

Phil Gunning
Anything with regards to how fish digest the nutrients that they ingest.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) (Theory) : Molecular Biology Virtual Lab II : Biotechnology and Biomedical Engineering : Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual Lab. To amplify a given region of DNA(region of interest).

Polymerase chain reaction, better known as PCR, is one of the technologies that not only made a tremendous impact on the scientific community, but also affected many aspects of our everyday lives. More than 30 years ago, the introduction of recombinant DNA technology as a tool for the biological sciences revolutionized the study of life. CRISPR: Move beyond differences. Charis Thompson.

This autumn, researchers and other experts will come together to discuss the scientific, ethical and policy issues associated with gene-editing research in humans. Plans for the international meeting were announced by the US National Academy of Sciences and the National Academy of Medicine after a study was published in which researchers used a gene-editing tool known as CRISPR to modify the genomes of non-viable human embryos1. Whether this meeting and others like it, planned in the United States, can help to forge a path for gene editing that takes into account all the relevant needs and concerns will depend on what efforts are made to integrate the diverse perspectives of people with different expertise and values.
A first step to such integration is understanding how different perspectives arise. Caution urged over editing DNA in wildlife (intentionally or not) David Scharf/Corbis Malaria-carrying mosquitoes (Anopheles gambiae) are a prime target for gene-editing techniques.
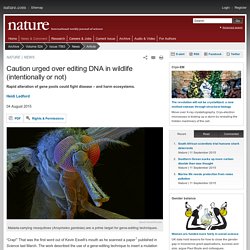
“Crap!” That was the first word out of Kevin Esvelt’s mouth as he scanned a paper1 published in Science last March. The work described the use of a gene-editing technique to insert a mutation into fruit flies that would be passed on to almost all of their offspring. Although intriguing, the report made Esvelt feel uneasy: if engineered flies escaped from a lab, the mutation could spread quickly through a wild population.
But that was exactly what exhilarated molecular biologist Anthony James at the University of California, Irvine. CRISPR, the disruptor. Illustration by Sébastien Thibault Three years ago, Bruce Conklin came across a method that made him change the course of his lab.
Conklin, a geneticist at the Gladstone Institutes in San Francisco, California, had been trying to work out how variations in DNA affect various human diseases, but his tools were cumbersome. When he worked with cells from patients, it was hard to know which sequences were important for disease and which were just background noise. CRISPR: Science can't solve it. Illustration by David Parkins This year, several leading researchers have sounded warnings about the risks of using the CRISPR gene-editing technique to modify human1 and other species' genomes in ways that could have “unpredictable effects on future generations”2 and “profound implications for our relationship to nature” (see go.nature.com/jq5sik).

Concerns are coming from the silicon sector as well. Last year, the physicist Stephen Hawking proclaimed that rapidly advancing artificial intelligence (AI) could destroy the human race. And in 2013, former Royal Society president Martin Rees co-founded the Centre for the Study of Existential Risk at the University of Cambridge, UK, in part to study threats from advanced AI. SAR-Free-to-Think. Louis Pasteur. French chemist and microbiologist Louis Pasteur (, French: [lwi pastœʁ]; December 27, 1822 – September 28, 1895) was a French biologist, microbiologist and chemist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, microbial fermentation and pasteurization.
He is remembered for his remarkable breakthroughs in the causes and prevention of diseases, and his discoveries have saved many lives ever since. He reduced mortality from puerperal fever, and created the first vaccines for rabies and anthrax. His medical discoveries provided direct support for the germ theory of disease and its application in clinical medicine. He is best known to the general public for his invention of the technique of treating milk and wine to stop bacterial contamination, a process now called pasteurization. Pasteur was responsible for disproving the doctrine of spontaneous generation. Ferdinand Cohn. Ferdinand Julius Cohn (24 January 1828 – 25 June 1898) was a German biologist.
Robert Koch. Robert Heinrich Herman Koch (/ˈkɔːx/;[3] German: [ˈkɔχ]; 11 December 1843 – 27 May 1910) was a celebrated German physician and pioneering microbiologist.
The founder of modern bacteriology, he is known for his role in identifying the specific causative agents of tuberculosis, cholera, and anthrax and for giving experimental support for the concept of infectious disease.[4] In addition to his trail-blazing studies on these diseases, Koch created and improved laboratory technologies and techniques in the field of microbiology, and made key discoveries in public health.[5] His research led to the creation of Koch’s postulates, a series of four generalized principles linking specific microorganisms to specific diseases that remain today the "gold standard" in medical microbiology.[5] As a result of his groundbreaking research on tuberculosis, Koch received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1905.[5] Personal life[edit] Research contributions[edit] Anthrax[edit] Cholera[edit]
Table of Contents. Table of Contents - Lectures presented at the FAO/UNDP Training Course in Fish Feed Technology, held at the College of Fisheries, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington, U.S.A., 9 October-15 December 1978 UNITED NATIONS DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMMEFOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONSRome, 1980.
Nutrition and Feeding for Sustainable Aquaculture Development in the Third Millennium. Habib, M.A.B., Hasan, M.R. and Akand, A.M. 1994.

