

Anti-aging acid guide. If wrinkles, dry skin and acne are transforming you into someone you don't recognize, this secret to rejuvenating skin could help fix your biggest skin problems and help you look younger, fast.
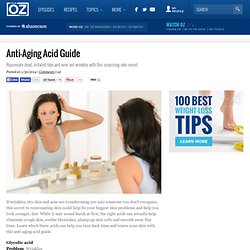
While it may sound harsh at first, the right acids can actually help eliminate rough skin, soothe blemishes, plump up skin cells and smooth away fine lines. Learn which three acids can help you turn back time and renew your skin with this anti-aging acid guide. Glycolic acidProblem: Wrinkles How it works: This wrinkle-fighting acid is an exfoliator that safely removes the outer layer of dead skin cells so that plump new cells can rise to the surface. Glycolic acid helps stimulate the growth of collagen, which is responsible for skin's elasticity and which breaks down with aging. Glycolic acid can help smooth out fine lines and diminish the appearance of wrinkles. Lactic acidProblem: Dry skin How it works: This acid helps skin look younger in two ways.
Anti-aging acid guide. Bha · chemical peel. Alpha hydroxy acid. Α-, β- and γ-hydroxy acids α-Hydroxy acids, or alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), are a class of chemical compounds that consist of a carboxylic acid substituted with a hydroxyl group on the adjacent carbon.
They may be either naturally occurring or synthetic. AHAs are well known for their use in the cosmetics industry. They are often found in products claiming to reduce wrinkles or the signs of aging, and improve the overall look and feel of the skin. They are also used as chemical peels available in a dermatologist's office, beauty and health spas and home kits, which usually contain a lower concentration of around 4%. Cosmetic applications[edit] AHAs are a group of organic carboxylic compounds.
Epidermal effect[edit] AHAs have a profound effect on keratinization; which is clinically detectable by the formation of a new stratum corneum. Dermal effects[edit] AHAs with greater bioavailability appear to have deeper dermal effects. Beta hydroxy acid. A beta hydroxy acid or β-hydroxy acid (BHA) is an organic compound that contains a carboxylic acid functional group and hydroxy functional group separated by two carbon atoms.
They are closely related to alpha hydroxy acids, in which the two functional groups are separated by one carbon atom. In cosmetics, the term beta hydroxy acid refers specifically to salicylic acid, which is used in some "anti-aging" creams and acne treatments. Upon dehydration, beta-hydroxy acids yield an alpha-beta unsaturated acid. Acidic properties[edit] Compared to non-hydroxylated carboxylic acids, this group of acids is stronger, although less strong than the alpha hydroxy acids. Chemical peel. A chemical peel is a body treatment technique used to improve and smooth the texture of the facial skin using a chemical solution that causes the dead skin to slough off and eventually peel off.[1] The regenerated skin is usually smoother and less wrinkled than the old skin.
Thus the term chemical peel is derived. Some types of chemical peels can be purchased and administered without a medical license, however people are advised to seek professional help from a dermatologist, esthetician, plastic surgeon, oral and maxillofacial surgeon, or otolaryngologist on a specific type of chemical peel before a procedure is performed. Types[edit] There are several types of chemical peels,[1] Citric acid. Citric acid is a weak organic acid with the formula C6H8O7.
It is a natural preservative/conservative and is also used to add an acidic or sour taste to foods and drinks. In biochemistry, the conjugate base of citric acid, citrate, is important as an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in the metabolism of all aerobic organisms. It consists of 3 carboxyl (R-COOH) groups. Citric acid is a commodity chemical, and more than a million tonnes are produced every year by fermentation. It is used mainly as an acidifier, as a flavoring, and as a chelating agent. Properties[edit] Citric acid crystal under polarized light, enlarged 200x At room temperature, citric acid is a white crystalline powder. In chemical structure, citric acid shares the properties of other carboxylic acids. Glycolic acid. Lactic acid. Lactic acid is an organic acid.
It has a molecular formula CH3CH(OH)COOH. It is white in solid state and it is miscible with water.[2] While in liquid state (dissolved state) it is a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as natural sources. Mandelic acid. Isolation and synthesis[edit] Mandelic acid was discovered while heating amygdalin, an extract of bitter almonds, with diluted hydrochloric acid.
The name is derived from the German "Mandel" for "almond". Salicylic acid.