

Functions of Water: Health Benefits. Did you know that your body weight is approximately 60 percent water?
Your body uses water in all its cells, organs, and tissues to help regulate its temperature and maintain other bodily functions. Because your body loses water through breathing, sweating, and digestion, it's important to rehydrate by drinking fluids and eating foods that contain water. The amount of water you need depends on a variety of factors, including the climate you live in, how physically active you are, and whether you're experiencing an illness or have any other health problems. Water Protects Your Tissues, Spinal Cord, and Joints Water does more than just quench your thirst and regulate your body's temperature; it also keeps the tissues in your body moist. Water – a vital nutrient. Water in our bodies The human body can last weeks without food, but only days without water.
The body is made up of 50 to 75 per cent water. Water forms the basis of blood, digestive juices, urine and perspiration, and is contained in lean muscle, fat and bones. Human Health - The Importance Of Water · Waterlogic. Functions of Water: Health Benefits. Water: How much should you drink every day? Water: How much should you drink every day? Water is essential to good health, yet needs vary by individual. These guidelines can help ensure you drink enough fluids. By Mayo Clinic Staff How much water should you drink each day? It's a simple question with no easy answer. Studies have produced varying recommendations over the years. No single formula fits everyone. 26.1 Body Fluids and Fluid Compartments – Anatomy and Physiology. Boundless Anatomy and Physiology. Extracellular fluid - Biology-Online Dictionary. Definition noun The body fluid outside the cell composed of blood plasma, interstitial fluid, lymph and transcellular fluid Supplement The extracellular fluid pertains to all body fluid outside the cell(s).
LOOP OF HENLE explained!! FUNCTION OF THE NEPHRON made easy!! Maintaining Water Volume: ADH and the Loop of Henle. Your kidneys have the ability to conserve or waste water.
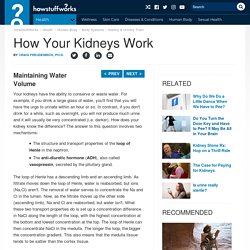
For example, if you drink a large glass of water, you'll find that you will have the urge to urinate within an hour or so. In contrast, if you don't drink for a while, such as overnight, you will not produce much urine and it will usually be very concentrated (i.e. darker). How does your kidney know the difference? The answer to this question involves two mechanisms: The structure and transport properties of the loop of Henle in the nephron.The anti-diuretic hormone (ADH), also called vasopressin, secreted by the pituitary gland. The loop of Henle has a descending limb and an ascending limb. Now, as the filtrate flows through the collecting ducts, which go back down through the medulla, water can be reabsorbed from the filtrate by osmosis. Loop of Henle. Loop of Henle - Interactive Biology, with Leslie Samuel. Hydration Testing. Assessment of hydration status of elite young male soccer players with different methods and new approach method of substitute urine strip.
Hydration Assessment of Athletes. Hydration4athletes. HYDRATION DURING ENDURANCE EXERCISE – THE RIGHT SUPPLY DURING A STAGE - PowerBar South Africa. Part II - HYDRATION FROM AN ENDURANCE ATHLETE'S PERSPECTIVE — BRITE COACHING. Why is starting hydrated so important?
"Once you begin sweating you're generally going to be fighting a losing battle against fluid and electrolyte loss, so starting off properly hydrated can be extremely beneficial," says co-founder of Precision Hydration Andy Blow. "When you're properly hydrated you have a larger reservoir of fluid to draw from over time than if you're dehydrated. " In our Part II of our 3-part series related to Nutrition, Hydration and Gut Health for endurance athletes, we will focus on dynamic topic of hydration, electrolytes and the individualization of fluid balance.
If you missed Part I (fuelling guidelines for the endurance athlete) please take some time to review the information as each aspect is optimized when working together. Becoming dehydrated during an endurance event can easily derail not only a potential breakthrough performance but it can also turn a functional athlete into a zombie stumbling aimlessly through a race course. Links: Sports Drinks For Endurance Athletes: The Good, The Bad, The Ugly. – EndurElite. Science of Hydration. TRS Hydration for endurance sports.
Why Water Is The Most Important Nutrient For Endurance Athletes. By Mike Darnley, MS,RD Many people do not think of water as a nutrient, possibly due to its simplicity or maybe because there is no energy provided by water.
Nevertheless, water is the most vital nutrient that we consume. Besides being a medium for cellular processes that occur in the body, water is the main component of blood, which is responsible for transporting nutrients and oxygen to tissues of the body. Water is also important for dissipating heat through evaporation from the skin. In addition to the role of water in survival, athletic performance can be compromised by only slight changes in hydration status(1). Because the primary focus of this paper is water, I will not go into detail about the need for oral rehydration solutions or carbohydrate solutions during exercise. Normally, we lose about 2 1/2 cups of water per day simply by evaporation from the skin and by regular breathing.
Water is the best source of fluid for exercise sessions lasting less than one hour (1). 1. 1. 26.3 Electrolyte Balance – Anatomy and Physiology. 3759170f099c8113fc865faef519ce27c578. 10.