

Antibody enzyme conjugate. Antibody-enzyme fusion proteins possess greater tumor specificity and potency.

Compared with traditional cancer treatments, it could reduce patient side effects. As a well-recognized expert in antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), Creative Biolabs provides antibody-enzyme conjugate development services for your cancer therapy research via conjugating monoclonal antibodies with various enzymes. Introduction Enzymes can be powerful weapons in the activity of anticancer, particularly when they are endowed with cancer-selectivity by targeting to tumor cells using specific antibodies. Advances in biomolecular technology have allowed the antibody-enzyme conjugates to provide tumor specificity of enzyme delivery. Antibody-directed Enzyme Prodrug Therapy (ADEPT) Since first described in the late 1980s, ADEPT has been widely applied for tumor treatment as it could localize to the target tumor antigen in vivo.
Antibody conjugates. Creative Biolabs has over a decade of working experience in antibody design and modification to fit various bio-conjugation strategies, especially for the development of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs).

As one major component of an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), the antibody is the key for target specificity and serves as the cargo to deliver the cytotoxic drug (payload). A payload drug can be attached to different sites on an antibody using diverse conjugation chemistry. Multiple endogenous amino acids can serve as potential conjugation sites. Adc services. Monoclonal antibody-based immunotherapies against cancer and other infectious diseases are highly advantageous comparing to conventional therapeutic approaches due to their high specificity and affinity towards well-defined targets. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) inherit such superiorities and more remarkably, expand the therapeutic window of the conjugated drugs (payloads), which are usually highly toxic and diverse in their biochemical nature.
ADC mode of action. ADC molecules travel to the tumor site via systematic circulation, bind to tumor surface antigens, and enter the tumor cells via receptor mediated endocytosis (internalization). The payload is released in the cytosol or lysosome to eliminate the cancer cell by disrupting important cellular pathways (microtubule assembly, DNA transcription, mRNA processing…). Three major components define an ADC—the monoclonal antibody, a cytotoxic payload, and a molecular linker that covalently bridges the other two components. Case Study. Adc services. Creative Biolabs is a leader in providing services for antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) development and analysis.

With the comprehensive analytical platform and experienced lab personnel, Creative Biolabs offers global clients with an integrated package for ADC biochemical characterization services to meet your novel ADC development goals. This package includes a variety of different modules, including ADC structural analysis, ADC stability analysis, drug to antibody ratio (DAR) evaluation, drug load distribution assessment, as well as linker and conjugation sites analysis. Compared to traditional anti-tumor drugs, ADCs utilize the specific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to achieve targeted delivery of cytotoxic small molecule drugs. The exquisite designs of an ADC can maximize the delivery of antitumor agents to the targeted tissue while minimize its toxic side effects to normal tissues.
ADC Biochemical Analysis. ADC Affinity Measurement. Creative biolabs is a leader in antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) development and we have established a comprehensive analytical platform to ensure high-quality and high-accuracy biochemical and in vitro efficacy characterization of a customized ADC.

We offer a customarily tailored analysis package to evaluate the binding affinity of an ADC towards its designated target antigen and Fc receptors using various approaches including surface plasmon resonance (SPR), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) flow cytometry assay. The elegant design of an antibody-drug conjugate is designated to achieve targeted delivery of the conjugated cytotoxic agents to tumor cells and drug release upon antigen binding and internalization, thus maximizing the antitumor effects while minimizing cytotoxicity to normal tissues. Adc custom products. Adc characterization. As a leader in antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) development, specialized teams in Creative Biolabs are experienced in characterizing ADC pharmacokinetics and we provide high-quality services and various assay formats for different analytes of an ADC.

Pharmacokinetics (PK) studies provide critical information regarding the behavior of a drug in circulation and its ultimate form after extensive in vivo metabolism. Results from PK studies often serve as guidelines for clinical trials designs, especially in the development of an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC). Due to the heterogeneous nature of ADCs, multiple analytes have to be assessed to reveal the ADC PK characteristics, making these studies more complex. Adc assessment. Empowered by our advanced high-resolution analytical platforms and experienced technical personnel, the analytical division at Creative Biolabs is fully competent and dedicated to serve as your one-stop-shop for ADC in vitro analysis and characterizations.

