

Permaculture Principles - The Big Picture. There are permaculture principles and permaculture ethics. The ethics are sometimes referred to as principles as well. I'll keep them separate. The permaculture ethics are at the centre of permaculture philosophy and are broad guidelines of how we should behave towards the earth and towards each other. The permaculture principles, or permaculture design principles, are the guidelines that you follow when you design a permaculture garden or bigger permaculture system.
Hydroponics. NASA researcher checking hydroponic onions with Bibb lettuce to his left and radishes to the right Hydroponics is a subset of hydroculture, the method of growing plants without soil, using mineral nutrient solutions in a water solvent.[1] Terrestrial plants may be grown with only their roots exposed to the mineral solution, or the roots may be supported by an inert medium, such as perlite or gravel.
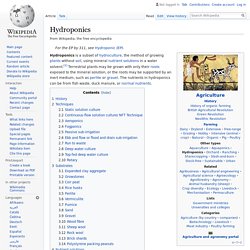
The nutrients in hydroponics can be from fish waste, duck manure, or normal nutrients. History[edit] Greenhouse. A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse) is a building or complex in which plants are grown.
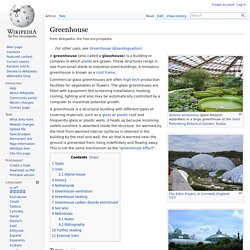
These structures range in size from small sheds to industrial-sized buildings. A miniature greenhouse is known as a cold frame. Commercial glass greenhouses are often high tech production facilities for vegetables or flowers. The glass greenhouses are filled with equipment like screening installations, heating, cooling, lighting and also may be automatically controlled by a computer to maximize potential growth. A greenhouse is a structural building with different types of covering materials, such as a glass or plastic roof and frequently glass or plastic walls; it heats up because incoming visible sunshine is absorbed inside the structure.
Edible Landscaping. Quality Vegetable Seeds through Suttons Seeds - Suttons Seeds and Plants.