

Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domains. Note: This site is moving to KnowledgeJump.com.
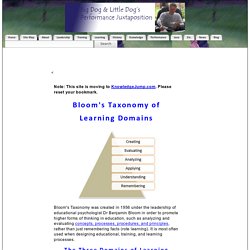
Please reset your bookmark. Bloom's Taxonomy was created in 1956 under the leadership of educational psychologist Dr Benjamin Bloom in order to promote higher forms of thinking in education, such as analyzing and evaluating concepts, processes, procedures, and principles, rather than just remembering facts (rote learning). It is most often used when designing educational, training, and learning processes. Bloom's 3 Learning Domains. Bloom_taxonomy. The Best Resources For Helping Teachers Use Bloom’s Taxonomy In The Classroom. Bloom’s & SOLO ‘are not Just Colorful Posters we Hang on the Wall’ is my two-part series at Education Week Teacher.

Bloom’s Taxonomy is talked about a lot in educational circles. However, if you believe a recent survey of visits to 23,000 U.S. classrooms, the higher-order thinking skills it’s ideally designed to promote doesn’t get much use. And I can understand why. About UDL. Instagrok.
Constructivism (learning theory) Jean Piaget: founder of Constructivism In past centuries, constructivist ideas were not widely valued due to the perception that children's play was seen as aimless and of little importance.
Jean Piaget did not agree with these traditional views, however. He saw play as an important and necessary part of the student's cognitive development and provided scientific evidence for his views. Today, constructivist theories are influential throughout much of the non-formal learning sector. One good example of constructivist learning in a non-formal setting is the Investigate Centre at The Natural History Museum, London.
For more detailed information on the philosophy of the construction of human knowledge, see constructivist epistemology. Formalization of the theory of constructivism is generally attributed to Jean Piaget, who articulated mechanisms by which knowledge is internalized by learners. It is important to note that constructivism is not a particular pedagogy. Leading Adult Learners: Preparing Future Leaders and Professional Development of Those They Lead. Learning Styles of Children. One size (style) does not fit all.
Effective teachers try to understand how individual children take in and process information. They realize that not all children learn the same way. Learning styles describe the ways in which individual children acquire information, evaluate it, and then examine their findings. Learning styles in general are applicable to all content areas and settings. Effective teachers try to present materials in ways that will interest children and help them to absorb the information. Learning types and learning styles. [Problemistics] [The problem of learning] Chapter 1 Learning types and learning styles Personality and learning Learning styles Learning types The school system The rationale against the school system The rationale for the school system The problem stated A possible solution A reformulation of the argument References Personality and learning (^) The study of personality as it emerges from the works of many psychologists (G.

Lindzey ed., 1970; B. Semenoff ed., 1970; L. J. Bischof, 1970) is primarily based on the highlighting of differences (e.g. types: Jung 1928, Spranger 1928; traits: Allport 1937, 1962; character structures: Horney 1937). Teaching And Learning In A Diverse World: Multicultural Education For Young ... - Patricia G. Ramsey. Multiple Intelligences: Gardner's Theory. This is a mirror of ERIC/AE Digest Series EDO-TM-96-01, September 1996 Amy C.

Brualdi ERIC/AE. Gardner's Multiple Intelligences. Howard Gardner of Harvard has identified seven distinct intelligences.

This theory has emerged from recent cognitive research and "documents the extent to which students possess different kinds of minds and therefore learn, remember, perform, and understand in different ways," according to Gardner (1991). According to this theory, "we are all able to know the world through language, logical-mathematical analysis, spatial representation, musical thinking, the use of the body to solve problems or to make things, an understanding of other individuals, and an understanding of ourselves. Three Different Learning Styles. Types of Learning Styles. Visual, Auditory, and Tactile Learning. Your learning style can be helpful in improving your grades.
Students learn in many ways, like seeing, hearing, and experiencing things first hand. But for most students, one of these methods stands out. Why is this important? Research has shown that students can perform better on tests if they change study habits to fit their own personal learning styles. For example, visual-learning students will sometimes struggle during essay exams, because they can't recall test material that was "heard" in a lecture.
However, if the visual learner uses a visual aid when studying, like a colorful outline of test materials, he or she may retain more information. A simple explanation of learning styles is this: some students remember best materials they've seen, some remember things they've heard, while others remember things they've experienced. How can you determine your learning style? You can also recognize your own style by looking over the characteristics. Visual Learner Characteristics. Types of Learning. Research Question What do we know about types of learning that can guide the design and delivery of professional development for faculty and administrators regarding equal access of students with disabilities to courses and programs?

Overview of Research Learning has been categorized in many ways. Three are discussed below. Bloom's Taxonomy Psychologist Benjamin Bloom developed a classification scheme for types of learning which includes three overlapping domains: cognitive, psychomotor, and affective. Knowledge (remembering information); comprehension (explaining the meaning of information); application (using abstractions in concrete situations); analysis (breaking down a whole into component parts); and synthesis (putting parts together to form a new and integrated whole).
For example, knowing that the ADA was passed in 1990 is knowledge. Tennant's A.S.K. Howard Gardner, multiple intelligences and education. Howard Gardner, multiple intelligences and education.
Howard Gardner’s work around multiple intelligences has had a profound impact on thinking and practice in education – especially in the United States. Here we explore the theory of multiple intelligences; why it has found a ready audience amongst educationalists; and some of the issues around its conceptualization and realization.
Contents: introduction · howard gardner – a life · howard gardner on multiple intelligences · the appeal of multiple intelligences · are there additional intelligences? · howard gardner’s multiple intelligences – some issues and problems · conclusion · further reading and references · how to cite this article I want my children to understand the world, but not just because the world is fascinating and the human mind is curious.