

Ancient Egypt - Gods, Pyramids, Mummies, Pharaohs, Queens, Hieroglyphics, History, Life in Ancient Egypt, Maps. The Cuneiform Writing System in Ancient Mesopotamia: Emergence and Evolution. Activity 1.

HISTORY OF MESOPOTAMIA. Between the rivers: 4500-3100 BC From about 4500 BC there are settlements on the edges of the marshes where the Tigris and the Euphrates reach the Persian Gulf.
Mesopotamia, the region between these two rivers, will be the area of one of the world's first two civilizations, the other being Egypt. Both are established a little earlier than 3100 BC. Unlike Egypt, where a stable society is established along hundreds of miles of the Nile, Mesopotamia will be characterized by constant warfare and a succession of shifting empires. Towns here shelter within thick protective walls. Sumer and Gilgamesh: 3100-2500 BC. Encyclopedia Britannica. History of Mesopotamia, history of the region in southwestern Asia where the world’s earliest civilization developed.
The name comes from a Greek word meaning “between rivers,” referring to the land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, but the region can be broadly defined to include the area that is now eastern Syria, southeastern Turkey, and most of Iraq. The region was the centre of a culture whose influence extended throughout the Middle East and as far as the Indus valley, Egypt, and the Mediterranean. This article covers the history of Mesopotamia from the prehistoric period up to the Arab conquest in the ... (100 of 43,476 words) <ul><li><a href="/EBchecked/media/2341/Sites-associated-with-ancient-Mesopotamian-history? TopicId=376828"><img src=" alt="Mesopotamia, history of" /><span>Sites associated with ancient Mesopotamian history.
Mesopotamia. The Money of Ancient Mesopotamia. Money is used to exchange goods.
If you have something I want, I can offer you money or gold or whatever for it. If you agree that the value is right, you take my money and give me the object. What I give you as money may be either symbolic, valuable, or some combination. In ancient Mesopotamia, what was used as money had a value of its own. Paper money is highly symbolic because the paper isn't useful for anything else and it represents a monetary value many, many times the value of the paper and ink. Ancient Mesopotamia. History - Ancient History in depth: Mesopotamia. Early Dynastic Mesopotamia. Around 2900 BC, after the flood, comes a time period called Early Dynastic, which lasts for about 600 years (there is a good deal of disagreement).
Mesopotamia through Shakespeare. Religion in Ancient Mesopotamia. Religion in Ancient Mesopotamia The people of Mesopotamia were polytheistic and believed that every aspect of their world was controlled by supernatural forces.
The great gods dominated religion in ancient Mesopotamia and many gods maintained their importance throughout the region's history. Cities and kingdoms were believed to be protected by individual gods and it was the duty of the ruler to act on the god's behalf, building temples and performing ceremonies to gain their blessings. Each person had his or her own personal gods (male and female) and smaller shrines have been discovered, for example at Ur, where ordinary people worshipped. Personal gods or major deities and could withdraw their support, which would lead to misfortune for the individual or even the entire kingdom. Mesopotamia. Ancient Civilization Contributions and Accomplishments - Birth of a City - Sumerian Art - Religion in Mesopotamia - Music - Writing Contributions of Mesopotamia Artifact - An artifact is a product of a particular time and place, more than that it represents the IDEAS and TECHNOLOGY of a particular civilization.

