

Truth. Truth is most often used to mean being in accord with fact or reality,[1] or fidelity to an original or to a standard or ideal.[1] The commonly understood opposite of truth is falsehood, which, correspondingly, can also take on a logical, factual, or ethical meaning.
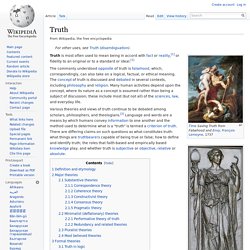
The concept of truth is discussed and debated in several contexts, including philosophy and religion. Many human activities depend upon the concept, where its nature as a concept is assumed rather than being a subject of discussion; these include most (but not all) of the sciences, law, and everyday life. Definition and etymology[edit] Certainty. Certainty is perfect knowledge that has total security from error, or the mental state of being without doubt.
Objectively defined, certainty is total continuity and validity of all foundational inquiry, to the highest degree of precision. Something is certain only if no skepticism can occur. Philosophy (at least historical Cartesian philosophy) seeks this state. Epistemology. A branch of philosophy concerned with the nature and scope of knowledge Epistemology (; from Greek ἐπιστήμη, epistēmē, meaning 'knowledge', and -logy) is the branch of philosophy concerned with the theory of knowledge.

Epistemology is the study of the nature of knowledge, justification, and the rationality of belief.