

1200 Calorie Exchange List. The 1200 calorie diabetic food exchange diet is a calorie restricted diet designed specifically for diabetics.
According to Dr. Michael Hall, most diabetics should consume between 1600 and 2000 calories each day. Having a clear understanding of meal planning and food exchange lists is essential for following this kind of diet. According to the National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse (NDIC), taking care of your diabetes requires you to learn what to eat, how much to eat and when to eat. 1,400 Calorie Diet Exchange Servings. The American Diabetes Association and the American Dietetic Association developed the diabetic exchange diet to help manage weight and blood sugar for the diabetic.
The diet divides foods into groups based on similarities in calorie and carbohydrate contents. Food items within each group can be exchanged for one another. The 1,800-calorie diabetic diet is appropriate for active women and men with diabetes. You should consult your doctor before starting this or any other diet plan. Starches are a major source of carbohydrate in the diet. Fruits are also a source of carbohydrates in the diet.
Low-fat and fat-free milk and yogurts are recommended for the diabetic to limit their intake of saturated fat, and the risk of heart disease. Meats are also a source of saturated fat in the diet. How to Understand a Diabetic Exchange Chart. Your diabetes eating plan: Exchange lists. Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan Your diabetes diet is simply a healthy-eating plan that will help you control your blood sugar.

Here's help getting started, from meal planning to exchange lists and counting carbohydrates. By Mayo Clinic Staff A diabetes diet — medically known as medical nutrition therapy (MNT) for diabetes — simply translates into eating a variety of nutritious foods in moderate amounts and sticking to regular mealtimes. Rather than a restrictive diet, a diabetes diet or MNT is a healthy-eating plan that's naturally rich in nutrients and low in fat and calories, with an emphasis on fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
Purpose If you have diabetes or prediabetes, your doctor will likely recommend that you see a dietitian to guide you on dietary changes and MNT that can help you control your blood sugar (glucose) level and manage your weight. When you eat excess calories and fat, your body responds by creating an undesirable rise in blood glucose. Create your healthy-eating plan. Diabetic Exchange FAQ's. Common questions about the Diabetic Exchange The exchange system allows the diabetic patient to quickly and accurately decide how much energy, protein, fat and carbohydrates a meal will typically contain and whether it is suitable for their requirements.

Although the diabetes exchange is a useful and clearly defined system, questions remain as to its exact effect on diabetes and diet. This section aims to dispel some of the myths surrounding the diabetic exchange system. Some diabetes patients who are wondering about the exchange system may find the following questions useful. What are ‘free foods’ and why can’t I eat lots of them? Diabetic Exchange food groups. Diabetic exchange was created to allow easy carbohydrate and sugar management A diabetic exchange diet is designed to allow you easy control over the amount of sugar and cholesterol you allow into your body.

A successful diabetic exchange diet will help to control you weight and your sugar levels. It is necessary to carefully measure food in a diabetic exchange diet, and it is generally recommended to eat 3 meals and one snack per day. The diabetic exchange divides foods into 6 specific groups, and measures food per serving size. Try the Food Exchange Calculator. Milk and yogurt. Sweets,desserts & other carbohydrates. Your diabetes diet can include sweets and desserts.
Just remember the ground rules: You can substitute food choices from this list for other carbohydrate-containing foods, such as those from the starches, fruit or milk exchange lists. Eat sweets and desserts as part of your meal. Free foods. Fruits. Starches. Nonstarchy vegetables. Fats. Meat and meat substitutes. The Diabetic Exchange List (Exchange Diet) Printer Friendly Version The Diabetic Exchange List (Exchange Diet) *The Exchange Lists are the basis of a meal planning system designed by a committee of the American Diabetes Association and the American Dietetic Association.
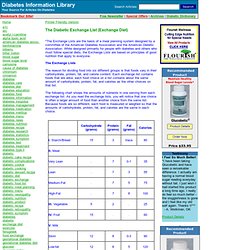
While designed primarily for people with diabetes and others who must follow special diets, the Exchange Lists are based on principles of good nutrition that apply to everyone. The Exchange Lists The reason for dividing food into six different groups is that foods vary in their carbohydrate, protein, fat, and calorie content. The following chart shows the amounts of nutrients in one serving from each exchange list.
You will notice symbols on some foods in the exchange groups. I. Each item in this list contains approximately fifteen grams of carbohydrate, three grams of protein, a trace of fat, and eighty calories. 1/2 cup of cereal, grain, or pasta = one serving1 ounce of a bread product = one serving Your dietitian can help you to be more exact. II. III. Exchange System: Historical Background. Prior to the development of exchange lists in 1950, meal planning for persons in the United States with diabetes was chaotic, with no agreement among the major organizations involved with diabetes and nutrition.
To solve this problem, the concept of "exchange," or "substitution," of similar foods was developed by the American Dietetic Association, the American Diabetes Association, and the U.S. Public Health Service. The goal was to develop an educational tool for persons with diabetes that would provide uniformity in meal planning and allow for the inclusion of a wider variety of foods. Definition. Diabetic Exchange Calculator : FoodSize.com – Food Portion Sizes – Educational Picture Guide. Food Exchange Calculator. Food exchange calculator The food exchange calculator analyses the carbohydrates, proteins and fats in grams and calories.

By grounding your foot in the diabetes exchange, you can use the food exchange calculator to work out how much carbohydrate, protein and fat is contained in your meal. The exchanges covered include starch, vegetables, fruit, milk, meat and fat. Diabetic Diet Food Exchange List. Home :: Diabetes Type And Diet | Pre-Diabetes & Symptoms | Diabetic Weight Loss Diet | Diabetes Food Pyramid | Diabetic Food Exchanges List | Carbohydrate Counting | Diabetic Diet Tips | Diabetes Management | What Is Glycemic Index Diabetes Food Exchange Below is the table of the foods the diabetic should take.

These foods are different from each other depending upon the calories they contain, so they should be taken accordingly. There should be three to five servings of vegetables, two to three servings of milk, and two to four servings of fruits in your daily diet.