Dietary carbohydrate utilisation of silver barb, Puntius gonionotus. In S.S. De Silva, ed. Hardy.pdf. Fish Matters Importance of aquatic foods in human nutrition and global food supply. Dietary supplementation of exogenous carbohydrase enzymes in fish nutrition. Understanding Fish Nutrition Feeds and Feeding. Fish Feed Management. Commercial fish feed. Manufactured feeds are an important part of modern commercial aquaculture, providing the balanced nutrition needed by farmed fish. The feeds, in the form of granules or pellets, provide the nutrition in a stable and concentrated form, enabling the fish to feed efficiently and grow to their full potential. Many of the fish farmed more intensively around the world today are carnivorous, for example Atlantic salmon, trout, sea bass, and turbot. In the development of modern aquaculture, starting in the 1970s, fishmeal and fish oil were key components of the feeds for these species.
They are combined with other ingredients such as vegetable proteins, cereal grains, vitamins and minerals and formed into feed pellets. Wheat, for example, is widely used as it helps to bind the ingredients in the pellets. Hatchery feeds[edit] High Impact Articles List. Impact Factor: 1.27* Index Copernicus Value: 5.2 * Aquaculture is the farming of aquatic organisms such as fish, prawns, molluscs, and aquatic plants related directly or indirectly to human consumption.
The journal provides an Open Access platform devoted to cultivate freshwater and saltwater populations under controlled conditions, and can be contrasted with commercial fishing. Nutrition and feeding of fish. Nutrition Feeding and Behavior of Fish. Feed nutrition feeding. Non starch polysaccharides and their role in fish nutrition. Trainee Environmental Scientist.
(Scottish Operations) South Shian, Nr Oban Educated to degree level in a scientific or environmental discipline, candidates are expected to have experience in at least some aspects of marine survey work and an interest in marine ecology. The role will assist with the organisation and execution of marine survey and monitoring work to meet the requirements of our various regulators. Familiarity with the regulatory regimes affecting Scottish aquaculture would be beneficial but not essential as training will be provided. The successful candidate will divide their time between working outdoors on Company sites and at the main production office at South Shian. The post will be based at South Shian, by Oban but will require short periods working at other company sites; a full driving licence is therefore essential. Interested applicants should send a copy of their CV and covering letter to tracy.bryant-shaw@scottishseafarms.com.
Universal Jobmatch jobs and skills search - Job details. Scottish Sea Farms Ltd Marine Husbandry Job description. News -First in Seafood News - Intrafish.com. Scotland's Aquaculture. The Aquaculturists. Expanding U.S. Aquaculture to the Open Ocean. FAO Fisheries & Aquaculture - Fishery and Aquaculture Country Profiles - The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. FAO Fisheries & Aquaculture - Cultured Aquatic Species Information Programme - Gadus morhua (Linnaeus, 1758)
Harnessing research that makes a difference. American Institute of Fishery Research Biologists. FAO GLOBEFISH - StatsDirect Medical Statistics Software. The Fish Health Regulations 1997. Biomin.net - AquaStar® - Probiotics for improving performance and efficiency in aquaculture. Fish Thrive in World’s First Open-Ocean Farm. This Research in Action article was provided to LiveScience in partnership with the National Science Foundation. Aquaculture, Fish Farming Information - Portal for aquaculture and fish farming - The Fish Site. American Institute of Fishery Research Biologists.
Nearly 40 year ago, a small volume (193 pp.) was published on ‘Fish Food Habits Studies.’ Integrated Taxonomic Information System. TED Studies: Marine Biology - The Deep Ocean. Module 3. Welcome to the Fascinating World of Fish. Fish Dissection - Gills exposed.