

Health Care Around the World. Author and Page information Health provision varies around the world.
Almost all wealthy nations provide universal health care (the US is an exception). Health provision is challenging due to the costs required as well as various social, cultural, political and economic conditions. There isn’t one answer to health care provision, but a number of systems and issues seem to be emerging. This page provides a high level overview. On this page: The health care challenge: services for those with need. Women's Health in the Developing World. While it is clear that both men and women suffer in poverty, gender discrimination means that women have far fewer resources to cope.

The United Nations says they are likely to be the last to eat and are routinely trapped in time-consuming, unpaid domestic tasks. It’s unsurprising, therefore, that women are also the group least likely to access necessary healthcare. Because their voices are rarely heard in decisions on managing an economy or sharing benefits and costs, infrastructure simply doesn’t work for the vast majority of women in the developing world (UN Women). Humanium.org - Health. Infant mortality The global situation of child mortality is dramatic, since a child dies every 4 seconds.
However, solutions do exist and an overwhelming majority of these deaths are easily preventable. Children with HIV/AIDS AIDS is a virus whose impact only increases from year to year. It kills millions of people and does not spare children who are direct victims (children with HIV) or indirect (orphans of AIDS). Suicide of children A sensitive subject whose causes are numerous and sometimes difficult to identify, suicide among children is a taboo phenomenon.
Adolescents Sexuality Adolescence represents a delicate phase in the transition between childhood and adulthood in which young people develop their personality and construct their identity. Children and Addictions Childhood illnesses Childhood is a period when the immune system is still being developed. World Health Organization. International Medical Humanitarian Aid. Death notes: Mapping the world’s mortality - Geographical Magazine. With global life expectancy rising continuously and fertility rates falling steadily, the world’s population is slowly ageing.
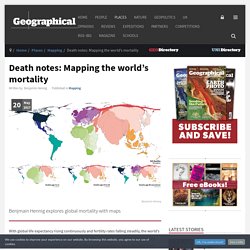
Both trends have led to a shift in the age at which people are dying. In 2015, approximately 8.5 per cent of the world’s population was estimated to be aged 65 and above. The Global Burden of Disease study has become a major milestone project in analysing and better understanding global health trends. It comprises comprehensive datasets about the causes and ages of mortality and their geographical distribution. Among the positive findings of the most recent study, published in 2015, was a ten-year rise in global life expectancy between 1980 and 2015, and a decline in deaths due to infectious and nutritional causes as well as maternal and child deaths. While overall trends look positive, problematic developments can be observed in regions affected by conflicts.
These patterns change gradually when looking at mortality of young adults (age 25 to 29). The top 10 causes of death. Of the 56.9 million deaths worldwide in 2016, more than half (54%) were due to the top 10 causes. Ischaemic heart disease and stroke are the world’s biggest killers, accounting for a combined 15.2 million deaths in 2016. These diseases have remained the leading causes of death globally in the last 15 years. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease claimed 3.0 million lives in 2016, while lung cancer (along with trachea and bronchus cancers) caused 1.7 million deaths.
Diabetes killed 1.6 million people in 2016, up from less than 1 million in 2000. Deaths due to dementias more than doubled between 2000 and 2016, making it the 5th leading cause of global deaths in 2016 compared to 14th in 2000. Lower respiratory infections remained the most deadly communicable disease, causing 3.0 million deaths worldwide in 2016. Road injuries killed 1.4 million people in 2016, about three-quarters (74%) of whom were men and boys. Leading causes of death by economy income group.
Australian Charity ending avoidable blindness. Australian Doctors International - Volunteer Doctors in PNG. Dramatic health learning > Anglican Overseas Aid. Our ‘Towards Abundant Life’ program in Mozambique aims to build community resourcefulness to reach their health and wellbeing goals.

ANCP Program Manager, Vanessa Little, recently witnessed how the project was positively changing the way couples approach family planning. The Equipa de Vida volunteers share their health knowledge with their communities. Family planning is not usually a primary focus in our projects, however the Towards Abundant Life program, funded through the Australian Government’s ANCP matching grant program, gives the community the freedom to tackle health issues that they feel are important. Speaking to the women in the region of Nampula about the work, Vanessa could clearly see that the positive impact of family planning education extends beyond just the lives of women; it also strengthens their families and the community as a whole. Actors in a theatre performance led by an Equipa de Vida team demonstrate family planning principles. “It was quite a show! Malaria. Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites.
The parasites are spread to people through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes, called "malaria vectors. "