

The Century: America's TIme - 1929-1936: Stormy Weather. The impact of the Depression on Germany. America9. 3.

Determined Opposition (BRASS) a Businessmen hated the New Deal because it interfered with their businesses and supported workers’ rights. Rich people accused Roosevelt of betraying his class. Henry Ford hired thugs to attack his trade union workers. b Republicans hated the expenditure, which they said was wasteful (‘boondoggling’ – jobs for the sake of jobs). C Activists like Huey Long (Senator for Louisiana who started a Share the Wealth’ campaign to confiscate fortunes over $3m) and Francis Townsend (who campaigned for a pension of $200 a month) said it did not go far enough. Lesson: Choices in Weimar Republic Elections. This lesson complements the resources from Chapter 4 of Holocaust and Human Behavior to help students investigate some of the choices available to Germans in elections in the early 1930s and understand the variety of reasons many Germans supported the Nazi Party.
After analyzing the platforms of three Weimar political parties—the Social Democrats, the Communists, and the Nazis—students will read short biographies of several German citizens. Using details from the biographies, the party platforms, and any information they have learned before this lesson about the Weimar Republic, students will then determine which political party they believe each citizen would have supported. The citizen biographies are fictional and were created for this lesson, in part to provoke discussion and reasoned argument; determining which party each individual would have supported is not always easy, and there is no correct answer.
Which Political Party 0. 7. The Wall Street Crash - How did it affect Germany? New Deal in California Teacher Resources. Digital History. Teacher Resources.

PBS Presentation: The Great Depression. Stories from the Great Depression. Why did Nazis come to power? This German election poster from 1930 says, “Work, Freedom, and Bread–Vote National Socialist!
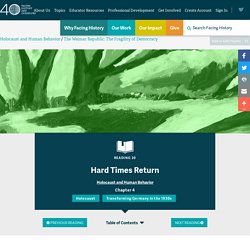
" German leaders, like their counterparts in other countries, looked for ways to end the depression. And like other leaders in 1929, they failed. The chancellor of the Weimar Republic that year was Hermann Müller, a Social Democrat. When he was unable to steer the country toward prosperity, President Paul von Hindenburg named a new chancellor a year later. This time, he chose Heinrich Brüning of the Catholic Center Party. Brüning convinced President Hindenburg to invoke Article 48 (see reading, Creating a Constitutional Government) to suspend the constitution so that the chancellor would be able to act quickly and decisively, without consulting the Reichstag, to address the severe economic crisis. To an increasing number of Germans, democracy appeared unable to cope with the economic collapse, and only the most extreme political parties seemed to offer clear solutions to the crisis.
Primary source Consequences Great Depression in Germany. In October of 1929, a worldwide depression began.
A depression is a severe economic downturn that forces businesses to decrease production and lay off workers. Germany felt the effects of the depression almost immediately. By 1932, 6 million Germans were unemployed in a nation of about 60 million people. Among them were Lea Langer Grundig, who was a Communist, and her husband, Hans. Like other job seekers, they stood in long lines at labor exchanges day after day: Lesson: The Weimar Republic: Historical Context and Decision Making. Overview To deepen your understanding of the ideas in this lesson, read Chapter 4 of Holocaust and Human Behavior.
Adolf Hitler did not gain power by a military coup; he gained power primarily through lawful means. How did this happen? Nazi revision (final).59935452. Digital History. Depression-Era Photographs: Worth a Thousand Words. Activity 1.
Work Progress Administration Introduce students to the Works Progress Administration (WPA) and its mission during the Great Depression. Established in 1935 as part of the New Deal, the WPA hired unemployed individuals for public works projects ranging from ditch-digging to producing plays. Though sometimes attacked as a "make work" program, the WPA is now credited with helping to stimulate recovery from the Depression by pouring billions of dollars into the national economy in the form of consumer purchasing power. Activity 2. World History Lesson 91 Great Depression. Calisphere: The Great Depression, 1929-1939. De crisisjaren: Samenleving in depressie. De jaren 1929-1940 worden meestal aangeduid als 'de crisisjaren' of als 'de grote depressie': een lange periode van krimp in de economie en van grote werkloosheid.
De crisis begon in oktober 1929 in de Verenigde Staten na de 'Beurskrach' en kreeg al snel de hele wereld in haar greep. Het aantal werklozen in Nederland bedroeg in 1930 circa 150.000 en kwam in 1935 op een hoogtepunt van bijna 600.000. Daarna daalde de werkloosheid wel enigszins, maar tot in de oorlog bleef het aantal werklozen boven de 350.000. Het was voor het eerst dat werkloosheid in Nederland zo'n omvang had bereikt en zo lang duurde. Van elke vier Nederlandse arbeiders was er één langer dan een jaar werkloos. De regering besloot de werklozen een financiële ondersteuning te geven. De regering Colijn koos er verder voor om de hand zoveel mogelijk op de knip te houden. Na de Tweede Wereldoorlog ontstonden er nieuwe ideeën over de aanpak van het werkloosheidsprobleem.
Life on the Plains - Remembering the Dust Bowl and Great Depression. Interviews with Survivors of the Great Depression. Stories from the Great Depression. BBC2 Documentary 1929 The Great Crash 1929. Adolf Hitler, Nazis come to power through the Great Depression. German Economy in the 1920s. German Economy in the 1920s By Daniel Castillo (author page), Dec. 2003 There were several characteristics which Germany possessed after the First World War which made them vulnerable to being manipulated by someone like Adolf Hitler.

As in most nations, the economic factors of the time play a significant role in determining how a society will behave. Germany was economically devastated after a draining defeat in World War I. Due to the Versailles treaty, Germany was forced to pay incredibly sizeable reparations to France and Great Britain. At first Germany tried to recover from the war by way of social spending. Even with all of Germany's economic shortcomings, it could have still been possible to make reparation payments if foreign countries had not placed protective tariffs on Germany's goods.
With Germany at its weakest and most vulnerable point, Hitler took the opportunity to begin his ascent to power. Hitler had two significant ideas that helped launch him in to power. The impact of the Great Depression on Germany. Weimar Republic. The webserver at Alpha History tells us you’re using an adblocking tool, plug-in or browser extension on your computer or network.
We understand that many people don’t like web-based advertising. Ads on websites can often be irrelevant, distracting and ‘in your face’. Without ads, however, our website would not exist – or it would not be free. Ads are how we fund the creation and delivery of our content. We love providing free textbook-quality content and resources to people like you.
If you would like to use our website and its resources, please disable your adblocker or whitelist our website. To access the Alpha History website, please complete one of the following steps: * Disable or deactivate your adblocking software, tool or plug-in. 10+ images about Great Depression - Teaching Resources on Pinterest. The Great Depression – Best of History Web Sites. Great Depression in the News “How does Obama’s economic policy compare to FDR’s?” – Star Exponent, January 5, 2011. The great depression resources. FED teaching resources Great Depression. Economic Episodes in American History: The Great Depression David Wheelock, vice president and deputy director of Research, gave a presentation on “The Great Depression” on July 11, 2013, as part of an economic education workshop at the Federal Reserve Bank of St.
Louis. Overview - The Great Depression - Themed Resources.