When does an artifact become art? - Art engages us emotionally or intellectually A piece of art should MOVE us, Tolstoy said it should INFECT us Many examples of artifacts are not what we'd call art in our society... yet when we look at these artifacts they make us think...and wonder...about the culture that produced it. Sumerian Accomplishments We know from relieve sculptures dating to 850 BC that the Sumerians were capable of using the wheel. Mesopotamia - LookLex Encyclopaedia. Mesopotamia's fame in world history relates to it being one of the cradles of civilization, it is by many considered home to the very first civilization in history, predating even Ancient Egypt.
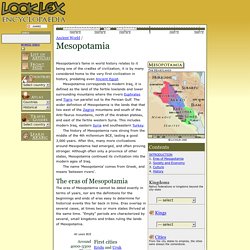
Mesopotamia corresponds to modern Iraq, it is defined as the land of the fertile lowlands and lower surrounding mountains where the rivers Euphrates and Tigris run parallel out to the Persian Gulf. The wider definition of Mesopotamia is the lands that that lies west of the Zagros mountains and south of the Anti-Taurus mountains, north of the Arabian plateau, and east of the fertile western Syria. This includes modern Iraq, eastern Syria and southeastern Turkey. Mesopotamia: Sailboats, Wheels, Cuneiform Writing. Ancient Mesopotamia. Collapse: Mesopotamia. Mesopotamia was known as the land between two rivers, the Tigris to the north and the Euphrates to the south.
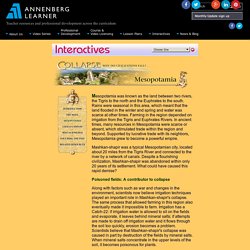
Rains were seasonal in this area, which meant that the land flooded in the winter and spring and water was scarce at other times. Farming in the region depended on irrigation from the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. In ancient times, many resources in Mesopotamia were scarce or absent, which stimulated trade within the region and beyond. Supported by lucrative trade with its neighbors, Mesopotamia grew to become a powerful empire. Mashkan-shapir was a typical Mesopotamian city, located about 20 miles from the Tigris River and connected to the river by a network of canals. Religion of Mesopotamia. Fast Facts About Mesopotamia | Mesopotamian Religion We can only speculate about early religion.
Mummies - Death and the Afterlife in Ancient Egypt. The British Museum of London, England, has the largest and most comprehensive collection of ancient Egyptian material outside of Cairo. Its spectacular collection consists of more than 100,000 objects. Displays include a gallery of monumental sculpture and the internationally famous collection of mummies and coffins. Egyptian objects have formed part of the collections of the British Museum since its beginning. The original start of the Museum was to provide a home for objects left to the nation by Sir Hans Sloane when he died in 1753, about 150 of which were from Egypt. European interest in Egypt began to grow in earnest after the invasion of Napoleon Bonaparte in 1798, particularly since Napoleon included scholars in his expedition who recorded a great deal about the ancient and mysterious country.
Queen Cleopatra VII - Last Pharaoh of Egypt. "For (as they say) it was not because her [Cleopatra's] beauty in itself was so striking that it stunned the onlooker, but the inescapable impression produced by daily contact with her: the attractiveness in the persuasiveness of her talk, and the character that surrounded her conversation was stimulating. It was a pleasure to hear the sound of her voice, and she tuned her tongue like a many-stringed instrument expertly to whatever language she chose.... " From Plutarch's Life of Mark Antony She may not have been an Egyptian, but she was Egypt's queen, ruling on her own rather than in the name of her husband.
Her relationships with the leaders of Rome led to scandals. History - Ancient History in depth: Akhenaten and the Amarna Period. Giza 3D. Important Facts about Cleopatra. This is part of a series (study guide) on the legendary Egyptian queen Cleopatra. On this page you'll find basic facts -- like her birthday and names of members of her family. The Cleopatra Study Guide: Overview | Important Facts | Study Questions | What Did Cleopatra Look Like? | Pictures | Timeline | Terms. Museum of Science : Ancient Egypt Science & Technology. Science and Technology in Mesopotamia (Mathematics, Astronomy and Astrology, and Medicine)
Mesopotamians are probably best known for invention of writing but their achievements in science and technology correspond to the level of socioeconomic development and are comparable with achievements of modern society. Harsh weather and environmental conditions required artificial irrigation, while construction of irrigation systems and building activities greatly influenced the development of mathematics. History: Egyptians. National Geographic. Writer Carl Hoffman traveled to Egypt in February 2011, a week after popular demonstrations led to the president's resignation. These are his observations. Tourism is Egypt’s second largest source of revenue, bringing in $13 billion in 2010. Egypt's ancient royalty used serious weapons - Technology & science - Science - LiveScience. Elite members of ancient Egypt, including the pharaoh himself, likely wielded ornate daggers, swords and axes in battle, or to personally execute prisoners, rather than using the shiny metal for ceremonial purposes, research suggests.
The weapons were used during the Bronze Age, a period between 5,000 and 3,000 years ago when the civilization was at its height, according to Daniel Boatright, an Egyptologist at Isle of Wight College in the United Kingdom. This finding is "strange considering the amount of literature that's been composed so far that basically says that all of them were for ritualistic purposes and were never used in battle," Boatright told LiveScience. Royalty are known to have gone into battle. Egypt: Science, Math, and Technology. Welcome to Living in Ancient Egypt. More Breeds Added! If you have any comments or ideas? Or need any kind of information about Ancient Egypt, please I'll be glad to help you! Webrings. Egypt Cult of the Sun God and Akhenaten's Monotheism. The Nile's Impact on Ancient Egypt.
Although most historians and geographers find it difficult to agree on many aspects of the Nile, including its length and source, virtually everyone acknowledges that Ancient Egypt could never have existed without the great body of water. Pyramid of Snefru at Maidum. Builder of several pyramids, Pharaoh Snefru, secured access to monument-building stone via military victories outside Egypt.
NOVA Online/Pyramids/Ancient Egypt. There are days when the sand blows ceaselessly, blanketing the remains of a powerful dynasty that ruled Egypt 5,000 years ago. Ancient Egypt. Egypt - History - From Ancient Times to the Modern Period. History - Ancient History in depth: Ancient Egypt and the Modern World. Ancient Egyptian Gods. Ancient Egyptians as Experts in Geometry.
What's Sacred About Geometry? The Egyptians desired to create harmony in everything around them. The Stargazers of Ancient Egypt. Introduction to Ancient Egypt. Best Ancient Egypt Maps ~ Ancient Egypt Facts. Making an Ancient Egyptian Mummy. Making an Ancient Egyptian Mummy. Discover the Egyptians. Ancient Egypt Timeline and Lesson Plans: Timeline of the Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, and the New Kingdom.