

Delphi method. The Delphi method (/ˈdɛlfaɪ/ DEL-fy) is a structured communication technique, originally developed as a systematic, interactive forecasting method which relies on a panel of experts.[1][2][3][4] The experts answer questionnaires in two or more rounds. After each round, a facilitator provides an anonymous summary of the experts’ forecasts from the previous round as well as the reasons they provided for their judgments. Thus, experts are encouraged to revise their earlier answers in light of the replies of other members of their panel.
It is believed that during this process the range of the answers will decrease and the group will converge towards the "correct" answer. Finally, the process is stopped after a pre-defined stop criterion (e.g. number of rounds, achievement of consensus, stability of results) and the mean or median scores of the final rounds determine the results.[5] History[edit] The name "Delphi" derives from the Oracle of Delphi. Key characteristics[edit] The Delphi Method: Techniques and Applications. The mind is but a barren soil; a soil which is soon exhausted, and will produce no crop, or only one, unless it be continually fertilized and enriched with foreign matter. -Sir Joshua Reynolds Reality is a name we give our collections of tacit assumptions about what is. We bring along these realities to give meaning to our interactions. Each of us maintains several of these realities--at least one for every significant set of others in our lives. We have domestic realities, parental-family realities, professional realities, sexual realities, organizational realities, stylistic realities....
Realities can be described as presumed agreements which give meaning to our thoughts and make reasonable our actions in each setting. I believe with others that there is nothing more practical than good theory. Another problem with examples is that they represent only a small fraction of the myriad of potential applications for this approach to Delphi inquiry. Real-time Delphi. Real-time Delphi (RTD) is an advanced form of the Delphi method.
The advanced method “is a consultative process that uses computer technology” [1] to increase efficiency of the Delphi process. Definition and idea[edit] Gordon and Pease [2] define the advanced approach as an innovative way to conduct Delphi studies that do not involve sequential “rounds” and consequently lead to a higher degree of efficiency with regard to the time frame needed to perform such studies. Friedewald, von Oertzen, and Cuhls [3] underline that aspect by writing, in “a Real-Time-Delphi, the participants do not only judge twice but can change their opinion as often as they like when they see the aggregated results of the other participants”. So, here it becomes clear that the Real-Time Delphi approach requires real-time calculation and provision of group responses. History[edit] Idea Management - Innovation Management - Crowdsourcing - Suggestion Box - Customer Feedback Software.
Kindling - Idea Management and Collaboration. LiquidFeedback - more than Liquid Democracy. Abaque de Régnier. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
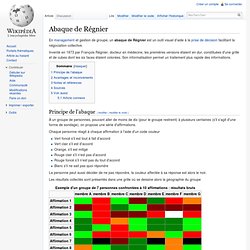
En management et gestion de groupe, un abaque de Régnier est un outil visuel d'aide à la prise de décision facilitant la négociation collective. Inventé en 1973 par François Régnier, docteur en médecine, les premières versions étaient en dur, constituées d'une grille et de cubes dont les six faces étaient colorées. Son informatisation permet un traitement plus rapide des informations. Principe de l'abaque[modifier | modifier le code] À un groupe de personnes, pouvant aller de moins de dix (pour le groupe restreint) à plusieurs centaines (s'il s'agit d'une forme de sondage), on propose une série d'affirmations. Collaborative Decision-Making. A Taxonomy of Ideas?
Novago - système de management des idées, portail. Arbre de connaissances. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
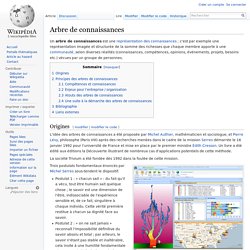
Un arbre de connaissances est une représentation des connaissances ; c'est par exemple une représentation imagée et structurée de la somme des richesses que chaque membre apporte à une communauté, selon diverses réalités (connaissances, compétences, opinions, événements, projets, besoins etc.) vécues par un groupe de personnes. Origines[modifier | modifier le code] La société Trivium a été fondée dès 1992 dans la foulée de cette mission. Exemple d'intégration des arbres de connaissances dans un outil décisionnel spécifique aux ressources humaines Trois postulats fondamentaux énoncés par Michel Serres sous-tendent le dispositif. Postulat 1 : « chacun sait » : du fait qu'il a vécu, tout être humain sait quelque chose ; le savoir est une dimension de l'être, indissociable de l'expérience sensible et, de ce fait, singulière à chaque individu.
Informations sur les arbres de connaissances.