

Julie Rowe
Trigonometry. Coaching & Professional Learning. GROWTH MINDSET. GCSE Mathematics. 5 Great TED Talks on How to Prese... Research advice and resources. Assessment. Carol Dweck. Rubric Gallery: List of public rubrics: RCampus. Dipsticks: Efficient Ways to Check for Understanding. What strategy can double student learning gains? According to 250 empirical studies, the answer is formative assessment, defined by Bill Younglove as "the frequent, interactive checking of student progress and understanding in order to identify learning needs and adjust teaching appropriately.
" Unlike summative assessment, which evaluates student learning according to a benchmark, formative assessment monitors student understanding so that kids are always aware of their academic strengths and learning gaps. Meanwhile, teachers can improve the effectiveness of their instruction, re-teaching if necessary. "When the cook tastes the soup," writes Robert E. Stake, "that's formative; when the guests taste the soup, that's summative.
" Alternative formative assessment (AFA) strategies can be as simple (and important) as checking the oil in your car -- hence the name "dipsticks. " In the sections below, we'll discuss things to consider when implementing AFAs. 5 Tips for a More Meaningful Rubric. Sarah Wike Loyola , Upper School Spanish Teacher, Spanish Team Leader, and Technology Mentor in Charlotte, NC Posted 06/08/2015 12:26PM | Last Commented 07/06/2015 2:30PM Every educator feels pretty darn cool the first few times they grade students' work.
What a powerful feeling it ignites in us, right? However, the reality of how much time we have to spend grading sets in quickly and the task becomes more and more monotonous. No teacher digs grading the same problems, essay prompts, responses, etc. over and over again, but it is a large part of what we do on a daily basis. So, why not make it meaningful? Teachers who use rubrics: set clear guidelines and expectations from the outset of the school year. hold students accountable for the work they produce in a justifiable way. let their students know on which areas they need concentrate the next time they are given a similar task. see improvement in their students’ work. Teachers who do not use rubrics: Be consistent. Still not convinced? 4 Easy Tips and Tricks for Creating Visually Engaging Rubrics. Lisa Yokana recently shared a useful rubric in her post on "Creating an Authentic Maker Education Rubric.
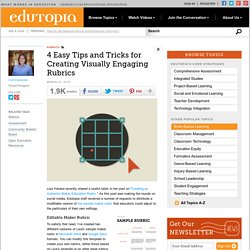
" As this post was making the rounds on social media, Edutopia staff received a number of requests to distribute a modifiable version of her sample maker rubric that educators could adjust to the particulars of their own settings. Editable Maker Rubric To satisfy that need, I’ve created two different versions of Lisa's sample maker rubric in Microsoft Word and Google Docs formats. You can modify this template to create your own rubrics, either those based on Lisa’s example or on other great rubrics, some of which are listed at the bottom of this post. In addition, here are some tips and tricks to help you make the most use out of this sample rubric template. Rubric Design Tips and Tricks Form follows function. Everything on your page should have a job.
With this sample rubric, I implemented several quick and easy design tricks to help improve overall functionality and experience. Nexgen Inquiry. 20 Questions To Guide Inquiry-Based Learning. 20 Questions To Guide Inquiry-Based Learning Recently we took at look at the phases of inquiry-based learning through a framework, and even apps that were conducive to inquiry-based learning on the iPad.
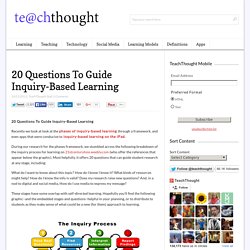
During our research for the phases framework, we stumbled across the following breakdown of the inquiry process for learning on 21stcenturyhsie.weebly.com (who offer the references that appear below the graphic). Most helpfully, it offers 20 questions that can guide student research at any stage, including: What do I want to know about this topic? How do I know I know it? These stages have some overlap with self-directed learning. References Cross, M. (1996). 5 Tools to Help Students Learn How to Learn.
Helping students learn how to learn: That’s what most educators strive for, and that’s the goal of inquiry learning.

That skill transfers to other academic subject areas and even to the workplace where employers have consistently said that they want creative, innovative and adaptive thinkers. Inquiry learning is an integrated approach that includes kinds of learning: content, literacy, information literacy, learning how to learn, and social or collaborative skills. Students think about the choices they make throughout the process and the way they feel as they learn. Those observations are as important as the content they learn or the projects they create. “We want students thinking about their thinking,” said Leslie Maniotes a teacher effectiveness coach in the Denver Public Schools and one of the authors of Guided Inquiry: Learning in the 21st Century. Formative Assessment Strategies.