

What existed before the big bang. It is difficult enough to imagine a time, roughly 13.7 billion years ago, when the entire universe existed as a singularity.
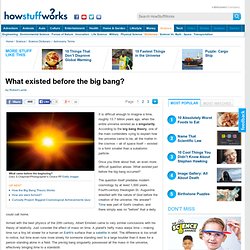
According to the big bang theory, one of the main contenders vying to explain how the universe came to be, all the matter in the cosmos -- all of space itself -- existed in a form smaller than a subatomic particle. Once you think about that, an even more difficult question arises: What existed just before the big bang occurred? The question itself predates modern cosmology by at least 1,600 years. Fourth-century theologian St. Augustine wrestled with the nature of God before the creation of the universe. Armed with the best physics of the 20th century, Albert Einstein came to very similar conclusions with his theory of relativity. Following this line of logic, the title of this article is fundamentally flawed. Case closed? Chronology of the universe. Illustration of evolution of the universe from the Big Bang (left).
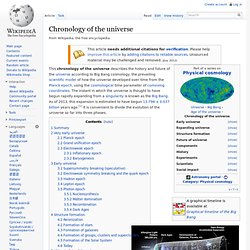
In this diagram, the universe is represented in two dimensions and the third (horizontal) dimension is time, increasing to the right. Summary[edit] The very earliest universe was so hot, or energetic, that initially no particles existed or could exist (except perhaps in the most fleeting sense), and the forces we see around us today were believed to be merged into one unified force. Space-time itself expanded during an inflationary epoch due to the immensity of the energies involved. Gradually the immense energies cooled – still to a temperature inconceivably hot compared to any we see around us now, but sufficiently to allow forces to gradually undergo symmetry breaking, a kind of repeated condensation from one status quo to another, leading finally to the separation of the strong force from the electroweak force and the first particles.
Very early universe[edit] Planck epoch[edit] Up to 10–43 second after the Big Bang. Lambda-CDM model. The ΛCDM or Lambda-CDM model is a parametrization of the Big Bang cosmological model in which the universe contains a cosmological constant, denoted by Lambda (Greek Λ), and cold dark matter (abbreviated CDM).
It is frequently referred to as the standard model of Big Bang cosmology, since it is the simplest model that provides a reasonably good account of the following properties of the cosmos: the existence and structure of the cosmic microwave backgroundthe large-scale structure in the distribution of galaxiesthe abundances of hydrogen (including deuterium), helium, and lithiumthe accelerating expansion of the universe observed in the light from distant galaxies and supernovae The model assumes that general relativity is the correct theory of gravity on cosmological scales.
Some alternative models challenge the assumptions of the ΛCDM model. Overview[edit] Lambda-CDM, Accelerated Expansion of the Universe. , is currently [2013] estimated to be 68.3%. History[edit] Successes[edit] Origins of the Universe, Big Bang Theory Information, Big Bang Facts, News, Photos. The most popular theory of our universe's origin centers on a cosmic cataclysm unmatched in all of history—the big bang. This theory was born of the observation that other galaxies are moving away from our own at great speed, in all directions, as if they had all been propelled by an ancient explosive force.
Before the big bang, scientists believe, the entire vastness of the observable universe, including all of its matter and radiation, was compressed into a hot, dense mass just a few millimeters across. This nearly incomprehensible state is theorized to have existed for just a fraction of the first second of time. Big bang proponents suggest that some 10 billion to 20 billion years ago, a massive blast allowed all the universe's known matter and energy—even space and time themselves—to spring from some ancient and unknown type of energy. Scientists can't be sure exactly how the universe evolved after the big bang.