The construction of an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) is the covalent coupling of a monoclonal antibody and a toxic payload drug via a linker molecule. The ultimate goal for an ADC development project is to deploy the resulted ADC into in vivo systems, both in model animals and eventually human patients, to cure cancer and other diseases utilizing its payload efficacy. However, prior to in vivo deployment, information regarding basic biochemical characteristics and in vitro efficacy must be acquired for a proper evaluation of the ADC to determine the proceedings and directions of the project.
We divide our ADC in vitro analysis services into: Acid labile Linker. As a well-recognized leader in antibody engineering and bio-conjugation, Creative Biolabs has established an advanced “DrugLnk” organic synthesis platform to promote the design and preparation of various drug-linker complexes containing pH-sensitivity linkers for antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) development.
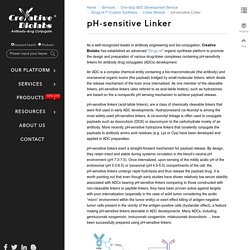
An ADC is a complex chemical entity containing a bio-macromolecule (the antibody) and one/several organic toxins (the payload) bridged by small molecular linkers, which dicate the release mechanism of the toxin once internalized. As one member of the cleavable linkers, pH-sensitive linkers (also refered to as acid-labile linekrs), such as hydrazones, are based on the a nonspecific pH sensing mechanism to achieve payload release. pH-sensitive linkers (acid-labile linkers), are a class of chemically cleavable linkers that were first used in early ADC developments.
Hydrazonesand cis-Aconityl is among the most widely used pH-sensitive linkers. Doxorubicins. With our advanced “DrugLnk” platform and extensive experience in synthetic chemistry and bio-conjugation, Creative Biolabs offers highly customized strategies for antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) production and targeted antibody therapy development using doxorubicin or doxorubicin derivatives as payloads.
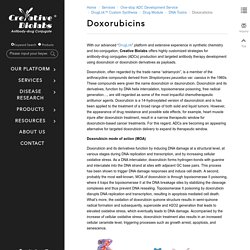
Doxorubicin, often regarded by the trade name “adriamycin”, is a member of the anthracycline compounds derived from Streptomyces peucetius var. caesius in the 1960s. These compounds were given the name doxorubicin or daunorubicin. Doxorubicin and its derivatives, function by DNA helix intercalation, topoisomerase poisoning, free radical generation…, are still regarded as some of the most impactful chemotherapeutic antitumor agents.
Adc linker. ADC design. ADC. Global Antibody-drug Conjugate (ADC) Clinical Trial Review. As innovative next-generation immunotherapeutic agents, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are being developed worldwide as a major strategy to combat cancer and other immunological disorders.

