

Vitamins, Minerals and Dietary Supplements Guidelines & Reviews. Vitamin - Wikipedia. A vitamin is an organic compound and a vital nutrient that an organism requires in limited amounts.
An organic chemical compound (or related set of compounds) is called a vitamin when the organism cannot synthesize the compound in sufficient quantities, and it must be obtained through the diet; thus, the term "vitamin" is conditional upon the circumstances and the particular organism. For example, ascorbic acid (one form of vitamin C) is a vitamin for humans, but not for most other animal organisms.
Supplementation is important for the treatment of certain health problems,[1] but there is little evidence of nutritional benefit when used by otherwise healthy people.[2] What are vitamins? What vitamins do I need? Vitamins are organic compounds which are needed in small quantities to sustain life.
We need to take vitamins from food because the human body either does not produce enough of them or none at all. Each organism has different vitamin requirements. For example, vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is necessary for humans but not for dogs, because dogs can produce (synthesize) enough for their own needs, while humans cannot. This article explains what vitamins are, what they do, and what foods provide each type. Fast facts on vitamins Here are some key points about vitamins. There are 13 known vitaminsVitamins are either water-soluble or fat-solubleFat-soluble vitamins are easier for the body to store than water-solubleVitamins always contain carbon, so they are described as "organic" What are vitamins? A vitamin is one of a group of organic substances, present in minute amounts in natural foodstuffs; they are essential to normal metabolism. Shop -
VITAMIN E: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions and Warnings ... Vitamins: MedlinePlus. Vitamin A - Wikipedia. This article is about the family of vitamers.
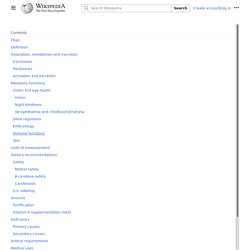
For the form usually used as a supplement, see Retinol. Chemical structure of retinol, one of the major forms of vitamin A Vitamin A is a group of unsaturated nutritional organic compounds that includes retinol, retinal, retinoic acid, and several provitamin A carotenoids (most notably beta-carotene).[1] Vitamin A has multiple functions: it is important for growth and development, for the maintenance of the immune system and good vision.[2][3] Vitamin A is needed by the retina of the eye in the form of retinal, which combines with protein opsin to form rhodopsin, the light-absorbing molecule[4] necessary for both low-light (scotopic vision) and color vision.[5] Vitamin A also functions in a very different role as retinoic acid (an irreversibly oxidized form of retinol), which is an important hormone-like growth factor for epithelial and other cells.[3][6] Vitamin A can be found in two principal forms in foods: Medical use[edit]
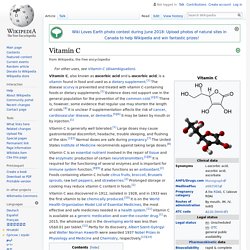
Vitamin C - Wikipedia. Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid and L-ascorbic acid, is a vitamin found in food and used as a dietary supplement.[1] The disease scurvy is prevented and treated with vitamin C-containing foods or dietary supplements.[1] Evidence does not support use in the general population for the prevention of the common cold.[2][3] There is, however, some evidence that regular use may shorten the length of colds.[4] It is unclear if supplementation affects the risk of cancer, cardiovascular disease, or dementia.[5][6] It may be taken by mouth or by injection.[1] Vitamin C is generally well tolerated.[1] Large doses may cause gastrointestinal discomfort, headache, trouble sleeping, and flushing of the skin.[1][3] Normal doses are safe during pregnancy.[7] The United States Institute of Medicine recommends against taking large doses.[8] Biology[edit] Significance[edit] Vitamin C is an essential nutrient for certain animals including humans.
Deficiency[edit] Discount Vitamins & Herbal Supplements from Puritan's Pride. Vitamin A — Health Professional Fact Sheet. Introduction. Vitamin - definition of vitamin by The Free Dictionary. Vitamín vitamin vitamiin vitamiini vítamín ビタミン 비타민 vitaminas vitamīns vitamină vitamínvitamínový วิตามิน Collins Spanish Dictionary - Complete and Unabridged 8th Edition 2005 © William Collins Sons & Co.
Collins English/French Electronic Resource. © HarperCollins Publishers 2005. Nature Made Vitamins, Minerals and Supplements. Vitamins & Supplements Center – Nutritional, Herbal, Dietary, and More. VITAMIN B12: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions and ... Vitamin D - Wikipedia. Vitamin D refers to a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphate, and zinc.
In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (also known as cholecalciferol) and vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol).[1] Cholecalciferol and ergocalciferol can be ingested from the diet and from supplements.[1][2][3] Very few foods contain vitamin D; synthesis of vitamin D (specifically cholecalciferol) in the skin is the major natural source of the vitamin. Dermal synthesis of vitamin D from cholesterol is dependent on sun exposure (specifically UVB radiation). Vitamin D from the diet or dermal synthesis from sunlight is biologically inactive; activation requires enzymatic conversion (hydroxylation) in the liver and kidney. . Vitamin D has a significant role in calcium homeostasis and metabolism. Vitamin A: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. Vitamin C Benefits, Sources, Supplements, & More.
Mark A.
Moyad, MD, MPH, senior research associate and Phil F. Jenkins Director, Complementary and Alternative Medicine, University of Michigan Urology Center. Phyo K. Vitamin D — Health Professional Fact Sheet. Niacin - Wikipedia. Niacin, also known as vitamin B3 and nicotinic acid, is an organic compound with the formula C 6H 5NO 2 and, depending on the definition used, one of the 20 to 80 essential human nutrients.
Pharmaceutical and supplemental niacin are primarily used to treat hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol) and pellagra (niacin deficiency).