

What does One Ton of CO2 Really Mean? A familiar answer to the question, “How much is one ton of CO2?”
Might sound something like this: “One ton of CO2, that’s like half an elephant, right? Wait, isn’t CO2 a gas? How does that even work?” I just learned that in 2005 the average coal-fired power plant in the US emitted 4,643,734 metric tons of CO2 (epa.gov). That’s right, those are all commas. 4.6 million metric tons of CO2. The problem is we don’t really know, not intuitively. Unfortunately, unless we are able to understand and conceptualize the costs of our actions to the environment, sustainable practices won’t become habits. So, just how much is 4.6 million metric tons of CO2? Hopefully, most institutions will never have to explain how much 4 million metric tons of emissions are. Justin Mullikin, AASHE Intern. CCS Alliance - CCS Alliance. DTI Oil & Gas - Maximising Recovery Programme (formerly SHARP) IOR Views. CO2 is an effective EOR agent, but its application has mainly been restricted to basins which have significant nearby subsurface sources of CO2, the Permian Basin in the USA being the only large scale example of CO2 flooding.
Concerns over the possible link between emissions of manmade greenhouse gases (predominantly CO2) and climate change have led to increased efforts to improve technology to reduce the cost of CO2 capture and introduce fiscal measures to promote CO2 sequestration. In this context CO2 EOR projects can add value by maximising hydrocarbon recovery and provide a possible bridge to a lower carbon emissions future by reducing the lifecycle cost of sequestration. CO2 EOR in the Permian Basin The Permian Basin of West Texas has a development history going back to 1920. Can baking soda save the environment?" FutureGen Alliance » Carbon Capture and Storage. One of the things that makes the FutureGen 2.0 power plant unique is its ability to capture the CO2 created during the electricity generation process, compress it and pump it into deep geologic formations thousands of feet below the earth’s surface where it is permanently stored.
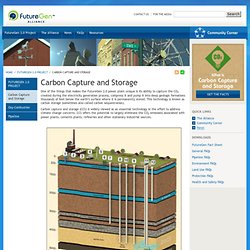
This technology is known as carbon storage (sometimes also called carbon sequestration). Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is widely viewed as an essential technology in the effort to address climate change concerns. CCS offers the potential to largely eliminate the CO2 emissions associated with power plants, cements plants, refineries and other stationary industrial sources. Independent scientists have rigorously studied several types of rock formations that can be used to store CO2. After the carbon dioxide is injected, the Alliance will continue to monitor it by conducting periodic surveys with a sophisticated monitoring, verification, and accounting protocol.
Powerplant CCS Blog - Latest in CO2 Sequestration at Power Plants. Super critical coal power plant to come up in Malaysia Super critical coal fired power plant coming up at Malaysia.
Carbon Capture and Storage Events The Second International Forum on Transportation of Co2 by Pipeline: The Second International Forum on Transportation of Co2 by pipeline (22 – 23 June 2011) is organized by Tiratsoo Technical and Clarion in Newcastle, UK. This international forum will come at the issues from these six technical perspectives: State of the Art Economics Materials Regulations [...] Hydrological Cycle and Climate Change Hydrological cycle refers to the movement of water in various forms within different spheres of the earth surface. Science News, Articles and Information. Enhanced Oil Recovery Projects with CO2. Challenges, Standards and more. Read the rest of this entry » CO2 Enhanced Oil Recovery World over, many countries are grappling with the twin challenges of reducing dependence on foreign energy sources as well as decreasing emissions of greenhouse gases, the topic of carbon dioxide (CO2) enhanced oil recovery (EOR) has therefore received increased attention.

