

String theory. Mitchell Feigenbaum. Mitchell Jay Feigenbaum (born December 19, 1944) is a mathematical physicist whose pioneering studies in chaos theory led to the discovery of the Feigenbaum constants.
Biography[edit] Feigenbaum was born in New York City,[1] to Polish and Ukrainian Jewish immigrants. He attended Samuel J. Tilden High School, in Brooklyn, New York, and the City College of New York. In 1964 he began his graduate studies at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). After short positions at Cornell University and the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, he was offered a longer-term post at the Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico to study turbulence in fluids. Edward Norton Lorenz. Edward Norton Lorenz (May 23, 1917 – April 16, 2008)[1][2] was an American mathematician and meteorologist, and a pioneer of chaos theory.[3] He introduced the strange attractor notion and coined the term butterfly effect.
Biography[edit] Lorenz was born in West Hartford, Connecticut.[4] He studied mathematics at both Dartmouth College in New Hampshire and Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts. From 1942 until 1946, he served as a meteorologist for the United States Army Air Corps. After his return from World War II, he decided to study meteorology.[2] Lorenz earned two degrees in the area from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology where he later was a professor for many years. Edward Lorenz, father of chaos theory and butterfly effect, dies at 90. Edward Lorenz, an MIT meteorologist who tried to explain why it is so hard to make good weather forecasts and wound up unleashing a scientific revolution called chaos theory, died April 16 of cancer at his home in Cambridge.
He was 90. A professor at MIT, Lorenz was the first to recognize what is now called chaotic behavior in the mathematical modeling of weather systems. In the early 1960s, Lorenz realized that small differences in a dynamic system such as the atmosphere--or a model of the atmosphere--could trigger vast and often unsuspected results. Henri Poincaré.
French mathematician, physicist, engineer, and philosopher of science Jules Henri Poincaré (,[4] ;[5][6][7] French: [ɑ̃ʁi pwɛ̃kaʁe] ( listen);[8][9] 29 April 1854 – 17 July 1912) was a French mathematician, theoretical physicist, engineer, and philosopher of science.
He is often described as a polymath, and in mathematics as "The Last Universalist",[10] since he excelled in all fields of the discipline as it existed during his lifetime. As a mathematician and physicist, he made many original fundamental contributions to pure and applied mathematics, mathematical physics, and celestial mechanics.[11] In his research on the three-body problem, Poincaré became the first person to discover a chaotic deterministic system which laid the foundations of modern chaos theory.
He is also considered to be one of the founders of the field of topology. The Poincaré group used in physics and mathematics was named after him. Jurassic Park (2/10) Movie CLIP - Chaos Theory (1993) HD. Chaos Theory for Beginners; An Introduction. Life finds a way beauty of the unpredictable and display it in the most awesome patterns.

Nature, when looked upon with the right kind of eyes, presents herself as one of the most fabulous works of art ever wrought. Chaos Theory. What is chaos theory. Chaos theory is the study of nonlinear dynamics, in which seemingly random events are actually predictable from simple deterministic equations.
In a scientific context, the word chaos has a slightly different meaning than it does in its general usage as a state of confusion, lacking any order. Chaos, with reference to chaos theory, refers to an apparent lack of order in a system that nevertheless obeys particular laws or rules; this understanding of chaos is synonymous with dynamical instability, a condition discovered by the physicist Henri Poincare in the early 20th century that refers to an inherent lack of predictability in some physical systems. The two main components of chaos theory are the ideas that systems - no matter how complex they may be - rely upon an underlying order, and that very simple or small systems and events can cause very complex behaviors or events. Chaos theory.
A double rod pendulum animation showing chaotic behavior.
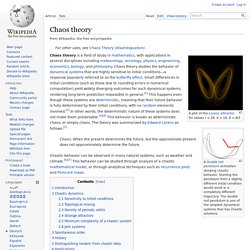
Starting the pendulum from a slightly different initial condition would result in a completely different trajectory. The double rod pendulum is one of the simplest dynamical systems that has chaotic solutions. Chaos: When the present determines the future, but the approximate present does not approximately determine the future. Chaotic behavior can be observed in many natural systems, such as weather and climate.[6][7] This behavior can be studied through analysis of a chaotic mathematical model, or through analytical techniques such as recurrence plots and Poincaré maps. Introduction[edit] Chaos theory concerns deterministic systems whose behavior can in principle be predicted. Chaotic dynamics[edit] The map defined by x → 4 x (1 – x) and y → x + y mod 1 displays sensitivity to initial conditions.
BBC Four - The Secret Life of Chaos, Butterfly Effect. BBC Four - The Secret Life of Chaos, Mandelbrot. BBC Four - The Secret Life of Chaos. The Secret Life of Chaos. Chaos theory has a bad name, conjuring up images of unpredictable weather, economic crashes and science gone wrong.
But there is a fascinating and hidden side to Chaos, one that scientists are only now beginning to understand. It turns out that chaos theory answers a question that mankind has asked for millennia - how did we get here? In this documentary, Professor Jim Al-Khalili sets out to uncover one of the great mysteries of science - how does a universe that starts off as dust end up with intelligent life? How does order emerge from disorder? It's a mind-bending, counterintuitive and for many people a deeply troubling idea. But Professor Al-Khalili reveals the science behind much of beauty and structure in the natural world and discovers that far from it being magic or an act of God, it is in fact an intrinsic part of the laws of physics. The natural world is full of awe-inspiring examples of the way nature transforms simplicity into complexity. The Secret Life Of Chaos - Vìdeo Dailymotion.