

Square Kilometre Array. The Square Kilometre Array (SKA) is a radio telescope in development in Australia and South Africa which will have a total collecting area of approximately one square kilometre.[1] It will operate over a wide range of frequencies and its size will make it 50 times more sensitive than any other radio instrument.
It will require very high performance central computing engines and long-haul links with a capacity greater than the current global Internet traffic.[2] It will be able to survey the sky more than ten thousand times faster than ever before. Upsilon Andromedae d. TheoryvsHypothesis.jpg (JPEG Image, 960×742 pixels) Scientists build graphene from scratch, heralds new age of designer materials. You’ve heard of “designer babies,” the idea that you can customize a baby by altering its DNA, but now a team of researchers from Stanford University and the Department of Energy have meddled around with the very fabric of reality and created the very first “designer electrons.”
As you probably know, the bulk of the universe is made up from just a few dozen elements, and each of these elements is made up of just a few subatomic particles: electrons, protons, neutrons, quarks, and so on. For the most part, the properties of every material — its flexibility, strength, conductivity — is governed by the bonds between its constituent atoms, which in turn dictate a molecule’s arrangement of electrons. This is most obvious in elements like carbon, where a single element can form materials as different as charcoal, graphene, and diamond, all by virtue of different electron arrangements.
The Lily Garden. Sheila Nix: The Beginning of the End of AIDS. Everyone loves a good "they said it couldn't be done" story.
From a man on the moon to a personal computer in every home, the nostalgic in each of us loves to reflect about how, throughout history, individuals have run up against the status quo, defied the odds, and achieved something inspirational for society at-large. Those of us in the AIDS advocacy community have experienced our fair share of doubters telling us "it can't be done. " 30 years ago when HIV/AIDS cases were first documented, it was a mysterious infection that couldn't be treated.
Positive diagnosis was a death sentence. With no treatment, stigma and fear grew, representing what Dr. In the early 2000s, as President Bush and bipartisan Congressional leaders were launching a program called PEPFAR and as the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria was just getting started, the doubters loomed large. Not a GIF. 5G. 5G (5th generation mobile networks or 5th generation wireless systems) also known as Tactile Internet[1] denotes the next major phase of mobile telecommunications standards beyond the current 4G/IMT-Advanced standards. 5G does not describe any particular specification in any official document published by any telecommunication standardization body.
Although updated standards that define capabilities beyond those defined in the current 4G standards are under consideration, those new capabilities are still being grouped under the current ITU-T 4G standards. Background of 5G[edit] Mobile generations typically refer to non–backwards-compatible cellular standards following requirements stated by ITU-R, such as IMT-2000 for 3G and IMT-Advanced for 4G. Konstantin Tsiolkovsky. Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky (Russian: Константи́н Эдуа́рдович Циолко́вский, IPA: [kɐnstɐnˈtʲin ɪdʊˈardəvʲɪt͡ɕ t͡sɨɐlˈkofskʲɪj] ( ); Polish: Konstanty Ciołkowski; 17 September [O.S. 5 September] 1857 – 19 September 1935) was a Russian and Soviet rocket scientist and pioneer of the astronautic theory.
Along with his followers, the German Hermann Oberth and the American Robert H. Visible spectrum. Solar spectrum.
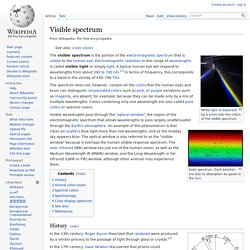
Dark patches are due to absorption by gases in the Sun. Grow light. Dual spectrum compact fluorescent grow light.
Actual length is about 40 cm (16 in) A grow light or plant light is an artificial light source, generally an electric light, designed to stimulate plant growth by emitting an electromagnetic spectrum appropriate for photosynthesis. Grow lights are used in applications where there is either no naturally occurring light, or where supplemental light is required. Sodium-vapor lamp. A sodium vapor lamp A sodium-vapor lamp is a gas-discharge lamp that uses sodium in an excited state to produce light.
There are two varieties of such lamps: low pressure and high pressure. Low-pressure sodium lamps are highly efficient electrical light sources, but their yellow light restricts applications to outdoor lighting such as street lamps.[1] High-pressure sodium lamps have a broader spectrum of light than the low pressure, but still poorer color rendering than other types of lamps.[2] Low pressure sodium lamps only give monochromatic yellow light and so inhibit color vision at night. Because sodium-vapor lamps cause less light pollution than mercury-vapor lamps, many cities that have large astronomical observatories employ them.[3] Low-pressure sodium[edit] An unlit 35W LPS/SOX lamp A running 35W LPS/SOX lamp. Extreme points of Earth. This is a list of extreme points of Earth, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than, higher or lower in altitude than, or farthest inland or out to sea from, any other locations on the landmasses, continents or countries.