Studies reveal that CO2 -EOR has a substantial immediate- to long-term role to play in both increasing domestic oil production in a responsible way, and in sequestering CO2 underground. CO2 EOR can add value by maximizing oil recovery while at the same time offering a bridge to a reduced carbon emissions future. It also reduces the cost of sequestering CO2 by earning revenues for the CO2 emitter from sales of CO2 to oil producers. Now, how does injecting CO2 into the pore spaces of a rock aid in crude oil recovery? When carbon-dioxide is injected into an oil reservoir, it mixes readily with the residual crude oil/ stranded oil. Image Courtesy: NETL More from here – CCST @ MIT. Institute - Carbon Capture And Storage. Carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide (chemical formula CO2) is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of 2 oxygen atoms each covalently double bonded to a single carbon atom.
It is a gas at standard temperature and pressure and exists in Earth's atmosphere in this state, as a trace gas at a concentration of 0.039 per cent by volume.[1] The environmental effects of carbon dioxide are of significant interest. Atmospheric carbon dioxide is the primary source of carbon in life on Earth and its concentration in Earth's pre-industrial atmosphere since late in the Precambrian eon was regulated by photosynthetic organisms. Carbon dioxide is an important greenhouse gas; burning of carbon-based fuels since the industrial revolution has rapidly increased the concentration, leading to global warming. It is also a major source of ocean acidification since it dissolves in water to form carbonic acid,[5] which is a weak acid as its ionization in water is incomplete. History Chemical and physical properties . Uses. Amid U.S.-China Energy Tension, "Clean Coal" Spurs Teamwork. The world's two largest energy consumers have clashed over their choices for fueling their economies, with solar industry subsidies and China's oil imports from Iran particular sore points.

But with Xi's stop in Washington an important one on his path to take over China's presidency later this year, and the two leaders hoping to highlight cooperation, energy offers an opportunity for the two nations to emphasize their collaboration: The deals they've struck on projects to clean up coal. In China, coal is king. U.S. energy companies, from small start-ups to one of the nation's largest utilities, Duke Energy, have concluded that they must work with China to keep a hand in technology to reduce the greenhouse gas emissions of coal-fired electricity: carbon capture and storage (CCS). Carbon capture and storage. Schematic showing both terrestrial and geological sequestration of carbon dioxide emissions from a coal-fired plant An integrated pilot-scale CCS power plant was to begin operating in September 2008 in the eastern German power plant Schwarze Pumpe run by utility Vattenfall, in the hope of answering questions about technological feasibility and economic efficiency.
CCS applied to a modern conventional power plant could reduce CO2 emissions to the atmosphere by approximately 80–90% compared to a plant without CCS.[4] The IPCC estimates that the economic potential of CCS could be between 10% and 55% of the total carbon mitigation effort until year 2100.[4] Storage of the CO2 is envisaged either in deep geological formations, or in the form of mineral carbonates. Deep ocean storage is no longer considered feasible because it greatly increases the problem of ocean acidification.[6] Geological formations are currently considered the most promising sequestration sites.
Carbon Capture and Storage. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS), or carbon sequestration, is a means of separating out carbon dioxide when burning fossil fuels, collecting it and subsequently “dumping” it underground or in the sea.
CCS is an integrated concept consisting of three distinct components: CO2 capture, transport and storage (including measurement, monitoring and verification). All three components are currently found in industrial operation today, although mostly not for the purpose of CO2 storage. A 2010 Government Accountability Office report noted that the largest demonstration of carbon capture in a coal plant was at a pilot scale (TRL 7) or less, and that demonstration of large scale integrated CCS systems is a technical challenge that is at least 10-15 years away from being realized.[1] System Overview. Carbon Capture and Sequestration 101. A Department of Energy artist rendering of the next-generation FutureGen power plan, which, if built, will employ carbon capture and storage. March 6, 2009 Download this brief (pdf) CCS is at the center of the debate , primed by the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act and President Obama’s budget blueprint, on how to reduce U.S. Role of Carbon Capture Technologies in Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction Models: A Parametric Study for the U.S. Power Sector - PESD.
This paper analyzes the potential contribution of carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies to greenhouse gas emissions reductions in the U.S. electricity sector.

Focusing on capture systems for coal-fired power plants until 2030, a sensitivity analysis of key CCS parameters is performed to gain insight into the role that CCS can play in future mitigation scenarios and to explore implications of large-scale CCS deployment. By integrating important parameters for CCS technologies into a carbon-abatement model similar to the EPRI Prism analysis (EPRI, 2007), this study concludes that the start time and rate of technology diffusion are important in determining the emissions reduction potential and fuel consumption for CCS technologies.
Comparisons with legislative emissions targets illustrate that CCS alone is very unlikely to meet reduction targets for the electric-power sector, even under aggressive deployment scenarios. Peabody Energy : Home. RTI International. Carbon Capture and Storage. CCS Overview: What Is CCS? DOE Carbon Sequestration Program. NETL: Carbon Storage. EPA Geologic Sequestration of CO2. Click Here for Regulations.gov For access to supporting documents relating to the development ofGeologic Sequestration Regulations,click the following link:
Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum. Building an Underground 'Highway' for Carbon Dioxide — A blog on Environmental Happenings by Dean Bill Chameides.