

Map: Where carbon emissions are the greatest. When you map carbon dioxide emissions in the atmosphere around the world, the result is very similar to population density — which makes sense, since human activity is the overwhelming source of fossil fuel emissions.
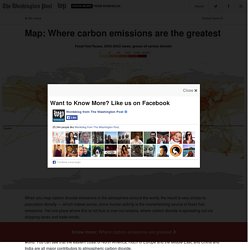
Yet one place where this is not true is over our oceans, where carbon dioxide is spreading out via shipping lanes and trade winds. This map by Kennedy Elliott of The Washington Post uses data from the Earth System Research Laboratory of the National Oceanic and Atmosphere Administration to chart the levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide around the world. You can see that the eastern coast of North America, much of Europe and the Middle East, and China and India are all major contributors to atmospheric carbon dioxide. But many of the world’s biggest shipping routes, especially in East Asia and between Europe and the U.S., show up as surprisingly polluted, given their location.
For an interactive version of the map, look below or click here. What Is Global Warming? Climate Change: Vital Signs of the Planet: Government Resources. NASA is an expert in climate and Earth science.
While its role is not to set climate policy or prescribe particular responses or solutions to climate change, its purview does include providing the robust scientific data needed to understand climate change and evaluating the impact of efforts to combat it. NASA then makes this information available to the global community – the public, policy- and decision-makers and scientific and planning agencies around the world.
(For more information, see NASA's role.) The following selected resources from U.S. government organizations provide information about options for responding to climate change. Data and Information Data related to climate change that can help inform and prepare America’s communities, businesses and citizens. Produced by a team of more than 300 experts and guided by a 60-member Federal Advisory Committee, this report summarizes current and future impacts of climate change on the United States. Individual Action. New Climate Change Report Warns of Dire Consequences.
Global Warming & Climate Change. Nine maps that show how climate change is already affecting the US. Business warned to prepare for catastrophic impacts. PricewaterhouseCoopers, the world's largest professional services firm, is not known for scaremongering.

So it is worth paying particular attention to its latest annual low carbon economy index. Behind the understated language, it points to a catastrophic future unless radical action is taken now to combat climate change. "Business leaders have been asking for clarity in political ambition on climate change," says partner Leo Johnson. "Now one thing is clear: businesses, governments and communities across the world need to plan for a warming world – not just 2C, but 4C or even 6C. " Melting Of Antarctic Ice Sheet Might Be Unstoppable.
Hide captionA NASA photo shows the Thwaites Glacier in West Antarctic.
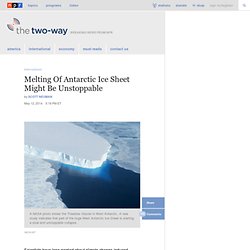
A new study indicates that part of the huge West Antarctic Ice Sheet is starting a slow and unstoppable collapse. A NASA photo shows the Thwaites Glacier in West Antarctic. A new study indicates that part of the huge West Antarctic Ice Sheet is starting a slow and unstoppable collapse. Taking Climate Change Seriously Climate change is about people, not just science and politics -- it is an inter-generational ethics issue.
The earth is the Lord's, and in Genesis, God entrusts us with caring for Creation. The earth that we leave to future generations is already being changed by climate change, and so far, our nation has done little to stop climate pollution. The Clean Power Plan, announced Monday by the EPA, is a great step forward for our country in taking climate change seriously. The policy will treat carbon the way it should be treated -- as a pollutant that's harming our health and our planet. It will reduce our carbon pollution 30 percent below 2005 levels by 2030, but will allow each state the flexibility to decide how it reaches that goal. Climate Change Study Finds U.S. Is Already Widely Affected. The effects of human-induced climate change are being felt in every corner of the United States, scientists reported Tuesday, with water growing scarcer in dry regions, torrential rains increasing in wet regions, heat waves becoming more common and more severe, wildfires growing worse, and forests dying under assault from heat-loving insects.

Such sweeping changes have been caused by an average warming of less than 2 degrees Fahrenheit over most land areas of the country in the past century, the scientists found. If greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane continue to escalate at a rapid pace, they said, the warming could conceivably exceed 10 degrees by the end of this century. “Climate change, once considered an issue for a distant future, has moved firmly into the present,” the scientists declared in a major new report assessing the situation in the United States. “Yes, climate change is already here,” said Richard B. Obama plan to reduce pollution will allow some states to increase emissions. Barack Obama's new power plant rules will still allow some states to increase their share of the carbon pollution that causes climate change, officials admitted for the first time on Wednesday.
Obama and supporters cast the new rules for power plants as an historic step to fighting climate change and protecting public health. But some of the dirtiest and most coal-heavy states – such as West Virginia and Kentucky – will be allowed to maintain or even increase their emissions under the plan, according to analysts. It also hasn't stopped leaders from those same states, West Virginia and Kentucky, from trying to block the rules in Congress or through the courts.
The Environmental Protection Agency, which produced the 645-page regulation, said it was possible individual states could increase their emissions while still meeting the overall target of the plan for a 30% cut in national emissions from 2005 levels by 2030.