

The Science Behind Foldit. Scientists Decode Thought into Language. What's the Latest Development?
Scientists have taken the first steps toward decoding our thoughts into language. By observing which parts of the brain respond to specific sounds, neuroscientists at UC Berkeley were able to reverse engineer our ideas into spoken words. "The team monitored the brain waves of 15 patients who were undergoing surgery for epilepsy or tumours, while playing audio of a number of different speakers reciting words and sentences.
" They then used a computer model to tell them which brain regions were firing when different sounds were played. What's the Big Idea? This research represents the latest step in our ability to bridge the gap between a purely physical understanding of the brain and knowing how it affects real world phenomena like image and sound. Photo credit: shutterstock.com. Perception of Science: in popular culture vs. actual science - Lounge of the Universe Cafe. Ariel Garten: Know thyself, with a brain scanner. NextNature.net – Exploring the Nature caused by People.
Tracy Metz – Nature is an Agreement « NextNature.net. Cancer. Infectious Diseases. Babies with three parents possible within three years. It came as the Department of Health ordered a public consultation on whether the technology should be moved from the lab to patients, which will be followed by a Commons debate on the ethics of the issue.
The Health Secretary has the power to lift the regulations and if both the scientific and political criteria are satisfied, the therapy could be trialled in humans within two to three years. The research is aimed at tackling diseases passed down through families via mutated mitochondria, structures which supply power to cells. Although 99.8 per cent of our DNA, including all our visible characteristics, is inherited evenly from our father and mother and stored in the nucleus of cells, a tiny fraction resides in the mitochondria and is passed down only by the mother. Faults in the mitochondria affect about one in 200 children in Britain each year, causing severe and incurable diseases such as muscular dystrophy or ataxia in about one in 6,500 people.
Learn.Genetics™ Infrared Image Shows Helix Nebula in Fresh Light. The nearby Helix nebula just received the piercing infrared gaze of a giant telescope in Chile, and the resulting image reveals cold gas normally hidden among warmer star-lit material.
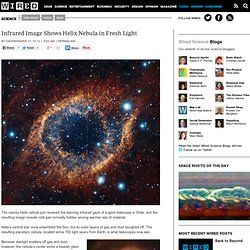
Helix’s central star once resembled the Sun, but its outer layers of gas and dust sloughed off. The resulting planetary nebula, located some 700 light-years from Earth, is what telescopes now see. Because starlight scatters off gas and dust, however, the nebula’s center emits a blueish glare in visible light (right). To see inside, astronomers aimed the VISTA telescope at the Paranal Observatory in Chile at the Helix.
The telescope’s sensors picked up on infrared light, a wavelength invisible to the naked eye. The above image released today shows the central region of gas and dust extends at least 4 light years, not 2 light years as was previously thought. Learn.Genetics™ ‘To understand is to perceive patterns’ Cell Size and Scale. Drew Berry: Animations of unseeable biology. The Shorty Awards - Honoring the best of Twitter and social media. To Know, but Not Understand: David Weinberger on Science and Big Data. Why Humans Are So Smart…and Groovy. Mimicking the brain, in silicon. For decades, scientists have dreamed of building computer systems that could replicate the human brain’s talent for learning new tasks.
MIT researchers have now taken a major step toward that goal by designing a computer chip that mimics how the brain’s neurons adapt in response to new information. This phenomenon, known as plasticity, is believed to underlie many brain functions, including learning and memory. With about 400 transistors, the silicon chip can simulate the activity of a single brain synapse — a connection between two neurons that allows information to flow from one to the other. The researchers anticipate this chip will help neuroscientists learn much more about how the brain works, and could also be used in neural prosthetic devices such as artificial retinas, says Chi-Sang Poon, a principal research scientist in the Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology.
Modeling synapses Debate resolved. New Scientist TV: Best videos of 2011: Malaria invades blood cell. Shrimp that lives in water four times hotter than boiling point. Rimicaris hybisae was found 5,000m beneath the Caribbean sea By Gavin Allen Updated: 18:28 GMT, 10 January 2012 A new species of shrimp has been discovered living deeper than any seen before in the world's most extreme deep sea volcanic vents.
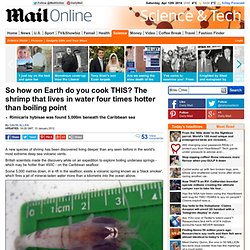
British scientists made the discovery while on an expedition to explore boiling undersea springs - which may be hotter than 450C - on the Caribbean seafloor. Some 5,000 metres down, in a rift in the seafloor, exists a volcanic spring known as a 'black smoker', which fires a jet of mineral-laden water more than a kilometre into the ocean above. No little discovery: Rimicaris hybisae, the world's deepest known vent shrimp, was found at a depth of 5,000 metres. Scientist creates lifelike cells out of metal. Science Bulletins: Earth's Green Carbon Machine. Chronology of Events in Science, Mathematics, and Technology. Synthetic Biology Explained.