

Hubble Discoveries - Dark Energy. HubbleSite - Out of the ordinary...out of this world. Hubblecast. Hubble Goes to the eXtreme to Assemble Farthest-Ever View of the Universe. Hubble Goes to the eXtreme to Assemble Farthest-Ever View of the Universe Like photographers assembling a portfolio of best shots, astronomers have assembled a new, improved portrait of mankind's deepest-ever view of the universe.
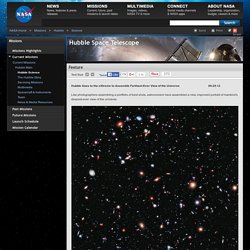
(Credit: NASA; ESA; G. Illingworth, D. Magee, and P. Oesch, University of California, Santa Cruz; R. Called the eXtreme Deep Field, or XDF, the photo was assembled by combining 10 years of NASA Hubble Space Telescope photographs taken of a patch of sky at the center of the original Hubble Ultra Deep Field. The Hubble Ultra Deep Field is an image of a small area of space in the constellation Fornax, created using Hubble Space Telescope data from 2003 and 2004. The new full-color XDF image is even more sensitive, and contains about 5,500 galaxies even within its smaller field of view. Hubble pointed at a tiny patch of southern sky in repeat visits (made over the past decade) for a total of 50 days, with a total exposure time of 2 million seconds. Related Link. Hubble Heritage Gallery of Images. About MAST. Celestia: Home. About CANDELS.
Space observatory. Space observatories and their wavelength working range Spitzer, Hubble and XMM with their most important parts depicted A space observatory is any instrument (such as a telescope) in outer space that is used for observation of distant planets, galaxies, blackholes ,nebulae , galaxies, and other outer space objects.

This category is distinct from other observatories located in space that are pointed toward Earth for the purpose of reconnaissance and other types of information gathering. And collected their information in record. It also search new things in Cosmo's. Introduction[edit] A large number of observatories have been launched into orbit, and most of them have greatly enhanced our knowledge of the extraterrestrial universe. Space-based astronomy is even more important for frequency ranges which are outside the optical window and the radio window, the only two wavelength ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum that are not severely attenuated by the atmosphere. History[edit] Observatory. Astronomical observatories[edit] Ground-based observatories[edit] Ground-based observatories, located on the surface of Earth, are used to make observations in the radio and visible light portions of the electromagnetic spectrum.

Most optical telescopes are housed within a dome or similar structure, to protect the delicate instruments from the elements. Telescope domes have a slit or other opening in the roof that can be opened during observing, and closed when the telescope is not in use. Chronology of Telescopes, Observatories, and Observing Technology. Planetarium. The new planetarium and exhibition centre at ESO Headquarters.[1] A planetarium (plural planetaria or planetariums) is a theatre built primarily for presenting educational and entertaining shows about astronomy and the night sky, or for training in celestial navigation.

A dominant feature of most planetaria is the large dome-shaped projection screen onto which scenes of stars, planets and other celestial objects can be made to appear and move realistically to simulate the complex 'motions of the heavens'. The celestial scenes can be created using a wide variety of technologies, for example precision-engineered 'star balls' that combine optical and electro-mechanical technology, slide projector, video and fulldome projector systems, and lasers. Whatever technologies are used, the objective is normally to link them together to provide an accurate relative motion of the sky. History[edit] Early[edit] The oldest, still working planetarium can be found in the Dutch town Franeker.
Domes[edit] The James Webb Space Telescope. About Webb's Orbit The James Webb Space Telescope will observe primarily the infrared light from faint and very distant objects.

But all objects, including telescopes, also emit infrared light. To avoid swamping the very faint astronomical signals with radiation from the telescope, the telescope and its instruments must be very cold. Therefore, Webb has a large shield that blocks the light from the Sun, Earth, and Moon, which otherwise would heat up the telescope, and interfere with the observations.
To have this work, Webb must be in an orbit where all three of these objects are in about the same direction. The L2 orbit is an elliptical orbit about the semi-stable second Lagrange point . The James Webb Space Telescope. Hubble has spotted an ancient galaxy that shouldn't exist.