

National Curriculum. History exemplification standards file level 3 | History | Standards Files | Exemplification for fou History exemplification standards file level 3 | History | Standards Files | Exemplification for foundation subjects | Assessment | Key stages 3 & 4 | National Curriculum Access Key Definitions Skip navigation Access key details Home page Latest updates Site map Search Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Terms and conditions The DfE is conducting a review of the primary and secondary National Curriculum.
This site contains the statutory programmes of study for National Curriculum subjects which maintained schools must follow until… QCDA Last update: 2011. Personal, Learning and Thinking Skills at Key Stage 3 - Thirty lesson plans with activities and assessment. Introduction The introduction includes information on: how this resource works how to teach personal, learning and thinking skills step-by-step guidance on what you need to think about before getting started.
Keystage History - Advice for teaching history, lessons, planning and resources for Key Stage history at KS1, KS2, KS3 and GCSE. RSA Opening Minds. Personal%20Learning%20and%20Thinking%20Skills%20Guidance.pdf. HISTORICAL THINKING CONCEPTS. The Historical Thinking Project works with six distinct but closely interrelated historical thinking concepts.

To think historically, students need to be able to: Establish historical significance Use primary source evidence Identify continuity and change Analyze cause and consequence Take historical perspectives, and Understand the ethical dimension of historical interpretations. Taken together, these concepts tie “historical thinking” to competencies in “historical literacy.” In this case, “historical literacy” means gaining a deep understanding of historical events and processes through active engagement with historical texts.
Historically literate citizens can assess the legitimacy of claims that there was no Holocaust, that slavery wasn't so bad for African-Americans, that aboriginal rights have a historical basis, and that the Russian experience in Afghanistan serves as a warning to the Canadian mission there. National Curriculum Key Stage 3. Publication date: 6th August 2014 National Curriculum Key Stage 3 The latest version of the National Curriculum was published by the Department of Education in July 2013 and is expected to be implemented from September 2014 (although free schools and academies, like independent schools, can choose to devise their own curriculum).
Details of the curriculum itself can be found here. The 2014 curriculum has no prescribed attainment target or level descriptors. Advice from the HA on assessment and planning for progression can be found here. General advice on curriculum design and planning schemes of work within the new Key Stage 3 curriculum can be found here. Resources relating to the following areas can be found here: National curriculum in England: history programmes of study. Purpose of study A high-quality history education will help pupils gain a coherent knowledge and understanding of Britain’s past and that of the wider world.

It should inspire pupils’ curiosity to know more about the past. Teaching should equip pupils to ask perceptive questions, think critically, weigh evidence, sift arguments, and develop perspective and judgement. Learning Concept Map. Learning Topics Learning Concept Map Click on a desired topic on the below concept map or use the topic list on the left.
More Learning Concepts Informal/Formal Learning — Social Learning & Media — Blended Learning — The Three Representational Modes: Linguistic Learning, Nonlinguistic Learning, and Affective Learning — Self, Metacognition, Cognition, and Knowledge Systems — Interactive Mindmap of Learning Models — Cognitive Task Analysis — A Table of Five Design Models Notes. Study History. Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy (text-only) – Center for Excellence in Learning and Teaching. Go back to main Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy page.
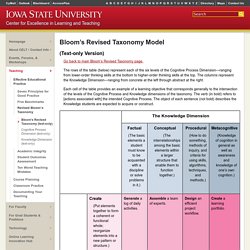
The rows of the table (below) represent each of the six levels of the Cognitive Process Dimension—ranging from lower-order thinking skills at the bottom to higher-order thinking skills at the top. The columns represent the Knowledge Dimension—ranging from concrete at the left through abstract at the right. Each cell of the table provides an example of a learning objective that corresponds generally to the intersection of the levels of the Cognitive Process and Knowledge dimensions of the taxonomy. The verb (in bold) refers to [actions associated with] the intended Cognitive Process. The object of each sentence (not bold) describes the Knowledge students are expected to acquire or construct. Go back to main Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy page.