

Want to Become an Innovator? National Centre for Technology in Education) - Step 1: Review & Prioritise. Frugal engineering. In May 2012 The Financial Times newspaper called the concept "increasingly fashionable".[6] Several US universities have programs that develop frugal solutions.
Such efforts include the Frugal Innovation Lab at Santa Clara University and a two quarter project course at Stanford University, the Entrepreneurial Design for Extreme Affordability program.[7] Variety of terms[edit] Many terms are used to refer to the concept. "Frugal engineering" was coined by Carlos Ghosn, the joint chief of Renault and Nissan, who stated, "frugal engineering is achieving more with fewer resources In India, the words "Gandhian"[9] or "jugaad", Hindi for a stop-gap solution,[10] are sometimes used instead of "frugal". At times this no frills approach can be a kind of disruptive innovation.[12] History[edit] Notable innovations[edit] An Indian woman using her Nokia 1100 ChotuKool fridge Jaipur leg Mobile banking Nokia 1100 Sorghum beer Solar light bulb Tata Nano.
How to make constant and consistent improvement in your playing. Learning Styles Online.com - including a free inventory. Formation en informatique, e-learning, cours et tuto - bureautique - professionnelle - particulier par Vodeclic. MindShare. E-Learning Process Illustration. You Want E-Learning Success, But Are You Prepared to Go All the Way? Many of us take a Field of Dreams approach to elearning.

If we build it, they will learn. But the reality is that elearning is just an event in the timeline of learning and not the entire learning process. And in some ways, the elearning course is an intrusion on the person’s natural learning process. Because of this, we want to make sure that the investment we make in elearning produces the results we desire. Sure enough, the elearning course is important because it can compress time and save resources. In today’s post I want to look at some things to consider before and after you build your elearning course. Motivated to Learn: How do you get people interested in what you have to offer? 1. Portfolio. E-Learning products offering web based online fleet driver training that is compliant and offers audit and reporting capabilities. The Drive Smarter system provides your organisation with SCORM compliant e-Learning solutions that offer video-based training via our web interface, along with audit and reporting capabilities via our administrator back-office application.
Option 1: e-Learn Complete Drive Smarter e-Learn Complete offers you the ability to provide a long-term ‘drip-feed’ of information to your drivers. When selecting this option, you have the opportunity to choose 12 modules from our line-up and dictate the order in which the modules are taken. Typically, an organisation opts for an individual to take one module per month over a 12-month period. This is followed by quarterly refresher modules in years two and three. How Do You Communicate with Your E-Learners? Years ago, I was enrolled in a course on video production.

Each week we were given assignments to do. At the end of the week, the whole class would sit down and we’d review our projects. One of the objectives was to have the other students share what they got out of the video before they knew what I intended to communicate. It was always eye opening to see how others perceived what I produced. Often what the audience got from the video was not what I had intended. Through that process, I learned that it’s not enough to just put information together and assume that somehow the viewer would understand what I meant. It All Starts with Understanding the Communication Process Clear communication is critical when you design your elearning course because what you present isn’t always received by the learner the way you intend it.
Here’s a simple illustration of what happens as learners go through an elearning course. The second image shows how three different learners process the information. Linking feedback to the learning process — Faculty Development. It is very important to ensure that the feedback given to the learner is aligned with the overall learning outcomes of the programme, teaching session or clinical activity in which the learner is engaged.
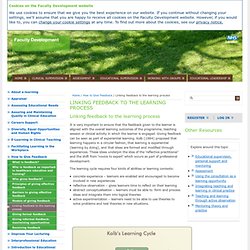
Giving feedback can be seen as part of experiential learning. Kolb (1984) proposed that learning happens in a circular fashion, that learning is experiential (learning by doing), and that ideas are formed and modified through experiences. These ideas underpin the idea of the ‘reflective practitioner’ and the shift from ‘novice to expert’ which occurs as part of professional development. The learning cycle requires four kinds of abilities or learning contexts: This cycle is similar to the ‘plan – do – reflect – act’ cycle which is often used in appraisals.
If we consider that one of the tasks of those giving feedback is to help the learner achieve their learning goals, then Hill (2007) suggests that we need to start with an understanding of: Print module to PDF Further information. Formation informatique en ligne - elearning informatique - formation bureautique - cours bureautique - tuto informatique - Autoformation informatique - Vodeclic.
AngelList Connects Start-Ups With Investors. Khan Academy. National Geographic Magazine.