

Example: Comparison of transparent conductive materials. This is going to be a short article, based on this table I’ve created: Comparison of transparent electrodes.

This presents a way of comparing materials by their properties directly, using their embodied energy to calculate their cost. The data is from the LCA study, “Environmental and Economic Assessment of ITO-free Electrodes for Organic Solar Cells” [link, paywalled] The results are both satisfying and interesting. Comparison of transparent conductors. Chemical engineers find high-yield method of making xylene from biomass. A team of chemical engineers led by Paul J.
Dauenhauer of the University of Massachusetts Amherst has discovered a new, high-yield method of producing the key ingredient used to make plastic bottles from biomass. The process is inexpensive and currently creates the chemical p-xylene with an efficient yield of 75-percent, using most of the biomass feedstock, Dauenhauer says. The research is published in the journal ACS Catalysis. Dauenhauer, an assistant professor of chemical engineering at UMass Amherst, says the new discovery shows that there is an efficient, renewable way to produce a chemical that has immediate and recognizable use for consumers. He says the plastics industry currently produces p-xylene from petroleum and that the new renewable process creates exactly the same chemical from biomass. Chemical engineers boost petrochemical output from biomass by 40 percent. Chemical engineers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, using a catalytic fast pyrolysis process that transforms renewable non-food biomass into petrochemicals, have developed a new catalyst that boosts the yield for five key "building blocks of the chemical industry" by 40 percent compared to previous methods.
This sustainable production process, which holds the promise of being competitive and compatible with the current petroleum refinery infrastructure, has been tested and proven in a laboratory reactor, using wood as the feedstock, the research team says. "We think that today we can be economically competitive with crude oil production," says research team leader George Huber, an associate professor of chemical engineering at UMass Amherst and one of the country's leading experts on catalytic pyrolysis.
"The ultimate significance of our research is that products of our green process can be used to make virtually all the petrochemical materials you can find. Indium tin oxide. Absorption of glass and ITO glass ITO grains on glass substrates with a few nano-particle impurities Indium tin oxide is one of the most widely used transparent conducting oxides because of its two chief properties, its electrical conductivity and optical transparency, as well as the ease with which it can be deposited as a thin film.
As with all transparent conducting films, a compromise must be made between conductivity and transparency, since increasing the thickness and increasing the concentration of charge carriers will increase the material's conductivity, but decrease its transparency. Thin films of indium tin oxide are most commonly deposited on surfaces by physical vapor deposition. Environmental and economic assessment of ITO-free electrodes for organic solar cells. Volume 97, February 2012, Pages 14–21 Dedicated to the Global Organic Photovoltaics (GOPV) conference in Hangzhou, China.

