

Short walks 'could cut diabetes risk in older people' 12 June 2013Last updated at 00:46 ET Walking for 15 minutes after meals could prevent "potentially damaging" blood sugar spikes A 15-minute walk after each meal could prevent older people developing type-2 diabetes, a study has found.
The post-meal walks control blood sugar as well as one long walk, research by George Washington University suggested. Best Foods For Your Heart (Including Oil) We'd rather you didn't rush out and thrust your face straight into a bag of chips, but the official line when it comes to anything fried is that vegetable oil is perfectly fine as part of a heart-healthy diet.
Researchers at the University of Missouri and the University of Illinois have published a new study that reveals there is no link between consuming vegetable oil and the inflammation that is associated with heart disease. In fact, to maintain a healthy diet for your heart, you need to be consuming between two to four teaspoons a day. (Not Mary Poppins cough-syrup style - but preferably on salads or using it to cook food with.) Previously, studies indicated that vegetable oils, which are rich in linoleic acid (LA) could be harmful to people because they promote inflammation in animals.
Loading Slideshow Vegetable oilLinoleic acid is essential to keep your heart healthy, so try to consume between two to four teaspoons a day. Candidate Sepsis Drug Could Prevent Flu Deaths. Out of options. In some severe cases in the H1N1 influenza pandemic in 2009 the virus was resistant against all antiviral compounds, leaving doctors without drugs. Credit: Zhang Xiaowei/Xinhua/Newscom The 1918 Spanish flu killed up to 40 million people. The swine flu pandemic in 2009 killed an estimated 284,000.
Now, scientists have discovered a substance that could help doctors save lives during future influenza pandemics. At the moment, doctors have only one class of compounds available to combat influenza. Instead of targeting the virus, immunologist Stefanie Vogel at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, tried to interfere with the host immune system. Brain Games Versus Nature Documentaries. It seems brain-training games—online tests, quizzes, games, or flash cards designed to improve attention, memory, creativity, and concentration—are everywhere.
But do they work? A recent study published in the journal PLoS ONE says … maybe not. (Learn about the brain.) Brain's 'Clock' Disrupted In People With Depression. By: Stephanie Pappas, LiveScience Senior Writer Published: 05/13/2013 03:04 PM EDT on LiveScience Disrupted sleep is so commonly a symptom of depression that some of the first things doctors look for in diagnosing depression are insomnia and excessive sleeping. Now, however, scientists have observed for the first time a dysfunctional body clock in the brains of people with depression. People with major depression , also known as clinical depression, show disrupted circadian rhythms across brain regions, according to a new study published today (May 13) in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 'Weight loss gut bacterium' found. Bacteria that live in the gut have been used to reverse obesity and Type-2 diabetes in animal studies.
Research, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, showed that a broth containing a single species of bacteria could dramatically alter the health of obese mice. It is thought to change the gut lining and the way food is absorbed. Similar tests now need to be take place in people to see if the same bacteria can be used to shed the pounds. The human body is teeming with bacteria - the tiny organisms outnumber human cells in the body 10 to one. WHO says new coronavirus may be passed person to person. 12 May 2013Last updated at 14:46 ET The World Health Organisation says it is closely monitoring the novel coronavirus The World Health Organization says it appears likely that the novel coronavirus (NCoV) can be passed between people in close contact.
Could eating peppers prevent Parkinson's? Dietary nicotine may hold protective key. New research reveals that Solanaceae -- a flowering plant family with some species producing foods that are edible sources of nicotine -- may provide a protective effect against Parkinson's disease.

The study appearing today in Annals of Neurology, a journal of the American Neurological Association and Child Neurology Society, suggests that eating foods that contain even a small amount of nicotine, such as peppers and tomatoes, may reduce risk of developing Parkinson's. Parkinson's disease is a movement disorder caused by a loss of brain cells that produce dopamine. Symptoms include facial, hand, arm, and leg tremors, stiffness in the limbs, loss of balance, and slower overall movement. Nearly one million Americans have Parkinson's, with 60,000 new cases diagnosed in the U.S. each year, and up to ten million individuals worldwide live with this disease according to the Parkinson's Disease Foundation. For the present population-based study Dr. Turning old hearts. Two Harvard Stem Cell Institute researchers -- one a stem cell biologist and one a practicing cardiologist at Brigham and Women's Hospital -- have identified a protein in the blood of mice and humans that may prove to be the first effective treatment for the form of age-related heart failure that affects millions of Americans.

