

Cartes de la Bataille de Normandie - Encyclopédie D-Day. Ranks and insignia of NATO armies officers. Rank comparison chart of all armies/ land forces of NATO member states.
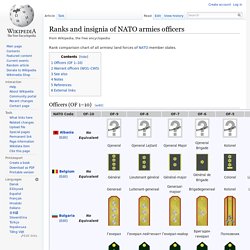
Officers (OF 1–10)[edit] Remark: NATO STANAG 2116 lists Officer Designates (listed here as OF(D)) of some countries alongside OF-1 ranks. Warrant officers (WO1–CW5)[edit] Warrant Officers (WO) and Chief Warrant Officers (CW) in the US Military rank below officers but above officer candidates and enlisted servicemen. The first warrant officer rank, WO1 does not have a "commission" associated with it, instead having a "Warrant" from the Secretary of the Army.
Ranks and insignia of NATO armies enlisted. Ranks and insignia of NATO. Ranks and insignia of NATO are combined military insignia used by the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization.
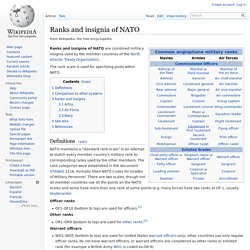
The rank scale is used for specifying posts within NATO. Definitions[edit] NATO maintains a "standard rank scale" in an attempt to match every member country's military rank to corresponding ranks used by the other members. The rank categories were established in the document STANAG 2116, formally titled NATO Codes for Grades of Military Personnel. There are two scales, though not all member countries use all the points on the NATO scales and some have more than one rank at some points (e.g. many forces have two ranks at OF-1, usually lieutenants): Officer ranks OF1–OF10 (bottom to top) are used for officers.[1]
Batterie de Merville : Mur de l'Atlantique. Stichting Bunkerbehoud, English projects. Juno. Le Mur de l'Atlantique - Der Atlantikwall - Fortifications.
- Reconstitution Historique - .. ... ... APP-6A. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
L'APP-6A, signes conventionnels représentant les systèmes terrestres[1] est un standard de l'OTAN qui définit les marques cartographiques représentant les systèmes terrestres. L'APP-6A est devenu officiel en décembre 1999. L'accord de normalisation de l'OTAN qui couvre l'APP-6A est le STANAG 2019 (4e édition), promulgué en décembre 2000. L'APP-6A a remplacé l'APP-6 (dernière version en juillet 1986), qui avait été promulgué en novembre 1984. NATO Military Symbols for Land Based Systems. NATO Military Symbols for Land Based Systems was the NATO standard for military map marking symbols.
It was published as Allied Procedural Publication 6A (APP-6A). The symbols are designed to enhance NATO’s joint interoperability by providing a standard set of common symbols. APP-6A constitutes a single system of joint military symbology for land based formations and units, which can be displayed for either automated map display systems or for manual map marking. It covers all of the joint services and can be used by them.
History[edit] The first basic military map symbols began to be used by western armies in the decades following the end of the Napoleonic Wars. APP-6A was promulgated in December 1999. The U.S. is the current custodian of APP-6A, which is equivalent to MIL-STD-2525A. Symbol sets[edit] APP-6A recognises five broad sets of symbols, each set using its own SIDC (Symbol identification coding) scheme: Icon-based symbols[edit] The fill is the area within a symbol. Battle of Antietam. The Battle of Antietam /ænˈtiːtəm/ also known as the Battle of Sharpsburg, particularly in the South, fought on September 17, 1862, near Sharpsburg, Maryland, and Antietam Creek as part of the Maryland Campaign, was the first major battle in the American Civil War to take place on Union soil.
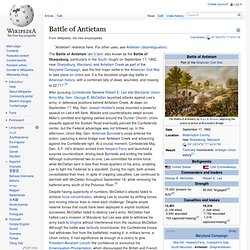
It is the bloodiest single-day battle in American history, with a combined tally of dead, wounded, and missing at 22,717.[4] Despite having superiority of numbers, McClellan's attacks failed to achieve force concentration, allowing Lee to counter by shifting forces and moving interior lines to meet each challenge. Despite ample reserve forces that could have been deployed to exploit localized successes, McClellan failed to destroy Lee's army. McClellan had halted Lee's invasion of Maryland, but Lee was able to withdraw his army back to Virginia without interference from the cautious McClellan.
Background and the Maryland Campaign[edit] Maryland Campaign, actions September 3 to 15, 1862. Confederate. Antietam Confederate order of battle. The following Confederate States Army units and commanders fought in the Battle of Antietam of the American Civil War.
The Union order of battle is listed separately. Order of battle compiled from the army organization during the campaign,[1] the casualty returns[2] and the reports.[3]