

Creativity & Problem Solving. Where do ideas come from? Game Mechanics & Design. Game Theory. Games and Game Design with BrainPOP. The Global Education Conference is pleased to announce a new partnership with BrainPOP®, a leading creator of animated, curricular content, to develop a new gaming strand for the 2012 Global Education Conference.

In addition to general session strands for teachers and students on curriculum, policy, and leadership, we are now seeking proposals for the new strand’s game-based learning sessions. The third annual Global Education Conference is an online international education extravaganza, slated to take place November 12-17, 2012. Neurology of Gaming, Infographic « All Kinds of Minds.
As with most things, “gaming” (or being engaged in video games) has both positives and negatives when it comes to developing minds.

Too much gaming, and the positive effects are overshadowed by the negative. Yet, the right balance can add another avenue for pursuing educational goals and achievement. As a result, more and more programs are using gaming to reach and teach students in ways they never could before. Therapy programs, schools, and even research scientists have all benefitted from the strategic use of games to increase successes. Markov chain. A simple two-state Markov chain A Markov chain (discrete-time Markov chain or DTMC[1]), named after Andrey Markov, is a mathematical system that undergoes transitions from one state to another on a state space.
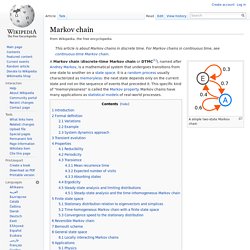
It is a random process usually characterized as memoryless: the next state depends only on the current state and not on the sequence of events that preceded it. This specific kind of "memorylessness" is called the Markov property. Markov chains have many applications as statistical models of real-world processes. Markov chain. SPIEGEL ONLINE - Nachrichten.