When the protein, called GDF-11, was injected into old mice, which develop thickened heart walls in a manner similar to aging humans, the hearts were reduced in size and thickness, resembling the healthy hearts of younger mice. Even more important than the implications for the treatment of diastolic heart failure, the finding by Richard T. Lee, a Harvard Medical School professor at BWH, and Amy Wagers, a professor in Harvard's Department of Stem Cell and Regenerative Biology ultimately may rewrite our understanding of aging. A report on Lee and Wagers's findings was published today by the journal Cell.
Positive social support at work shown to reduce risk of diabetes. Cases of type 2 diabetes continue to rise in the US.

And while the development of the disease is more commonly associated with risk factors such as obesity, high blood pressure, and physical inactivity, research has shown that stress can also have a significant impact. Now Dr. Sharon Toker of Tel Aviv University's Faculty of Management has found that low levels of social support and high levels of stress in the workplace can accurately predict the development of diabetes over the long term -- even in employees who appear to be healthy otherwise. Published in the Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, the study contributes to an ongoing body of research linking work conditions to physical and mental health.
Pets may help reduce your risk of heart disease. Having a pet might lower your risk of heart disease, according to a new American Heart Association scientific statement.
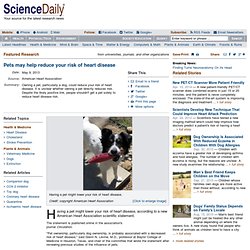
The statement is published online in the association's journal Circulation. "Pet ownership, particularly dog ownership, is probably associated with a decreased risk of heart disease," said Glenn N. Air pollution increases risk of insulin resistance in children. New research shows that growing up in areas where air pollution is increased raises the risk of insulin resistance (the prescursor to diabetes) in children.

