

Public-key cryptography. An unpredictable (typically large and random) number is used to begin generation of an acceptable pair of keys suitable for use by an asymmetric key algorithm.
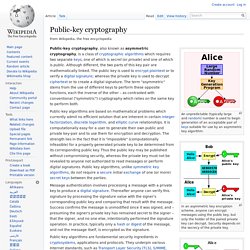
In an asymmetric key encryption scheme, anyone can encrypt messages using the public key, but only the holder of the paired private key can decrypt. Security depends on the secrecy of the private key. In the Diffie–Hellman key exchange scheme, each party generates a public/private key pair and distributes the public key. After obtaining an authentic copy of each other's public keys, Alice and Bob can compute a shared secret offline. The shared secret can be used, for instance, as the key for a symmetric cipher. Protection Tools. SSL. Certificate Authority. Secret Key Cryptography. Public Key Cryptography. Hashing. Sniffing. Spoofing.