

Mangrove conservation in singapore: international coastal cleanup. Mangroves. Mangroves live life on the edge.
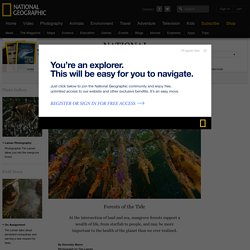
With one foot on land and one in the sea, these botanical amphibians occupy a zone of desiccating heat, choking mud, and salt levels that would kill an ordinary plant within hours. Yet the forests mangroves form are among the most productive and biologically complex ecosystems on Earth. Birds roost in the canopy, shellfish attach themselves to the roots, and snakes and crocodiles come to hunt. Mangroves provide nursery grounds for fish; a food source for monkeys, deer, tree-climbing crabs, even kangaroos; and a nectar source for bats and honeybees. As a group, mangroves can’t be defined too closely. These plants are also landbuilders par excellence.
Despite their strategic importance, mangroves are under threat worldwide. Mangrove. A mangrove forest in Palawan, Philippines.
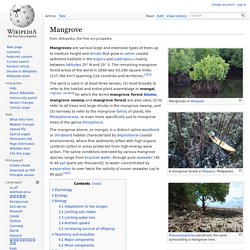
Mangroves are various large and extensive types of trees up to medium height and shrubs that grow in saline coastal sediment habitats in the tropics and subtropics—mainly between latitudes 25° N and 25° S. The remaining mangrove forest areas of the world in 2000 was 53,190 square miles (137,760 km²) spanning 118 countries and territories.[1][2] The mangrove biome, or mangal, is a distinct saline woodland or shrubland habitat characterized by depositional coastal environments, where fine sediments (often with high organic content) collect in areas protected from high-energy wave action. Rainforests Facts.
Facts about Rainforests Do you know how many tropical rainforest plants have been identified as having anti-cancer properties?

Or how many continents around the world contain rainforests? How can we save rainforests? Zoom Rainforest. Advertisement.

EnchantedLearning.com is a user-supported site. As a bonus, site members have access to a banner-ad-free version of the site, with print-friendly pages.Click here to learn more. Saving the Rainforest. What is a Rainforest and why are they Important? - Conserve Energy Future. Rainforests Facts. Rainforests for kids. Where are the Rainforests? Rainforests: facts, figures, news, and pictures. Rainforests for kids. Amazing Facts About Tropical Rainforests - Ella H. The tropical rain forest is a forest of tall trees in a region of year-round warmth.

An average of 50 to 260 inches (125 to 660 cm.) of rain falls yearly. Rain forests belong to the tropical wet climate group. The temperature in a rain forest rarely gets higher than 93 °F (34 °C) or drops below 68 °F (20 °C); average humidity is between 77 and 88%; rainfall is often more than 100 inches a year. Why Save the Rain Forest? Imagine what it is like to walk through a rain forest.

