

Introduction to the Aztecs exhibition: Melbourne Museum. A pot in the shape of Tláloc, the Aztec rain god.
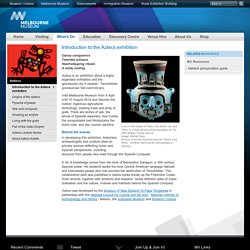
Tláloc is a Nahuatl word that translates as 'He Who Makes Things Sprout'.Image: Michel ZabeSource: Consejo Nacional para la Cultura y las Artes - Instituto Nacional de Antropología e Historia Canny conquerorsTalented artisansHeart-stopping ritualsA nasty ending Aztecs is an exhibition about a highly organised civilisation and the spectacular city it created - Tenochtitlán (pronounced Teh-notch-tit-lan).
Visit Melbourne Museum from 9 April until 10 August 2014 and discover the Aztecs’ ingenious agricultural technology, bustling trade and array of gods. Was the Aztec Empire Really All Powerful? The Aztec Civilization. BBC Bitesize - KS2 History - The Aztec Empire. Tarlton Law Library - Aztec and Maya Law - online exhibit. The Aztec empire was made up of a series of city-states known as altepetl.

Each altepetl was ruled by a supreme leader (tlatoani) and a supreme judge and administrator (cihuacoatl). The Aztec World. A kingdom of blood.

SEP, Department of Education. The capital city of the Aztecs, Tenochtitlán, was an engineering masterpiece. Aqueducts and canals snaked through the city, channelling pure water to possibly 200,000 inhabitants each day. In 1978, while digging in the basement of a bookstore, workers for Mexico City's power company hit a huge stone disk. History of Mexico - The Aztec Empire. THE RISE OF THE AZTEC EMPIRE By John P.

Schmal The Aztec Empire of 1519 was the most powerful Mesoamerican kingdom of all time. The multi-ethnic, multi-lingual realm stretched for more than 80,000 square miles through many parts of what is now central and southern Mexico. Aztec Civilization. The Aztec Empire flourished between c. 1345 and 1521 CE and, at its greatest extent, covered most of northern Mesoamerica.
Aztec warriors were able to dominate their neighbouring states and permit rulers such as Motecuhzoma II to impose Aztec ideals and religion across Mexico. Highly accomplished in agriculture and trade, the last of the great Mesoamerican civilizations was also noted for its art and architecture which ranks amongst the finest ever produced on the continent. The Aztec state is actually the most well documented Mesoamerican civilization with sources including archaeology, native books (codices) and lengthy and detailed accounts from their Spanish conquerors - both by military men and Christian clergy. Historical Overview Sometime around 1100 CE the city-states or altepetl which were spread over central Mexico began to compete with each other for local resources and regional dominance. TenochtitlAn Religion. History for Kids: Aztecs, Maya, and Inca.
Back to History.
Aztecs. The first European to visit Mexican territory was Francisco Hernandez de Cordoba, who arrived in Yucatan from Cuba with three ships and about 100 men in early 1517.
Cordobars reports on his return to Cuba prompted the Spanish governor there, Diego Velasquez, to send a larger force back to Mexico under the command of Hernan Cortes. In March 1519, Cortes landed at the town of Tabasco, where he learned from the natives of the great Aztec civilization, then ruled by Moctezuma (or Montezuma) II. Defying the authority of Velasquez, Cortes founded the city of Veracruz on the southeastern Mexican coast, where he trained his army into a disciplined fighting force. Cortes and some 400 soldiers then marched into Mexico, aided by a native woman known as Malinche, who served as a translator.
Thanks to instability within the Aztec empire, Cortes was able to form alliances with other native peoples, notably the Tlascalans, who were then at war with Montezuma. P B S : C o n q u i s t a d o r s - C o r t é s. In the decade before the Spanish arrived in Mexico, Aztec Emperor Montezuma II and his people were filled with a sense of foreboding.
A series of evil omens had foretold of calamities to come. People. Aztec History. Nahuatl (Aztec) Family. The Nahuatl (or Nahua) languages form the southernmost family of the Uto-Aztecan stock.
Nahuatl has over a million and a half speakers, more than any other family of indigenous languages in Mexico today. The name “Nahuatl” (pronounced in two syllables, ná-watl) comes from the root nahua ([nawa]) which means ‘clear sound’ or ‘command’. Aztecs (Mexica) During the twelfth century AD the Mexica were a small and obscure tribe searching for a new homeland.
Eventually they settled in the Valley of Mexico and founded their capital, Tenochtitlan, in 1345. At the beginning of the sixteenth century it was one of the largest cities in the world. Warfare was extremely important for the Mexica people and led them to conquer most of modern-day central and southern Mexico. They controlled their huge empire through military strength, a long-distance trading network and the tribute which conquered peoples had to pay.
Aztec Calendar : Mexico Culture & Arts. Dale Hoyt Palfrey Mexica/Aztec Calendar Systems The Civil Calendar The solar year was the basis for the civil calendar by which the Mexicas (Aztecs) determined the myriad ceremonies and rituals linked to agricultural cycles. The calendar was made up of 18 months, each lasting 20 days. The months were divided into four five-day weeks. Beginner's Guide to the Aztec Empire of Central Mexico. Aztec Math Decoded, Reveals Woes of Ancient Tax Time. April 3, 2008 Today's tax codes are complicated, but the ancient Aztecs likely shared your pain. To measure tracts of taxable land, Aztec mathematicians had to develop their own specialized arithmetic, which has only now been decoded. By reading Aztec records from the city-state of Tepetlaoztoc, a pair of scientists recently figured out the complicated equations and fractions that officials once used to determine the size of land on which tributes were paid.
Two ancient codices, written from A.D. 1540 to 1544, survive from Tepetlaoztoc. They record each household and its number of members, the amount of land owned, and soil types such as stony, sandy, or "yellow earth. " "The ancient texts were extremely detailed and well organized, because landowners often had to pay tribute according to the value of their holdings," said co-author Maria del Carmen Jorge y Jorge at the National Autonomous University in Mexico City, Mexico. "Rule of Thumb" and Other Body Parts "It's just very natural. Aztec mythology.
Greatest Aztec. Image above by Guido Galvani and María Sánchez Vega, courtesy Templo Mayor project, National Institute of Anthropology and History, MexicoPhotographs by Kenneth Garrett and Jesús López On the edge of Mexico City's famed Zócalo plaza, next to the ruins of the Aztec sacred pyramid known as the Templo Mayor, the remains of an animal—perhaps a dog or a wolf—were discovered. It had been dead for 500 years and lay in a stone-lined shaft eight feet deep. It is likely the animal had no name, nor an owner. Yet the anonymous canine had evidently meant something to someone. It wore a collar made of jade beads and turquoise plugs in its ears.
The archaeological team, led by Leonardo López Luján, unearthed the so-called Aristo-Canine in the summer of 2008, two years into an excavation that began when foundation work for a new building revealed an astonishing object. Aztec Gods and Goddesses - Ancient / Classical History. Huitzilopochtli Huitzilopochtli was the Aztec god of the obsidian knife who sprang forth from his mother's belly to kill his siblings.
Quetzalcoatl. Aztecs and the Aztec Civilization. The Aztec Capital City of Tenochtitlan - Aztec Culture. Aztec Religion.