

Karl Popper. Karl Raimund Popper CH FBA FRS[4] (28 July 1902 – 17 September 1994) was an Austrian-British[5] philosopher and professor at the London School of Economics.[6] He is generally regarded as one of the greatest philosophers of science of the 20th century.[7][8] Popper is known for his rejection of the classical inductivist views on the scientific method, in favour of empirical falsification: A theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified, meaning that it can and should be scrutinized by decisive experiments.
If the outcome of an experiment contradicts the theory, one should refrain from ad hoc manoeuvres that evade the contradiction merely by making it less falsifiable. Personal life[edit] Family and training[edit] Karl Popper was born in Vienna (then in Austria-Hungary) in 1902, to upper middle-class parents. He worked in street construction for a short amount of time, but was unable to cope with the heavy labour. Expert Political Judgment: How Good Is It? How Can We Know? - Philip E. Tetlock. Mechanism design. The Stanley Reiter diagram above illustrates a game of mechanism design.
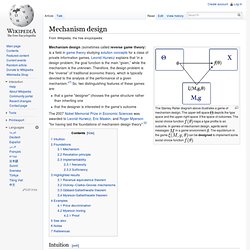
The upper-left space depicts the type space and the upper-right space X the space of outcomes.