhæθɔr/ or /ˈhæθər/;[2] Egyptian: ḥwt-ḥr and from Greek: Άθωρ, "mansion of Horus")[1] is an Ancient Egyptian goddess who personified the principles of joy, feminine love, and motherhood.[3] She was one of the most important and popular deities throughout the history of Ancient Egypt.
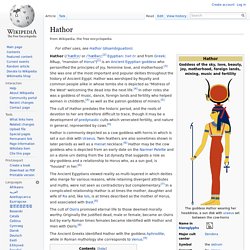
Hathor was worshiped by Royalty and common people alike in whose tombs she is depicted as "Mistress of the West" welcoming the dead into the next life.[4] In other roles she was a goddess of music, dance, foreign lands and fertility who helped women in childbirth,[4] as well as the patron goddess of miners.[5] The cult of Hathor predates the historic period, and the roots of devotion to her are therefore difficult to trace, though it may be a development of predynastic cults which venerated fertility, and nature in general, represented by cows.[6] Hathor is commonly depicted as a cow goddess with horns in which is set a sun disk with Uraeus.
Maat. The earliest surviving records indicating Maat is the norm for nature and society, in this world and the next, were recorded during the Old Kingdom, the earliest substantial surviving examples being found in the Pyramid Texts of Unas (ca. 2375 BCE and 2345 BCE).[2] Later, as a goddess in other traditions of the Egyptian pantheon, where most goddesses were paired with a male aspect, her masculine counterpart was Thoth and their attributes are the same.
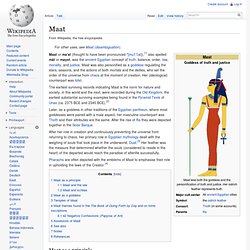
After the rise of Ra they were depicted together in the Solar Barque. Atum. Atum (/ɑ-tum/), sometimes rendered as Atem or Tem, is an important deity in Egyptian mythology.
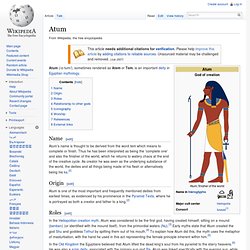
Name[edit] Atum's name is thought to be derived from the word tem which means to complete or finish. Thoth. Thoth played many vital and prominent roles in Egyptian mythology, such as maintaining the universe, and being one of the two deities (the other being Ma'at) who stood on either side of Ra's boat.[5] In the later history of ancient Egypt, Thoth became heavily associated with the arbitration of godly disputes,[6] the arts of magic, the system of writing, the development of science,[7] and the judgment of the dead.[8] Name[edit] Etymology[edit] The Egyptian pronunciation of ḏḥwty is not fully known, but may be reconstructed as *ḏiḥautī, based on the Ancient Greek borrowing Θώθ [tʰɔːtʰ] Thōth or Theut and the fact that it evolved into Sahidic Coptic variously as Thoout, Thōth, Thoot, Thaut as well as Bohairic Coptic Thōout.
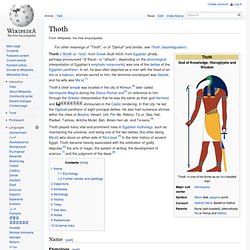
According to Theodor Hopfner,[12] Thoth's Egyptian name written as ḏḥwty originated from ḏḥw, claimed to be the oldest known name for the Ibis although normally written as hbj. Hathor.