With the combination of a monoclonal antibody and extremely toxic chemical payloads, these bio-macromolecule “warheads” are by far one of the most powerful weapons in the immunotherapy arsenal, bearing the hope as “the beginning of the end” to the battle against cancer. An ADC is formulated by conjugating a toxic payload with a monoclonal antibody via a small chemical linker. The antibody portion of an ADC serves as a molecular guidance system that accurately delivers the toxic payload to the tumor site for target elimination with minimum collateral damage to the healthy tissues. The payloads used in ADCs interrupt crucial intracellular pathways (microtubule dynamics, DNA structure and integrity, as well as gene transcription and translation…) and often exert extreme toxicity. Duocarmycin. Creative Biolabs offers customarily prepared high quality antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) using duocarmycin and duocarmycin analogs as payloads for targeted anti-cancer therapies and a variety of other applications.
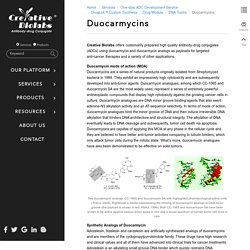
Duocarmycin mode of action (MOA) Duocarmycins are a series of natural products originally isolated from Streptomyces bacteria in 1988. They exhibit an impressively high cytotoxicity and are subsequently developed into anti-tumor agents. Duocarmycin analogues, among which CC-1065 and duocarmycin SA are the most widely used, represent a series of extremely powerful antineoplastic compounds that display high cytotoxicity against the growing cancer cells in culture. Disulfide Linker. Creative Biolabs has extensive professional expertise in providing customarily designed payload-linker complexes for antibody drug conjugate (ADC) development. With state-of-art equipment, advanced techniques, as well as the “DrugLnk” organic synthesis platform, scientists from Creative Biolabs are dedicated to design and synthesize payload-linker complexes containing disulfide linkers to fulfill clients’ requirements in a highly productive and cost-effective way. Disulfide linkers (sometimes refered to as glutathione-sensitive linkers) are a family of chemically cleavable linkers that non-selevtively release the payload drug upon the exposure to an altered chemical environment, which in this case, is the higher reducing potential within the tumor cells compared to that of the criculating plasma.
ADC Linkers. Auristatins. Creative Biolabs offers customized services for the design and production of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) using auristatin and auristatin derivatives as payloads. With years of experience in the ADC research, scientists at Creative Biolabs are confident to provide clients with high-quality auristatin ADCs with appropriate linkers to meet your demands. Auristatin Mode of Action (MOA) Auristatins are a family of complex analogues to the native antineoplastic product dolastatin 10. They are 100 to 1000 times more toxic than Doxorubicin, a conventional cancer chemotherapy medication. The potent agent, dolastatin 10 is a five-subunit penta-peptide discroverde by Pettit et al. from the sea hare Dolabella auricularia in 1987 and chemical modification to dolastatin 10 were applied to generate auristatins. Binding of MMAE, an Auristatin derivative, to the α and β tubulin subunits solved by co-crystallography. Modifications of Auristatins. What is an ADC. Monoclonal antibody-based immunotherapies against cancer and other infectious diseases are highly advantageous comparing to conventional therapeutic approaches due to their high specificity and affinity towards well-defined targets.
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) inherit such superiorities and more remarkably, expand the therapeutic window of the conjugated drugs (payloads), which are usually highly toxic and diverse in their biochemical nature. ADC mode of action. ADC molecules travel to the tumor site via systematic circulation, bind to tumor surface antigens, and enter the tumor cells via receptor mediated endocytosis (internalization). The payload is released in the cytosol or lysosome to eliminate the cancer cell by disrupting important cellular pathways (microtubule assembly, DNA transcription, mRNA processing…).
Three major components define an ADC—the monoclonal antibody, a cytotoxic payload, and a molecular linker that covalently bridges the other two components. Conjugation in chemistry. Antibody chemistry. Antibody conjugation service. ADC platform. The work here at Creative Biolabs to create antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are empowered by our advanced technical platforms that are dedicated to provide our clients with high quality products, customized services, and specialized consultation for ADC development projects. ADCs are next-generation precision medicines that target specific surface antigens and fight diseases by delivering cytotoxic payload drugs into the antigen-bearing cells.
ADCs are trending in immunotherapy and are believed to have high potential and wide applications in treating various types of cancer, fungal or bacterial infections, cardiovascular disorders, and immune diseases. Anti drug conjugate. ADCs. Peptide Linker. Antibody conjugates. Antibody design. Conjugate dar. Conjugate meaning. Conjugation of dar. Conjugation site. Dar conjugate. Adc antibody. Peptide Linker. Cleavable linker. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) combine the cytotoxic potency of a drug with the target specificity of an antibody. In the development of ADCs, the design of suitable linkers is crucial for the stable and efficient delivery of the cytotoxic drug to the target cells.
Thus, choosing the right antibody-drug linkage often plays a key role in optimizing the therapeutic efficacy and tolerability of ADCs. An ideal linker should possess exceeding stability in systemic circulation, and readily releases the cytotoxic payload in its active form upon reaching the target site. Linker design for ADCs is highly dependent on the biolology of the target cells, the characteristics of the antibody, and the structure of the drug molecule. Selection of the optimal linker is achieved through efficacy and toxicity assessments for each individual ADC construct. Ipatasertib mechanism of action.
Creative Biolabs is a leader in antibody engineering, modification, and production. Ipatasertib. Adc. Adc development. Linker peptide. Akt inhibitor. Cysteine Conjugation. ADC Linkers. Maleimide conjugation. The carbohydrate moiety on an antibody is located at the hinge region of the Fc domain, with a sufficient distant from the variable region that regulates antigen interaction. Auristatins. Antibody fluorophore. Fluorophores are a family of chemical compounds that can emit light upon the adsorption of energy from an excitation light source. For a certain fluorophore, there is a specific excitation and emission spectrum. Typically, the wavelengths of light that can cause the maximum excitation and be captured from the maximum emission (Excitation/Emission) are used to refer to a given fluorophore.
Most fluorophores are small organic compounds with 20–100 atoms, but there are also exceptions with larger sizes, e.g., natural fluorescent proteins. Fluorophores can be used either alone, together with other fluorescent agents, or as the fluorescent tags in a conjugate, e.g., a fluorophore-labeled antibody. Conjugate dar. ADC Manufacturing. Adcs. Antibody ADC. Adc chemistry. Her2 adc. Erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2(ERBB2), commonly referred to as HER2, is an epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor family tyrosine kinase. It is also referred to as ERBB2, NEU, NGL, TKR1, CD340, MLN 19, or HER-2/neu under different circumstances and it is a unique EGF receptor. There is no reported ligand that interacts with HER2. It is not susceptible to any epidermal growth factor binding. Adc custom products. Taxoids. Thailanstatin a. Adept antibody. Tubulin filaments. Conjugate meaning.