

Educators must begin incorporating digital citizenship instruction as soon as students have access to technology, which for many begins as early as kindergarten. Because digital citizenship instruction does not fall within the confines of the academic curriculum standards, the majority of instruction must come from school librarians and their collaboration with classroom teachers (Preddy, 2016). Students will continuously participate in digital environments throughout their lives, and instruction must apply to all levels from elementary school through high school and beyond. In creating this collection, I curated resources for K-12 educators including lesson plans, videos, games, articles, and other resources addressing online etiquette, cyberbullying, and online privacy. Through continued instruction, educators can help prepare students to safely and effectively participate in the digital world.
References
Preddy, L. (2016). The critical role of the school librarian in digital citizenship education. Knowledge Quest, 44(4), 4–5.
Zook, C. (2019, December 10). What is digital citizenship & how do you teach it? Applied Educational Systems.
Rethinking digital citizenship. Kid, you posted WHAT?! How to raise a digital citizen. Accountability & responsibility in a digital world. Cyber-bullying Facts – Top 10 Forms of Cyber Bullying. Getting the Most Out of the Internet Ruff Ruffman. A Majority of Teens Have Experienced Some Form of Cyberbullying. Name-calling and rumor-spreading have long been an unpleasant and challenging aspect of adolescent life.
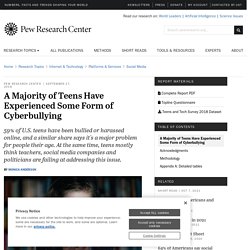
But the proliferation of smartphones and the rise of social media has transformed where, when and how bullying takes place. A new Pew Research Center survey finds that 59% of U.S. teens have personally experienced at least one of six types of abusive online behaviors. The most common type of harassment youth encounter online is name-calling. Some 42% of teens say they have been called offensive names online or via their cellphone. The Data – The Digital Citizenship. Recent Tweets @therealroseanne would love to connect to discuss how we can teach kids the challenges of the digital realm and how to proceed cautiously.
Can be contacted via thedigitalcitizenship.com. thanks. About 3 months ago from Digital Citizenship's Twitter via Twitter for iPhone Meet Our Team Meet our Digital Citizenship team. Teens, Social Media, and Privacy. Teens share a wide range of information about themselves on social media sites; indeed the sites themselves are designed to encourage the sharing of information and the expansion of networks.
However, few teens embrace a fully public approach to social media. Instead, they take an array of steps to restrict and prune their profiles, and their patterns of reputation management on social media vary greatly according to their gender and network size. These are among the key findings from a new report based on a survey of 802 teens that examines teens’ privacy management on social media sites: Teens are sharing more information about themselves on social media sites than they did in the past. Harvard case offers reminder of perils of online misbehavior. The racist social-media posts were originally shared only among friends — in text messages and a Google document.
But someone took screenshots, which led Harvard University to revoke an offer of admission to a Parkland high school survivor. The decision announced Monday serves as a reminder to aspiring college students and all young people that online comments, even those considered private, can resurface and be used against them. It’s relatively unusual for colleges to rescind admission offers. Reading, Writing, Cyber Civics: Schools Grapple With Creating Good Digital Citizens.
Faced with problems like cyber-bullying, fake news and social media addiction, schools are dedicating class time to teaching students how to use digital tools responsibly.
While the approaches of schools in the Roaring Fork Valley may differ, they share the same goal of teaching kids to be good digital citizens. Tim Connolly and his 6th graders are talking cyber civics at the Waldorf School on the Roaring Fork today. He reads scenarios about things like creating fake Snapchat accounts or responding to hurtful online comments. They jump in to discuss. Digital Citizenship in 2020 and Beyond. Digital citizenship has been defined as helping youth “practice respectful and tolerant behaviors toward others” online.
With the ubiquitous growth in personal device and social media use among youth – coupled with the adoption of more web-based technologies for education – many schools in the US and abroad have sought to teach digital citizenship practices to youth of all ages. This is conveyed by teachers, counselors, librarians, IT staff, and professionals at school, and hopefully is supported by similar instruction at home given the amount of time that kids outside of school are on their devices and connecting with others. Recently, the concept has garnered an increased amount of attention as educators and other youth-serving professionals are reminded about the importance of appropriate attitudes, actions, and interactions online with so many students doing distance learning during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Let’s talk through the main takeaways. These numbers are encouraging. What Is Digital Citizenship & How Do You Teach It? As a career readiness curriculum developer, we often hear from teachers who have questions about a variety of topics they are required to teach.

From soft skills to 21st Century skills, you have a lot of topics to cover. And one of the most important ones is digital citizenship. However, even with the increased focus on teaching digital citizenship, there isn't much direction for career readiness teachers about what they are actually supposed to teach. Teaching Digital Citizenship in the School Library. What is “digital citizenship”?

Well, in broad terms, it’s the set of norms that define the appropriate and responsible use of technologies. As technology and social media constantly evolve, it is important that we, as school librarians, stay abreast of cutting-edge trends so we can best guide our stakeholders in best practices. Five Steps for Integrating Digital Citizenship into Daily Learning. Teaching children to use media resources has always been a priority during my 30 years as an educator.
This priority has evolved over the course of my career, as has my role in teaching it. Today, we help students not only find reliable resources, but also become good digital citizens. Digital citizenship is about more than online safety. It’s about creating thoughtful, empathetic human beings who can wrestle with important ethical questions at the intersection of technology and humanity. The Educator's Guide to Student Data Privacy. Educational games for kids to help teach digital citizenship and digital literacy skills. The Carnegie Cyber Academy - An Online Safety site and Games for Kids.
Cyberbully Zombies Attack. I'm a Digital Citizen. Citizenship in the Digital Age. Cyberbullying Facts. Technology Unit: Digital Citizenship. Digital Citizenship Curriculum. Teaching Privacy. Internet and Right-to-Privacy Issues - Procedures For Teachers - Religion & Ethics NewsWeekly. Prep — Preparing for the lessonSteps — Conducting the lessonExtension — Additional Activities Prep Media Components Computer Resources: Modem: 56.6 Kbps or fasterBrowser: Netscape Navigator 4.0 or above or Internet Explorer 4.0 or abovePersonal computer (Pentium II 350 MHz or Celeron 600 MHz) running Windows® 95 or higher and at least 32 MB of RAM Macintosh computer: System 8.1 or above and at least 32 MB of RAM Bookmarked Sites and Video Resources:

Who To Call- cyberbullying and other helplines. We have collated a selection of helplines that offer various levels of support for problems ranging from cyberbullying and revenge porn, to mental health and suicide prevention. Although we do our best to monitor the effectiveness and reliability of any external organizations that we link to – we cannot accept responsibility for any problems resulting in the use of these resources. Bullying & Cyberbullying Helplines. Educator Resources- cyberbullying.org. Trace my Shadow- Examine your online footprint. MAC Address Logs on Router Logging of MAC addresses is usually done only on the immediate router or host that provides the IP address to MAC address association. Although on some networks the MAC address is logged as well on some routers within the local network.