

Louis XIV of France. Louis XIV (5 September 1638 – 1 September 1715), known as Louis the Great (Louis le Grand) or the Sun King (le Roi-Soleil), was a monarch of the House of Bourbon who ruled as King of France from 1643 until his death.[1] His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the longest of any monarch of a major country in European history.[2]
Middle Ages. Middle Ages. From Academic Kids.
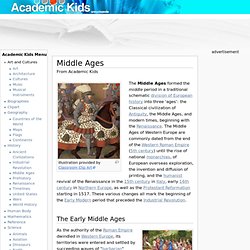
Chivalry. Black death. Black Death. Spread of the Black Death in Europe (1346–53) The Black Death is thought to have originated in the arid plains of central Asia, where it then travelled along the Silk Road, reaching the Crimea by 1343.[6] From there, it was most likely carried by Oriental rat fleas living on the black rats that were regular passengers on merchant ships.
Spreading throughout the Mediterranean and Europe, the Black Death is estimated to have killed 30–60% of Europe's total population.[7] In total, the plague reduced the world population from an estimated 450 million down to 350–375 million in the 14th century. The aftermath of the plague created a series of religious, social, and economic upheavals, which had profound effects on the course of European history. It took 150 years for Europe's population to recover. [citation needed] The plague recurred occasionally in Europe until the 19th century. Chronology. The Black Death (Bubonic Plague) During the Hundred Years' War, a lot of people in Europe were very poor and hungry because the soldiers fighting the war had wrecked their farms.

Then people began to catch a terrible sickness that was spreading along Mongol trade routes from China through Central Asia to Europe beginning in 1328 AD. This sickness was the bubonic plague. Bacteria caused the plague, getting inside people usually when infected fleas bit them. When you caught the plague you got big black spots called buboes on your armpits and behind your knees and on your neck. Republic of Genoa. Geography[edit] When the Republic of Genoa was established in the early 11th century, it consisted of the city of Genoa and the surrounding areas.
As the commerce of the city increased, so did the territory of the Republic. In 1015, the entirety of Liguria was part of the Republic of Genoa. After the First Crusade in 1098, Genoa gained settlements in Syria. The majority of them were lost during the campaigns of Saladin. Major territorial possessions[edit] History[edit] Rise[edit] Bubonic Plague (the Black Death) Bubonic plague was one of the most feared diseases of the ancient and medieval worlds.
Nobody could tell what caused it, and most people who got it died within a few days, screaming in pain. And when one or two people in a village got it, usually it spread to everyone else, and many of them died. Plague caused a fever, and black spots on your chest sometimes, and sometimes great big black swellings on your armpits and at the top of your legs. That's why they called it the Black Death. These swellings got hard like rocks and hurt, and then in a day or two people usually died.
Today we do know what causes bubonic plague: it's a bacterium. DNA evidence shows that the plague came first from China, but the first recorded instance of people getting bubonic plague was in Constantinople about 570 AD. Plague epidemics were much worse in places where people were crowded together and didn't get enough to eat. More about bubonic plague (with pictures) Main medicine page Main science page or.
Hundred Years War. Dome of the Rock. Hagia Sophia. The church contained a large collection of holy relics and featured, among other things, a 15-metre (49 ft) silver iconostasis.
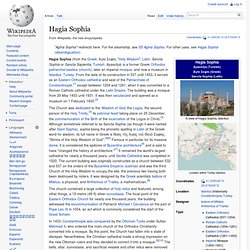
The focal point of the Eastern Orthodox Church for nearly one thousand years, the building witnessed the excommunication of Patriarch Michael I Cerularius on the part of Pope Leo IX in 1054, an act which is commonly considered the start of the Great Schism. In 1453, Constantinople was conquered by the Ottoman Turks under Sultan Mehmed II, who ordered this main church of the Orthodox Christianity converted into a mosque. By this point, the Church had fallen into a state of disrepair. Nevertheless, the Christian cathedral made a strong impression on the new Ottoman rulers and they decided to convert it into a mosque.[9][10] The bells, altar, iconostasis, and sacrificial vessels and other relics were removed and the mosaics depicting Jesus, his Mother Mary, Christian saints and angels were also removed or plastered over.
History[edit] First church[edit] Horses in the Middle Ages. This 15th-century depiction of Charlemagne and Pope Adrian I shows a well-bred medieval horse with arched neck, refined head and elegant gait.
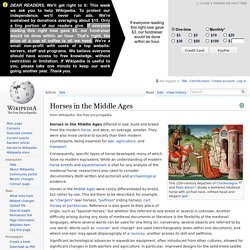
Horses in the Middle Ages differed in size, build and breed from the modern horse, and were, on average, smaller. They were also more central to society than their modern counterparts, being essential for war, agriculture, and transport. Consequently, specific types of horse developed, many of which have no modern equivalent. While an understanding of modern horse breeds and equestrianism is vital for any analysis of the medieval horse, researchers also need to consider documentary (both written and pictorial) and archaeological evidence. Significant technological advances in equestrian equipment, often introduced from other cultures, allowed for significant changes in both warfare and agriculture.
Breeding[edit] This 15th-century battle scene shows the powerfully-built horses used in warfare.
Medieval Islamic History for Kids! Mongols. The Mongols, or Mongolic peoples, are a Central and Northern Asian (Inner Asia) ethno-linguistic group.
Although the largest Mongolic group consists of the inhabitants of Mongolia, they also live as minorities across Northern Asia, including in Russia, China, and many of the former Soviet Union states. Mongolic peoples belonging to the Buryat ethnic group live predominantly in what is now the autonomous Republic of Buryatia, Russia. In China, they live mainly either in Inner Mongolia or, less commonly, in Xinjiang. Mongolic peoples are bound together by a common culture and language, a group of related tongues known as Mongolic languages.
Definition. Medieval History.