You pass hundreds of trees, many more than 125 feet high. You see orchids, ferns, and other exotic plants growing on tree trunks. Above, sunlight filters through the canopy of leaves, but you are walking in deep shade. Preserve The Rainforest. By saving the plants and trees of the rainforest you are contributing twofold – first by eliminating the continuing release of these greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and the subsequent destruction brought about by burning our most precious storage containers – the trees – and second by reversing the existing carbon dioxide emissions through the absorption of carbon by the plants and trees.
Trees in the rainforest work like the lungs of the earth in reverse fashion from our own breathing. Trees absorb carbon dioxide emissions in the atmosphere and release clean oxygen. Tropical rainforest. A tropical rainforest is an ecosystem type that occurs roughly within the latitudes 28 degrees north or south of the equator (in the equatorial zone between the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn).
This ecosystem experiences high average temperatures and a significant amount of rainfall. Rainforests can be found in Asia, Australia, Africa, South America, Central America, Mexico and on many of the Pacific, Caribbean, and Indian Ocean islands. National Geographic. In Brazil, which houses 30 percent of the remaining tropical rain forest on Earth, more than 50,000 square miles of rain forest were lost to deforestation between 2000 and 2005.
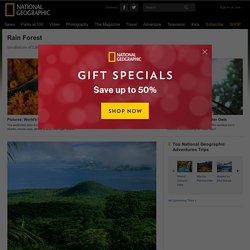
Biologists worry about the long-term consequences. Drought may be one. Some rain forests, including the Amazon, began experiencing drought in the 1990s, possibly due to deforestation and global warming. Efforts to discourage deforestation, mainly through sustainable-logging initiatives, are underway on a very limited basis but have had a negligible impact so far. Where are Rainforests Located? Facts on the Rainforest Sydney. Tropical rainforest. A tropical rainforest is an ecosystem type that occurs roughly within the latitudes 28 degrees north or south of the equator (in the equatorial zone between the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn).
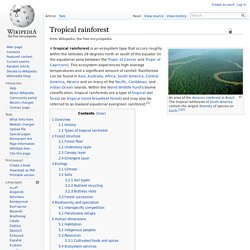
This ecosystem experiences high average temperatures and a significant amount of rainfall. Rainforests can be found in Asia, Australia, Africa, South America, Central America, Mexico and on many of the Pacific, Caribbean, and Indian Ocean islands. Within the World Wildlife Fund's biome classification, tropical rainforests are a type of tropical wet forest (or tropical moist broadleaf forest) and may also be referred to as lowland equatorial evergreen rainforest.[3] Overview. Tropical rainforest climate. Worldwide zones of Tropical rainforest climate (Af). A tropical rainforest climate, also known as an equatorial climate, is a tropical climate usually (but not always) found along the equator. What Are the Pollution Issues in the Amazon Rainforest?
What is a Rainforest? What is a Rainforest? What is a Rainforest? Rainforest Information for Kids Sydney. Why Save the Rain Forest? How do Animals Change to Adapt to the Temperate Rain Forest Enviornments. Written by: Megan Coogle•edited by: Donna Cosmato•updated: 9/1/2010 Animals adapt naturally to their environment. This is evident in places like the temperate rain forests where animals are adapting every day to change with the climate. Let's discover the answer to the question "how do animals change to adapt to the temperate rain forest?
" Asking "how do animals change to adapt to the temperate rain forest environments" is a question that can lead to a better understanding of the environment. It is possible to find large numbers of species of insects, mammals, reptiles and birds living in rain forests. What is a Rainforest? 50 Unusual Facts About Tigers - Listverse. Animals Animal Planet recently voted the impressively powerful tiger to be the world’s favorite animal. Yet a great deal of what we know about tigers is colored by common misconceptions or confusion with other large cats. Tigers are the most varied cat on earth, and have many unique features and interesting compulsions.
They are a magnificent creature which is sadly endangered due to human carelessness, but hopefully, if we learn a little about them, we can become more aware of this admirable animal, and help them grow in numbers once again. Rainforest. Tropical Rainforest. Rainforest Biomes. What is a Rainforest? Tropical rainforest. 10 species that may have just escaped extinction. Letters_from_birmingham.doc. What is a Rainforest? <html xmlns:v="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:vml" xmlns:o="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:office" xmlns=" <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=windows-1252"> <title>Endangered Rain Forest Animal.
Protect Endangered Rainforest Animals. Home to around two-thirds of all plant and animal species found on land — in addition to the millions of people who depend on them for survival — our remaining ancient forests are some of our most diverse ecosystems. They are also vitally important to the health of our planet, especially when it comes to regulating the climate. With so many of the world's forests already destroyed, we urgently need to protect what is left. Yet industry is still relentlessly converting forests into disposable products that end up in our shopping baskets - while pushing species to the brink of extinction, destroying the lives and livelihoods of forest communities and exacerbating global climate change.
We need your help to protect what forests remain. Our Motivation Around the world, forests are being logged for timber and paper pulp and cleared to grow mono-crops like soy and palm oil while also deteriorating from impacts of global warming. Learn more about our motivation. Our vision Our impact. Tigers endangered. The largest of all the Asian big cats, tigers rely primarily on sight and sound rather than smell. Protecting Biodiversity. Rainforest Animals. Rainforest Reptiles & Amphibians. Unfortunately, many herps are threatened by habitat loss, the pet trade, and environmental change. Time for action - Seed of Life. In less than two centuries of industrial revolution, the man has managed to deteriorate his habitat, the Earth, beautiful and fragile result of millions of years or evolution. We are totally convinced that time has come to act, to repair what can be repaired to prepare the future, so that humanity will have further progressed in its evolution in a more conscious and fair world, the Earth will still be capable of providing a shelter for its inhabitants.
Today, our planet is running out of steam because it doesn't have any longer its own natural means to compensate men's ecological print. 10 Easy Things You Can Do to Save Endangered Species. 1. Learn about endangered species in your area. Teach your friends and family about the wonderful wildlife, birds, fish and plants that live near you. Saving species from extinction. Important for survival. Threats to the Rainforests. Tigers. The tiger (Panthera tigris) is the largest cat species, reaching a total body length of up to 3.38 m (11.1 ft) over curves and weighing up to 388.7 kg (857 lb) in the wild.