

The Biology Project. Evolution. Genetic Drift. Mutations. In the living cell, DNA undergoes frequent chemical change, especially when it is being replicated (in S phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle).
Most of these changes are quickly repaired. Those that are not result in a mutation. Thus, mutation is a failure of DNA repair. Single-base substitutions A single base, say an A, becomes replaced by another. Missense mutations With a missense mutation, the new nucleotide alters the codon so as to produce an altered amino acid in the protein product.
EXAMPLE: sickle-cell disease. ANOTHER EXAMPLE: Patient A with cystic fibrosis (scroll down). Nonsense mutations With a nonsense mutation, the new nucleotide changes a codon that specified an amino acid to one of the STOP codons (TAA, TAG, or TGA). EXAMPLE: Patient B Here is a sampling of the more than 1000 different mutations that have been found in patients with cystic fibrosis. Silent mutations. The genetics of cystic fibrosis. References Cohn JA, Freidman KJ, Noone PG, et al.

Relation between mutations of the cystic fibrosis gene and idiopathic pancreatitis. Variation in Chromosome Number. Down Syndrome: Health Issues - Medical Essays and Information. Polyploidy. Cells (and their owners) are polyploid if they contain more than two haploid (n) sets of chromosomes; that is, their chromosome number is some multiple of n greater than the 2n content of diploid cells.
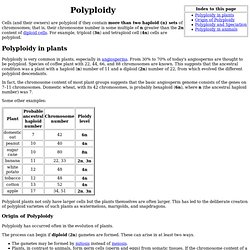
For example, triploid (3n) and tetraploid cell (4n) cells are polyploid. Polyploidy in plants. Understanding Evolution. Biston. BBC - Earth News - Raindrops drive flower evolution. The humble raindrop may have played an important role in the evolution of flowers, scientists in China have discovered.
A study of 80 species has revealed that flowers evolve different shapes and structures in part to prevent their pollen getting wet. Other flowers get round the problem by evolving waterproof pollen. The finding may help explain why so many species in rainy areas either have droopy flowers or close their petals. Many researchers, including Charles Darwin, have speculated that flowers may have evolved certain traits or structures to protect themselves against the damaging effects of rain, which can wash away pollen grains and dilute nectar. But few have experimentally tested the idea. Exhibit: Mutant Fruit Flies - Drosophila Genetics. Click on the small thumbnail pictures below to magnify the flies.

You'll see enlarged illustrations of fruit flies, Drosophila melanogaster. (In our real exhibit you'd be looking at the actual flies crawling around, looking for food or grooming their wings.) Compare the mutated flies to the normal flies. The fruit flies in this exhibit show just a few of the mutations that occur in natural fruit fly populations. The genetic instructions to build a fruit fly-or any other organism-are imprinted in its DNA, a long, threadlike molecule packaged in bundles called chromosomes.
To build a complete organism, many genes must work precisely together. Variety of dogs' coats explained. Just three genes account for the different coats of domestic dogs Wiry, smooth, curly or straight - the genetic reason for the array of coats of different dog breeds is surprisingly simple, say scientists.
Just three genes account for the coat types that make canine pets so diverse. The Biosphere and mass Extinctions. Kiwis for kiwi. It is unthinkable that kiwi should be allowed to disappear – the world would lose an intriguing bird genetically unchanged for millions of years.
Saving kiwi brings communities together, creates employment and helps restore native forests where many other native species also live, and therefore also benefit. Trust-supported restoration plantings also help lock carbon away, improve air and water quality, prevent erosion, and build healthy soils – the list goes on. It’s win–win all the way. New Zealand's icon ›› Kiwi are a natural fit with New Zealanders’ national psyche - we relate to their quirkiness, and are all proud to be called 'Kiwis' Kiwi species ›› What is Darwinism? What is Darwinism?

Joel Hanes n One Long Argument, Ernst Mayr (evolutionary biologist, and originator of the Biological Species Concept) summarizes Darwin's theories, and traces the history of their acceptance by the world scientific community. In the Preface , he begins: A modern evolutionist turns to Darwin's work again and again. This is not surprising, since the roots of all our evolutionary thinking go back to Darwin. In Chapter Four, "Ideological Opposition to Darwin's Five Theories", Mayr summarizes "Darwin's Theory", or "Darwinism", thus: In both scholarly and popular literature one frequently finds references to "Darwin's theory of evolution", as though it were a unitary entity.
Specials : Nature. Nature marks the anniversary of the publication of Charles Darwin's On The Origin Of Species 150 years ago, with a special on biodiversity.
As nations prepare progress reports on their pact to reduce the rate of loss of biodiversity by 2010, International Year of Biodiversity, Pavan Sukhdev urges governments to secure the flows of nature's 'public goods'. Meanwhile, William R. Turner and colleagues argue that natural ecosystems be made a bulwark against climate change, Robert J.