Highly Conductive and Transparent PEDOT:PSS Films with a Fluorosurfactant for Stretchable and Flexible Transparent Electrodes - Vosgueritchian - 2011 - Advanced Functional Materials. PEDOT:PSS. It is used as a transparent, conductive polymer with high ductility in different applications.
For example, AGFA coats 200 million photographic films per year with a thin, extensively-stretched layer of virtually transparent and colorless PEDOT:PSS as an antistatic agent to prevent electrostatic discharges during production and normal film use, independent of humidity conditions. If organic compounds, including high boiling solvents like methylpyrrolidone, dimethyl sulfoxide, sorbitol, ionic liquids and surfactants, are added conductivity increases by many orders of magnitude.[2][3][4] [5]This makes it also suitable as a transparent electrode, for example in touchscreens, organic light-emitting diodes and electronic paper to replace the traditionally used indium tin oxide.
Due to the high conductivity (up to 1000 S/cm are possible), it can be used as a cathode material in capacitors replacing manganese dioxide or liquid electrolytes. See also[edit] References[edit] Jump up ^ L. Little Allocation for an M/M/c queue. In queuing theory, an M/M/c queue is one where arrivals (λ) happen by a Markov (Poisson) process, average time spent in the queue (μ) is also a Markov/Poisson process, and there are c servers, and a unified queue for all servers.
This is commonly used to model call centers, but in natural economics we will use it to model products as services. As you know, I like to use computers as an example product-as-service, so we will use Little Allocation to make decisions on an example computer lab. First, some initialization: We’re going to make this very conservative, so let’s say people spend an average of 8 hours a day on the computer. I probably do, but I’m a terrible example of a normal person; This is just to make it more difficult. So, μ=8h=28800s Let’s make our population n=36, just because it doesn’t really matter. ) computers for our example lab, given the above parameters.
[Python] Little Allocation, v0.1. ?: Although many ternary operators are possible, the conditional operator is so common, and other ternary operators so rare, that the conditional operator is commonly (albeit incorrectly) referred to as the ternary operator.
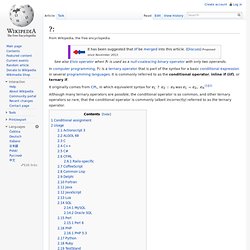
Conditional assignment[edit] ? : is used as follows: condition ? Value_if_true : value_if_false variable = condition ? Usage[edit] The conditional operator's most common usage is to make a terse simple conditional assignment statement. Int opening_time = (day == WEEKEND) ? Instead of the more verbose int opening_time; if (day == WEEKEND) opening_time = 12;else opening_time = 9; Actionscript 3[edit] condition ? ALGOL 68[edit] Both ALGOL 68's choice clauses (if and the case clauses) provide the coder with a choice of either the "bold" syntax or the "brief" form. Single if choice clause: if condition then statements [ else statements ] fi "brief" form: ( condition | statements | statements ) Chained if choice clause: C[edit] Rethinking our Priorities. The job I held before my current one was working as a server (among other things) in a high-end bakery.
My boss, the sous chef, loved to bake; she also ended up working at least 90 hours a week, worked often on her one day off a week, had to deal with whiny, bitchy customers who berated her for no reason, had fits of overwhelming stress that she sometimes took out on others, and generally had to bend over backwards to make money.
When I was on the clock, I was running around constantly, making sure everything was always perfect, and submitting to every whim of every customer, no matter how much I just wanted to set them on fire. We weren’t fulfilling some critical function of society, though. Priority levels defined more rigorously. As I’ve covered before, a computational economy uses preemption and priority levels for its allocation schemes.
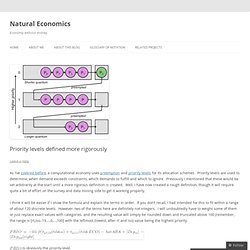
Priority levels are used to determine, when demand exceeds constraints, which demands to fulfill and which to ignore. Previously I mentioned that these would be set arbitrarily at the start until a more rigorous definition is created. Well, I have now created a rough definition, though it will require quite a bit of effort on the survey and data mining side to get it working properly.
I think it will be easier if I show the formula and explain the terms in order. Preemption (computing) The term preemptive multitasking is used to distinguish a multitasking operating system, which permits preemption of tasks, from a cooperative multitasking system wherein processes or tasks must be explicitly programmed to yield when they do not need system resources. In simple terms: Preemptive multitasking involves the use of an interrupt mechanism which suspends the currently executing process and invokes a scheduler to determine which process should execute next. Therefore, all processes will get some amount of CPU time at any given time. The term "preemptive multitasking" is sometimes mistakenly used when the intended meaning is more specific, referring instead to the class of scheduling policies known as time-shared scheduling, or time-sharing. Scheduling (computing) The scheduler is concerned mainly with: In practice, these goals often conflict (e.g. throughput versus latency), thus a scheduler will implement a suitable compromise.
Preference is given to any one of the above mentioned concerns depending upon the user's needs and objectives. In real-time environments, such as embedded systems for automatic control in industry (for example robotics), the scheduler also must ensure that processes can meet deadlines; this is crucial for keeping the system stable. Scheduled tasks can also be distributed to remote devices across a network and managed through an administrative back end. Aspects of a Natural Economy. I still feel much of what I’ve written is not accessible to the general public. This post will focus on an easily understandable overview of what defines a natural economy (NE). It may not include everything, but it will cover the most essential aspects. Semi-Automatic Little Allocation: Provides information on minimums to fulfill a given demand.
Rockström Restriction: Rigorous constraints to prevent over-exploitation (using resources faster than they can be replenished).