

New Version of Blooms Taxonomy for iPad. K-5 iPad Apps to Evaluate Creating: Part Six of Bloom's Revised Taxonomy. In 1948, the Swiss inventor George de Mestral returned from a hike with his dog covered in burs.

After examining how nature designed these clinging bristles under a microscope, it dawned on him that a similar structure could function as a clothing fastener. K-5 iPad Apps for Evaluating Evaluation: Part Five of Bloom's Revised Taxonomy. "Only those evaluations which are or can be made with distinct criteria in mind can be considered"1.

A student can set their own evaluation criteria or use standards given to them. In order for students to exercise this thinking, skill they need have command of strategies that help them set criteria and implement evaluation procedures. Several apps are useful for developing evaluative thinking or aide the evaluation process. Judgments in Terms of Internal Evidence: Checking Bloom divides this cognitive domain into two separate processes. K-5 iPad Apps for Applying: Part Three of Bloom's Revised Taxonomy. Bloom's Revised Taxonomy breaks each learning stage (remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate and create) into four separate levels of knowledge.

These levels include the factual, conceptual, procedural, and metacognitive. Together the levels of knowledge are making incremental movements from a factual understanding, to the personal command and realization of the learning process. The revised taxonomy also lists two cognitive processes within the applying stage: executing and implementing.1 These two processes illustrate the range of thinking skills possible within a stage. Executing requires the application of factual knowledge and refers to the ability to carry out learned procedures such as solving a long division problem. K-5 iPad Apps for Understanding: Part Two of Bloom's Revised Taxonomy. Benjamin Bloom's second stage, "understanding" occurs when new learning connects to prior knowledge.
At this point, students have the ability to make sense of what they have read, viewed, or heard and can explain this understanding clearly and succinctly to others. This particular learning stage balances precariously between communicating understanding and expressing opinion. Here the student demonstrates the ability to identify the main idea, generalize new material, translate verbal content into a visual form, transform abstract concepts into everyday terms, or make predictions. Writing and speaking are the most common way teachers "check for understanding," but mobile technology is helping to break this traditional mold.
K-5 iPad Apps According to Bloom's Taxonomy. An elementary library media specialist reviews iPad apps as they map to an updated version of Bloom's Taxonomy in this six-part series.
Diane Darrow is an artist, Reading Recovery teacher, and library media specialist at Bel Aire Elementary in Tiburon, CA. You can follow her on Twitter at @dianedarrow. In this six-part series, I will highlight apps useful for developing higher order thinking skills in grades K-5 classrooms. Each list will highlight a few apps that connect to the various stages on Bloom's continuum of learning. Given the size and current exponential growth of the app market, I will also assist educators in setting criteria necessary to identify apps that maintain the integrity of teaching for thinking.
Part One: K-5 iPad Apps for Remembering Part Two: K-5 iPad Apps for Understanding Part Three: K-5 iPad Apps for Applying. Bloomin' Apps. This page gathers all of the Bloomin' Apps projects in one place.Each image has clickable hotspots and includes suggestions for iPad, Android, Google and online tools and applications to support each of the levels of Bloom's Revised Taxonomy.I have created a page to allow you to share your favorite online tool, iOS, or Android app with others.
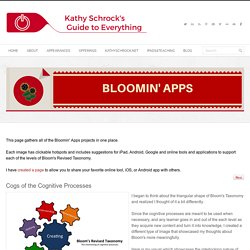
Cogs of the Cognitive Processes. Do students need to learn lower-level factual and procedural knowledge before they can do higher-order thinking? There is a prevailing conception that students must learn facts and procedural knowledge BEFORE they can then engage in so-called ‘higher-order’ thinking skills. Educators, parents, policymakers, online commentators, and others point to Bloom’s taxonomy (which typically has been portrayed as a pyramid) and say, “See? You have to do this stuff down here before you can do that stuff up top!” But that’s not how Bloom and his co-authors categorized the taxonomy: Bloom et al. discussed at length their decision to apply an Aristotelian categorization method in their taxonomy. The choice was significant, because an Aristotelian method creates distinct, bounded categories ordered by complexity without the hierarchical assumption that higher-level categories always entail instantiation of those lower in the taxonomy (e.g., when evaluating, it is not always necessary to first apply and synthesize).
Similarly, as the National Research Council stated a quarter-century ago: A Whole New Bloom ECC.png 1,190×768 pixels. A Whole New Bloom. Rethinking how students learn. I've started reading a new book in the past couple of days and already I have so many new things to think about!
The book is entitled 21st Century Skills - Rethinking How Students Learn and is edited by James Bellanca and Ron Brandt. In the preface to the book Ron Brandt explains why a focus on skills is so important. He writes "effective teaching involves students using skills to acquire knowledge" and explains how important it is that these skill are embedded into the curriculum and taught along with content. Visual Art as Critical Thinking. We've heard this story before.
The first thing to go in budget cuts is the visual art program or another related art. Proponents of arts education counter with the usual rhetoric on the importance of self-expression and creativity. I, myself, am a product of arts education. From the early age of kindergarten I was in musical theater. Understanding Creative Thinking And Critical Thinking.
By admin on October 24th, 2011 Understanding Creative Thinking And Critical Thinking The mind is a mysterious and magical thing, and the thought process is the same. Many people do not realize that there are two particular types of thinking, but most types of thoughts can be categorized as either creative or critical. “Creativity masters a process of making or producing, criticality a process of assessing or judging,” and this is a main difference between critical thinking and creative thinking (Paul & Elder, 2006, p.35, pp.6). There is a difference between being a critical thinker and a creative thinker, but good thinking requires both. Critical thinking may not sound like much fun, but it is important to the thought process. Recognizing 21st century learners. By: Rida Afrilyasanti 21st century learners Responding to the globalization era, schools need to expand what the schools are teaching to keep pace with the demands of our modern workforce and societal needs.

This is in line with Spencer’s (2010:1) enlightenment that the world is less static, collaboration is vital, and learning is a continual process. The environment in which students are exposed to is media rich, immediate, fast, engaging, dynamic and instant. Therefore, teachers should be able to enable their students to acquire skills needed in this current century. Furthermore, to meet the needs in globalization era, students have to acquire 21st century skills. 21st century learning. Text, Images, Music and Video. Bloomsapps. Using Blooms Taxonomy in education is a highly effective way to scaffold learning for the students.

With the recent popularity and pervasive nature of iOS devices in school districts it is essential for educators to understand how to implement Blooms in the classroom using the apps that are available. While this list is by no means fully comprehensive, it will assist educators in getting started when implementing iOS devices in the classroom. This site will change almost daily as it will be updated with new and exciting apps! If you find any that you have worked with in your classroom please email dmileham@e1b.org or tweet @bloomsapps or @dmileham75 with your suggestions. SOLO taxonomy. I am pleased to say that John Biggs himself has endorsed this representation of his ideas; "I've just found your website on SOLO et al. via google. Andy McPhee. Bloom’s Taxonomy was developed by Benjamin Bloom (right) and a team of other cognitive psychologists at the University of Chicago in the mid-1950s.
Of course, you knew that already. Healthcare educators have been using Bloom’s taxonomy for decades to build goals and objectives. The original levels cited by Bloom inlcude — come on, recite them with me now — knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. VisualBlooms - HOME. Blooming Google! Blooming Google. iLearn Technology. Tomorrow I am doing a training on the Treasures Supplement that I created over the summer.