

All about Crop Rotation for Vegetable Gardens – Hyperion Store. For centuries, wise gardeners have known that crop rotation is one of the best organic ways to have healthy vegetable gardens.
If you’re growing food at home, here’s what you need to know about rotating your crops. Crop Rotation - A Vital Component of Organic Farming. Long before we had synthetic fertilisers to maintain the land’s nutrients, and chemical pesticides and herbicides to keeps pests and weeds under control, we had crop rotation.
Crop rotation is a system of designing how to cycle a parcel of land through various crops, reducing the reliance on chemical fertilisers, pesticides and herbicides. It is how successful farmers nurtured their land over generations, and remains vitally important for farmers today wanting to nourish their local environment whilst growing good, healthy food. Crop Rotation - A Vital Component of Organic Farming. Crop Rotation Tips for Vegetable Gardens. For centuries, wise gardeners have known that crop rotation is one of the best organic ways to have healthy vegetable gardens.
If you’re growing food at home, here’s what you need to know about rotating your crops. Vegetable garden photo via Keith Lyons/Flickr Creative Commons. Companion Planting Chart & Crop Rotation Plan. Divide the vegetable plot into equal sections of four or more.
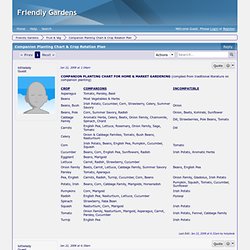
Decide which crops to grow. Then group them, firstly following plant family (linked to pests and diseases), then soil requirements and soil benefits. To rotate the beds as described below move each bed back one space so that legumes moves into the brassica bay and brassica moves to umbellifers for example: Year one: as belowYear two: legumes, onions, potato family, umbellifers, brassicasYear three: onions, potato family, umbellifers, brassicas, legumesYear four: potato family, umbellifers, brassicas, legumes, onionsYear five: umbellifers, brassicas, legumes, onions, potato family The following are family examples, soil requirements and soil benefits. Crop Rotation. The Importance of Crop Rotation Division into Beds Does the theory work?

Do you want equal amounts of each family type? Basic Principles What needs manure? Chart which shows the plant types. Rotation, rotation, rotationThe rules and breaking them. If there is one golden rule to organic vegetable gardening then it must be: "Rotate your vegetables so that they do not occupy the same ground until at least 3-4 years latter in order to prevent the buildup of diseases and depletion of certain nutrients as well as to break the pest cycle.
" Okay, you might be thinking that I am forgetting the other golden rule: "Take care of the soil and the plant will take care of itself" But I'm going to call that the cardinal rule so let's get back to: Rotation - the basics Rotation is considered one of the organic gardener's biggest allies in keeping healthy plants healthy but it can make planning the urban veggie patch a little bit trickier. What are the main rotation groups? This question is not as easy to answer as you imagine. 1. I could go on (these people do) but you may have already realized that the 'typical' rotation plan for an urban garden has 4 beds so that some families will be planted together. 1.
Feeders1. Crop Rotation - a gardening fact sheet by the Green Life Soil Co. Crop rotation is a simple procedure that involves not planting the same crop in the same soil for a period of years.

Depending on space available, the minimum recommended time is two years, while some gardeners prefer a rotation of up to six years. The purpose is to prevent a build up of pathogens in the soil which can infect and re-infect particular families of plants. Another purpose is that plants absorb different quantities of soil nutrients, and repeated plantings will quickly deplete the soil. Vegetable Crop Rotation Plans - Sow Seeds.
Crop rotation is the process of growing vegetables in their respective families and moving the families around a plot in a specific sequence so they are not grown on the same piece of land for at least 3 years.
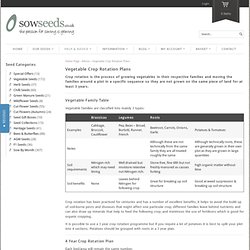
Vegetable Family Table Vegetable families are classified into mainly 3 types: Crop rotation has been practiced for centuries and has a number of excellent benefits, it helps to avoid the build up of soil-borne pests and diseases that might affect one particular crop; different families leave behind nutrients and can also draw up minerals that help to feed the following crop; and minimises the use of fertilisers which is good for organic cropping.
Crop Rotation. Crop rotation is a tactic that has been used for thousands of years to reduce the impact of pest and diseases on crops and to make better use of nutrients in the soil.
By planting crops in a tactical cycle you can avoid a build up of pathogen numbers or insect pests and their larvae in the soil reducing the stress placed on the plant in its effort to fighting off an overwhelming attack. This cyclical planting also allows nutrients to be used in a successional pattern and for nutrients to be added at critical times in the cycle. More on these concepts will be explained later. Crop rotation does not have to be complicated but it does require a little bit of organisation and planning. Kings Plant Barn - Vegetable Crop Rotation. Veggie Crop Rotation Improve your soil structure and nutrients, and reduce pest and disease risk by simple crop rotation.