The research is published in Diabetologia, the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), and is by Elisabeth Thiering and Joachim Heinrich, Helmholtz Zentrum München, Neuherberg, Germany, and colleagues. Previous studies have identified links between air pollution and other chronic conditions such as atherosclerosis and heart disease. Brain Scientists Can Delay The Ageing Process By Manipulating The Hypothalamus. Forget going to the gym, drinking less and giving up smoking, the ageing process could all be down to a tiny bit of the brain - and it can be manipulated.
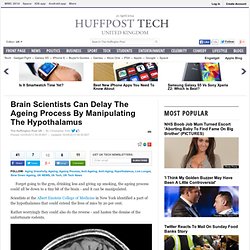
Scientists at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York identified a part of the hypothalamus that could extend the lives of mice by 20 per cent. Rather worryingly they could also do the reverse - and hasten the demise of the unfortunate rodents. The hypothalamus highlighted in the centre of the brain. Brain & Obesity: Neural Implant Could Curb Overeating, Mouse Study Suggests.
By: Denise Chow, LiveScience Staff Writer Published: 04/26/2013 09:18 AM EDT on LiveScience The brain may not seem like an obvious place to look for possible treatments for obesity, but researchers say implanting a device that stimulates a specific region of the brain may help curb the compulsion to overeat. The new study on obese mice found that deep brain stimulation (DBS), which involves implanting a device that sends electrical impulses to precise targets in the brain, may reduce binge eating and other obesity-related behaviors.
"Once replicated in human clinical trials, DBS could rapidly become a treatment for people with obesity due to the extensive groundwork already established in other disease areas," lead author Casey Halpern, a resident in the department of neurosurgery at the University of Pennsylvania's Perelman School of Medicine, said in a statement. [8 Reasons Our Waistlines Are Expanding] Rituximab in ITP – When and Why Does It Work? Presidents Column Linda J. Burns, MD Professor of Medicine, Division of Hematology, Oncology, and Transplantation, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis Training the Next Generation April 11, 2014. Egg White Protein May Help Lower Blood Pressure. Dark chocolate and antioxidant-rich cocoa may help bring down blood pressure by a few points, a Cochrane review affirmed.
Blood pressure fell by an average 2.8/2.2 mm Hg across the short-term trials using daily doses ranging from a spoon of cocoa powder to a full bar of chocolate, Karin Ried, PhD, and colleagues at the University of Adelaide, Australia, reported. How Prozac entered the lexicon. 9 April 2013Last updated at 21:32 ET By Tara McKelvey BBC News Magazine. US rice imports 'contain harmful levels of lead' 10 April 2013Last updated at 23:23 GMT By Jason Palmer Science and technology reporter, BBC News, New Orleans. The myth of the eight-hour sleep. Image copyright Other. Treatments, not prevention, dominate diabetes research. Research for diabetes is far more focused on drug therapies than preventive measures, and tends to exclude children and older people who have much to gain from better disease management, according to a Duke Medicine study.
By analyzing nearly 2,500 diabetes-related trials registered in ClinicalTrials.gov from 2007-10, the authors provide a broad overview of the research landscape for diabetes. New link between heart disease and red meat: New understanding of cardiovascular health benefits of vegan, vegetarian diets. A compound abundant in red meat and added as a supplement to popular energy drinks has been found to promote atherosclerosis -- or the hardening or clogging of the arteries -- according to Cleveland Clinic research published online this week in the journal Nature Medicine. The study shows that bacteria living in the human digestive tract metabolize the compound carnitine, turning it into trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), a metabolite the researchers previously linked in a 2011 study to the promotion of atherosclerosis in humans. Further, the research finds that a diet high in carnitine promotes the growth of the bacteria that metabolize carnitine, compounding the problem by producing even more of the artery-clogging TMAO.
The study tested the carnitine and TMAO levels of omnivores, vegans and vegetarians, and examined the clinical data of 2,595 patients undergoing elective cardiac evaluations. Higher mercury levels in humans associated with increased risk for diabetes. Huge disparities in hypertension seen across U.S. counties. One in five Americans is completely unaware that he or she is at risk for the second leading cause of premature death: high blood pressure. In the first ever analysis of awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension for every county, the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington revealed significant differences across the US.
The study found the largest burden of hypertension in the Southeast, the lowest prevalence in Colorado, and differences among genders, ethnic groups, and geographies. Appetite control could be rewired, say researchers. Increase potassium and cut salt to reduce stroke risk. China Deaths Spark Concern About Novel Avian Flu Strain. Macular degeneration: Cholesterol drugs 'may save sight' 10 Things Coffee Does to Your Body.
Bacteria find 'key to treating obesity without surgery' 'Under the skin' blood-testing device developed. New anti-clotting drug more effective than current treatment, study suggests. Niacin therapy shows no benefits, has some harmful effects. Alternative cholesterol-lowering drug for patients who can't tolerate statins. Sleep discovery could lead to therapies that improve memory. Sleep loss precedes Alzheimer's symptoms. Salty Food May Be a Culprit in Autoimmune Diseases. Common Parasite May Influence Human Behavior. Toxoplasmosis. Distinct niches in bone marrow nurture blood stem cells. Scientists find bone-marrow environment that helps produce infection-fighting T and B cells.
Scientists find genes linked to human neurological disorders in sea lamprey genome. Gut bacteria and obesity: Holy shit! Health and gut bacteria: Hard to stomach. Treating disease with microbes: Bugs in the system. The microbiome and health: Sniffing out hypertension. Chemical reaction keeps stroke-damaged brain from repairing itself. Villain stomach bug may have a sweet side: 'Bad' gut bacteria may help control diabetes. Diet Affects Sleep Patterns, Study Finds. Zinc helps against infection by tapping brakes in immune response. Tai Chi exercise may reduce falls in adult stroke survivors. Exercise may slow development of diabetic nerve pain. Stroke damage in mice overcome by training that 'rewires' brain centers. Overall eating patterns are most important for healthful eating. Can breakfast make kids smarter? New MRI analysis useful in predicting stroke complications caused by clot-busters.
Platelet. The role of ADP receptors in platelet function. [Front Biosci. 2006. Title. Effect of Adenosine A2 Receptor Stimulation on Platelet Activation-Aggregation: Differences Between Canine and Human Models. Physiological implications of adenosine recep... [J Cell Physiol. 2011. Adenosine inhibits the rise in intracellular calcium and platelet aggregation produced by thrombin: evidence that both effects are coupled to adenylate cyclase.
Chemical that fends off harm to organs: Purines fend off surgery-related damage. Patients with diabetes may not receive best treatment to lower heart disease risk, study suggests. Curbing car travel could be as effective as cutting calories. Silent stroke can cause Parkinson's disease. Even the smallest stroke can damage brain tissue and impair cognitive function. Antioxidant cookies made possible by grape seeds. Gazpacho consumption associated with lower blood pressure, study finds. Vitamin D can help infection-prone patients avoid respiratory tract infection. Women with higher carotenoid levels have reduced risk of breast cancer. How common 'cat parasite' gets into human brain and influences human behavior.
Obesity reversed in mice by manipulating production of an enzyme. Glycemic index. Moderate coffee consumption may reduce risk of diabetes by up to 25 percent. Could high insulin make you fat? Mouse study says yes. Double duty: Immune system regulator found to protect brain from effects of stroke.