
Tuberculosis. Tuberculosis. The classic symptoms of active TB infection are a chronic cough with blood-tinged sputum, fever, night sweats, and weight loss (the latter giving rise to the formerly common term for the disease, "consumption").
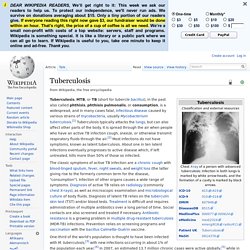
Infection of other organs causes a wide range of symptoms. Diagnosis of active TB relies on radiology (commonly chest X-rays), as well as microscopic examination and microbiological culture of body fluids. Diagnosis of latent TB relies on the tuberculin skin test (TST) and/or blood tests. Treatment is difficult and requires administration of multiple antibiotics over a long period of time. Social contacts are also screened and treated if necessary. Signs and symptoms The main symptoms of variants and stages of tuberculosis are given,[9] with many symptoms overlapping with other variants, while others are more (but not entirely) specific for certain variants. Pulmonary Extrapulmonary Causes Mycobacteria Risk factors A number of factors make people more susceptible to TB infections.
Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection: A Network Meta-analysisTreatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection: A Network Meta-analysis. From University College London, Public Health England, and Royal Free London National Health Service Foundation Trust, London, United Kingdom, and Bellvitge University Hospital-IDIBELL, Barcelona, Spain.
Financial Support: From the United Kingdom National Institute for Health Research (Drs. Abubakar, Stagg, and Lipman). Disclosures: Dr. Stagg reports other financial support from the World Health Organization and grants from the United Kingdom National Institute for Health Research (Department of Health) during the conduct of the study and personal fees and other financial support from Otsuka Pharmaceutical's public health group and nonfinancial support from Sanofi outside the submitted work. Dr. Requests for Single Reprints: Helen R.
Current Author Addresses: Drs. Dr. Mr. Natural ventilation reduces high TB transmission risk in traditional homes in rural KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. CROI 2013: Researchers Discuss Advances in Tuberculosis Treatment. Details Category: Tuberculosis (TB) Published on Monday, 11 March 2013 00:00 Written by Keith Alcorn RIFAQUIN study design (Jindani et al. CROI 2013. A new two-drug combination of rifapentine and moxifloxacin can allow tuberculosis (TB) treatment to be taken just once-weekly during the 4-month continuation phase, according to a presentation at the 20th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI 2013) last week in Atlanta. . [ Produced in collaboration with Aidsmap.com ] Background Shortening the duration of TB treatment from 6 months and reducing the number of doses of medication that need to be taken during the course of treatment could have a substantial impact on the number of people who complete treatment and are cured of TB.
A number of studies seeking to determine whether the standard TB treatment regimen can be shortened are underway. Rifapentine and Moxifloxacin The RIFAQUIN Study Results The study recruited 730 people with newly diagnosed smear-positive TB. References. Modeling the Role of Public Transportation in Sustaining Tuberculosis Transmission in South Africa. ↵*Correspondence to Dr.

Jason R. Andrews, Division of Infectious Diseases, Massachusetts General Hospital, 50 Staniford Street, 9th Floor, Boston, MA 02114 (e-mail: Jandrews6@partners.org). Abbreviation: HIV, human immunodeficiency virus. Received February 7, 2012. Accepted July 23, 2012. Current tuberculosis notification rates in South Africa are among the highest ever recorded. . © The Author 2013. TB guideline. Recommendations for Use of an Isoniazid-Rifapentine Regimen with Direct Observation to Treat Latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection. Totally Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in India. + Author Affiliations Correspondence: Zarir F.

Udwadia, MD, FRCP, P. D. Hinduja National Hospital and Medical Research Centre, Veer Savarkar Marg, Mahim, Mumbai 400 016, India (zarirfudwadia@gmail.com). Alarming levels of drug-resistant TB found worldwide. TB cases increasingly resistant to all drugs, study warns. A nurse administers a shot to a tuberculosis patient in India.
Photograph: Anupam Nath/AP Cases of tuberculosis that are resistant to virtually all drugs currently available to treat the disease are increasing at an alarming rate around the world, according to a study. The researchers also found a worrying increase in cases that were resistant to the entire class of oral second-line antibiotics known as fluoroquinolones, as well as one of the injectables – which is the criteria for being categorised as extensively drug-resistant (XDR TB).
Overall, they found that 6.7% of patients with drug-resistant strains had XDR TB, which is very hard and expensive to treat and takes years rather than months in affluent nations. In poorer countries, the necessary treatment is not available. The survey, by the US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention, found that XDR TB was most likely to develop when treatment for MDR TB had not been properly completed.
Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Strains Show Growth Worldwide. A Woman's 'Untreatable' TB Echoes Around the World. Database study of antibiotic resistant tuberculosis in the United Kingdom, 1994-6. The global increase in tuberculosis which has occurred in the 1980s and 1990s, and the associated re-emergence of resistance to antituberculous drugs, has focused attention on recent trends in resistance in Europe and the United States.1–3 In the United Kingdom overall drug resistance levels have been low.4 A surveillance system, the UK Mycobacterial Resistance Network (MYCOBNET), was established in 1994 by the Public Health Laboratory Service to record drug resistance in laboratory isolates of tuberculosis.
We used data from this network to examine resistance among people with newly diagnosed tuberculosis. Subjects, methods, and results We analysed the data on initial isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex referred to United Kingdom reference laboratories5 during 1994 to 1996. Initial isolates were defined as the first positive culture from a person from whom no positive culture had been recorded during the past 12 months. Comment Acknowledgments. The Competitive Cost of Antibiotic Resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.