The world[edit] Latitude and longitude[edit] The northernmost point of Earth is the geographic North Pole, in the Arctic OceanThe northernmost point on land is Kaffeklubben Island, north of Greenland (83°40′N 29°50′W / 83.667°N 29.833°W / 83.667; -29.833 (northernmost point on land)), which lies slightly north of Cape Morris Jesup, Greenland (83°38′N 32°40′W / 83.633°N 32.667°W / 83.633; -32.667 (Cape Morris Jesup)). Kola Superdeep Borehole. Coordinates: Kola Superdeep Borehole, 2007 For two decades it was also the world's longest borehole, in terms of measured depth along the well bore, until surpassed in 2008 by the 12,289-metre-long (40,318 ft) Al Shaheen oil well in Qatar, and in 2011 by 12,345-metre-long (40,502 ft) Sakhalin-I Odoptu OP-11 Well (offshore the Russian island Sakhalin).[2] Drilling[edit]
Luminous efficacy. The luminous efficacy of a source is a measure of the efficiency with which the source provides visible light from electricity.[4] The luminous efficacy of radiation describes how well a given quantity of electromagnetic radiation from a source produces visible light: the ratio of luminous flux to radiant flux.[5] Not all wavelengths of light are equally visible, or equally effective at stimulating human vision, due to the spectral sensitivity of the human eye; radiation in the infrared and ultraviolet parts of the spectrum is useless for illumination.
The overall luminous efficacy of a source is the product of how well it converts energy to electromagnetic radiation, and how well the emitted radiation is detected by the human eye. Efficacy and efficiency[edit] Minority rules: Scientists discover tipping point for the spread of ideas. Scientists at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have found that when just 10 percent of the population holds an unshakable belief, their belief will always be adopted by the majority of the society.
The scientists, who are members of the Social Cognitive Networks Academic Research Center (SCNARC) at Rensselaer, used computational and analytical methods to discover the tipping point where a minority belief becomes the majority opinion. The finding has implications for the study and influence of societal interactions ranging from the spread of innovations to the movement of political ideals. Other moons of Earth. Artist's conception of Earth with two moons Claims have existed for many decades that Earth might possess other natural satellites besides the Moon. Several candidates have been proposed, but not proven, and the Moon remains Earth's only known natural satellite.[1] Several genuine scientific searches for more moons were undertaken in the 19th and 20th centuries, but the field has also been the subject of several non-scientific proposals and possible hoaxes. These possible hoaxes, which were about objects of specific size and orbits, were poorly founded and all have been disproven.[2]
Video. Kerbal Space Program. Hands-on: Kerbal Space Program. July 8, 2011. Space shuttle Atlantis departs from Florida to cap off the US space program. It was a glorious, if not bittersweet moment. It left us asking: where do I go now to see super awesome rockets shoot off into space? Ah, that's where Squad's Kerbal Space Program comes in. Kerbal Space Program. Alcubierre drive. Two-dimensional visualization of the Alcubierre drive, showing the opposing regions of expanding and contracting spacetime that displace the central region.
The Alcubierre drive or Alcubierre metric (referring to metric tensor) is a speculative idea based on a solution of Einstein's field equations in general relativity as proposed by theoretical physicist Miguel Alcubierre, by which a spacecraft could achieve faster-than-light travel if a configurable energy-density field lower than that of vacuum (i.e. negative mass) could be created. Rather than exceeding the speed of light within its local frame of reference, a spacecraft would traverse distances by contracting space in front of it and expanding space behind it, resulting in effective faster-than-light travel.
History[edit] Alcubierre metric[edit] Time. The flow of sand in an hourglass can be used to keep track of elapsed time. It also concretely represents the present as being between the past and the future. Time is a dimension in which events can be ordered from the past through the present into the future,[1][2][3][4][5][6] and also the measure of durations of events and the intervals between them.[3][7][8] Time has long been a major subject of study in religion, philosophy, and science, but defining it in a manner applicable to all fields without circularity has consistently eluded scholars.[3][7][8][9][10][11] Nevertheless, diverse fields such as business, industry, sports, the sciences, and the performing arts all incorporate some notion of time into their respective measuring systems.[12][13][14] Some simple, relatively uncontroversial definitions of time include "time is what clocks measure"[7][15] and "time is what keeps everything from happening at once".[16][17][18][19] Temporal measurement and history[edit] World time[edit]
Fraunhofer Society. Stephen Hawking. Iron star. In astronomy, an iron star is a hypothetical type of star that could occur in the universe in 101500 years. The premise behind iron stars states that cold fusion occurring via quantum tunnelling would cause the light nuclei in ordinary matter to fuse into iron-56 nuclei. James Webb Space Telescope. Ultimate fate of the universe. Gravitational lens. Fritz Zwicky. Scientists trying to clone, resurrect extinct mammoth.