With food prices on the increase now is the time to plant your own veggies. Big Garden? Small Garden? Vegetable garden crop rotation. Organic vegetable gardening is about maximizing the soil quality while minimizing pests and other problems, all without using chemical additives. Communitygarden.org.au/wp-content/uploads/2009/08/crop_rotation.pdf. Urbanext.illinois.edu/gardenerscorner/issue_04/winter_05_04.cfm. In order to avoid soil fertility, pest, and disease problems, home gardeners need to practice crop rotation. “Most homeowners tend to grow the types of vegetables they like year after year,” said Maurice Ogutu, U of I Extension horticulturist. “Tomatoes and peppers are some of the vegetables commonly grown by many home gardeners. Due to the limited space in backyards, the ground cannot go fallow, leading to the growing of vegetables in the same area or spot year after year. For a sustainable & ethical future - Crop rotation.
Written by Gavin Hair-tearing fun – make it as simple or as complex as you wish; but do rotate your crops. Whether you use a spreadsheet, or paper and pencil, work out a workable plan for your plot. Why? Unlike most gardens, an allotment usually has relatively large "blocks" of crops – which can cause two problems. Growing the same vegetable in the same place, year after year, creates an ideal environment in which. Vegetable Garden: Crop Rotation Made Easy. Divide your garden into sections to make crop rotation easier. You don’t have to be a farmer to use the age-old practice of rotating crop families – in fact, for the home gardener, the process is vitally important to the health and productivity of your garden.
From disease prevention to nutrient balancing, the benefits of crop rotation make it worth the extra planning required to put the system in place. Here’s an easy way to plan a four-step crop rotation in a home garden regardless of the size. Reasons to Rotate Crops Disease Prevention: The main reason to rotate crops is to prevent the spread of plant disease. Garden Design: Crop Rotation. When you design crop rotation in your organic garden you should keep in mind one thing: different plants have different appetites. Like folks, plants fall into three categories: big eaters, lighter eaters, and caterers. This last batch of plants returns nutrients to the soil. Cover crops are often soil-building crops. In other words, they are crops that are grown specifically to be worked back in to the soil at the end of the season. Your Vegetable Garden: Crop Rotation. Quick guide to vegetable families for crop rotation.
Yes, You Can Practice Crop Rotation. July 31st, 2008 Email 7 users recommend If you rotate crops according to their nutritional requirements, then you can add soil amendments in rotation, too. Photo: Pat Schories by Cynthia HizerDecember 1996from issue #6 Where did I put the arugula two years ago? If you’re not keeping track of these details, you may not be getting the most out of your garden, or giving your vegetables all they need.
Rotating Vegetable Crops for Garden Success. This vegetable garden includes onions, tomatoes, and peppers in the foreground, squash toward the back, and beans along the edge. Next year, these crops will be rotated so that plants of the same family aren’t grown in the same spot two years in a row. To keep the vegetable garden healthy, avoid repeating the same planting plan in the same spot. This practice, called crop rotation, can feel a bit like juggling, but it’s important to prevent crop-specific pests and diseases from building up and carrying over from one season to the next in the soil. Crop rotation. Gardening Australia - Vegie Guide. Crop rotation is a practice designed to minimise pests and diseases, reduce chemical use, aid in building and maintaining healthy soil, and manage nutrient requirements - all which will maximise yield.
Crop Rotation for Growing Vegetables.