

Bible_timeline.gif (GIF Image, 1829x648 pixels) - Scaled (89%) The Bible Timeline Graph.
Customer Reviews: Hearts on Fire: Praying with Jesuits. William James. William James (January 11, 1842 – August 26, 1910) was an American philosopher and psychologist who was also trained as a physician.
The first educator to offer a psychology course in the United States,[2] James was one of the leading thinkers of the late nineteenth century and is believed by many to be one of the most influential philosophers the United States has ever produced, while others have labelled him the "Father of American psychology".[3][4][5] Along with Charles Sanders Peirce and John Dewey, he is considered to be one of the greatest figures associated with the philosophical school known as pragmatism, and is also cited as one of the founders of the functional psychology.
He also developed the philosophical perspective known as radical empiricism. James' work has influenced intellectuals such as Émile Durkheim, W. E. B. Early life[edit] William James was born at the Astor House in New York City. He took up medical studies at The Harvard Medical School in 1864. Pierre Teilhard de Chardin. Achaemenid Empire. The Achaemenid Empire (/əˈkiːmənɪd/; Old Persian: Pārsa;[9][10] New Persian: شاهنشاهی هخامنشی c. 550–330 BC), or First Persian Empire,[11] was an empire in Western and Central Asia, founded in the 6th century BC by Cyrus the Great.[11] The dynasty draws its name from king Achaemenes, who ruled Persis between 705 BC and 675 BC.
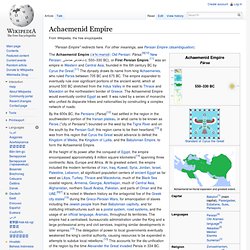
The empire expanded to eventually rule over significant portions of the ancient world, which at around 500 BC stretched from the Indus Valley in the east to Thrace and Macedon on the northeastern border of Greece. The Achaemenid Empire would eventually control Egypt as well. It was ruled by a series of monarchs who unified its disparate tribes and nationalities by constructing a complex network of roads. The historical mark of the Achaemenid Empire went far beyond its territorial and military influences and included cultural, social, technological and religious influences as well.
History[edit] Achaemenid Timeline[edit] Astronomical year numbering. Shia Islam. The Shia (Arabic: شيعة Shīʿah) represent the second largest denomination of Islam and adherents of Shia Islam are called Shias or the Shi'a as a collective or Shi'i individually.[1] Shi'a is the short form of the historic phrase Shīʻatu ʻAlī (شيعة علي) meaning "followers", "faction" or "party" of Muhammad's son-in-law and cousin Ali, whom the Shia believe to be Muhammad's successor in the Caliphate.
Twelver Shia (Ithnā'ashariyyah) is the largest branch of Shia Islam and the term Shia Muslim is often taken to refer to Twelvers by default. Shia Muslims constitute 10-20% of the world's Muslim population and 38% of the Middle East's entire population.[2] Although there are myriad Shi'i subsects, modern Shi'i Islam has been divided into three main groupings: Twelvers, Ismailis and Zaidis.[6][7][8][9] Etymology[edit] Beliefs[edit] Imamate[edit] Succession of Ali[edit] Oh people! Shia Muslims believe this to be Muhammad's appointment of Ali as his successor. Sunni Islam. Sunni Islam (/ˈsuːni/ or /ˈsʊni/) is the largest branch of Islam; its adherents are referred to in Arabic as ahl as-sunnah wa l-jamāʻah (Arabic: أهل السنة والجماعة), "people of the tradition of Muhammad and the consensus of the Ummah" or ahl as-sunnah (أهل السنة) for short.
In English, they are known as Sunni Muslims, Sunnis, and Sunnites. Sunni Islam is the world's largest religious body[1] and largest religious denomination for any religion in the world. Sunni Islam is sometimes referred to as the orthodox version of the religion.[2][3] The word "Sunni" is believed to come from the term Sunnah (Arabic: سنة), which refers to the sayings and actions of the prophet Muhammad as recorded in hadiths.[4] The primary collections consisting of Kutub al-Sittah accepted by Sunni orthodoxy, in conjunction with the Quran and binding consensus, form the basis of all jurisprudence within Sunni Islam.